USS Chivo
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Alou Diarra Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Alou DiarraTanggal lahir 15 Juli 1981 (umur 42)Tempat lahir Villepinte, PrancisTinggi 1,90 m (6 ft 3 in)Posisi bermain GelandangInformasi klubKlub saat ini Rennes (pinjaman dari West Ham United)Nomor 23Karier junior1987–1993 Aulnay-sous-Bois1993–1997 Villepinte1997–1999 Louhans-CuiseauxKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)1999–2000 Louhans-Cuiseaux 3 (0)2000–2002 Bayern München (A) 41 (5)2000–2002 Bayern München 0 (0)...

BMW Seri 7InformasiProdusenBMWMasa produksi1977–sekarangPerakitanDingolfing, Jerman[1]Lerma, Toluca, Meksiko[2][3][4]Bodi & rangkaKelasMobil mewah ukuran penuhBentuk kerangka4-pintu sedanTata letakmesin depan, penggerak roda belakangKronologiPendahuluBMW New Six BMW Seri 7 adalah jajaran mobil mewah ukuran penuh yang diproduksi oleh BMW. Diperkenalkan pertama kali tahun 1977, saat ini Seri 7 merupakan seri mobil termewah BMW dan hanya tersedia dalam ...

Gambuh Gambuh adalah teater dramatari Bali yang dianggap paling tinggi mutunya dan juga merupakan dramatari klasik Bali yang paling kaya akan gerak-gerak tari, sehingga dianggap sebagai sumber segala jenis tari klasik Bali. Diperkirakan Gambuh muncul sekitar abad ke-15 dengan lakon bersumber pada cerita Panji. Gambuh berbentuk teater total karena di dalamnya terdapat jalinan unsur seni suara, seni drama dan tari, seni rupa, seni sastra, dan lainnya. Gambuh dipentaskan dalam upacara-upacara De...

Seluang Rasbora borapatensis Klasifikasi ilmiah Domain: Eukaryota Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Chordata Kelas: Actinopterygii Ordo: Cypriniformes Famili: Cyprinidae Subfamili: Danioninae Genus: RasboraBleeker, 1859 Spesies tipe Rasbora cephalotaeniaBleeker, 1852 Spesies Lihat teks Ikan Seluang Ialah sekumpulan ikan dalam genus Rasbora. Ikan seluang merupakan ikan yang banyak terdapat di sungai di daerah asia tenggara, termasuk Malaysia, Brunei, dan Indonesia. Ikan ini bersisik seperti ikan Teng...

Pusat PeneranganTentara Nasional IndonesiaLambang Tentara Nasional IndonesiaNegara IndonesiaCabang Tentara Nasional IndonesiaTipe unitBadan Pelaksana Pusat TNIBagian dariTentara Nasional IndonesiaSitus webwww.tni.mil.idTokohKepalaMayor Jenderal TNI DR.R.Nugraha Gumilar,M.scWakil KepalaBrigadir Jenderal TNI (Mar) Freddy Ardianzah Pusat Penerangan Tentara Nasional Indonesia, disingkat (Puspen TNI) adalah Badan Pelaksana Pusat ditingkat markas besar Tentara Nasional Indonesia yang berkedudu...

Former Australian regional music festival Triple J's One Night StandGenreIndie rockindie pophip hopelectronicLocation(s)AustraliaYears active2004–2019; 2024Organised byTriple J (Australian Broadcasting Corporation) Triple J's One Night Stand is an annual music festival held in various regional Australian cities and towns that is promoted and organised by national youth radio station Triple J. The event ran for 15 years from its debut in 2004 until 2019, with one break in 2015 for Triple J's...

Swiss ice hockey player (born 1988) Ice hockey player Simon Bodenmann Bodenmann in 2016 with the SC BernBorn (1988-03-02) 2 March 1988 (age 36)Urnäsch, SwitzerlandHeight 5 ft 10 in (178 cm)Weight 183 lb (83 kg; 13 st 1 lb)Position Left wingShoots LeftNL teamFormer teams ZSC LionsKloten FlyersSC BernNational team SwitzerlandPlaying career 2006–present Simon Bodenmann (born 2 March 1988) is a Swiss professional ice hockey forward who is...

Voce principale: Unione Sportiva Lecce. Unione Sportiva LecceStagione 2000-2001Sport calcio Squadra Lecce Allenatore Alberto Cavasin Presidente Mario Moroni Serie A13º posto Coppa ItaliaOttavi di finale Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Vugrinec, Chimenti (34) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Lucarelli (12)Totale: Lucarelli, Vugrinec (14) 1999-2000 2001-2002 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa voce raccoglie le informazioni riguardanti l'Unione Sportiva Lecce nelle competizioni uffici...

West Virginian folklore creature Flatwoods MonsterFolkloreHumanoid, ExtraterrestrialFirst attestedSeptember 12, 1952Other name(s)Braxton County Monster, Green MonsterCountryUnited StatesRegionFlatwoods, West Virginia Part of a series on theParanormal Main articles Astral projection Astrology Aura Bilocation Breatharianism Clairvoyance Close encounter Cold spot Crystal gazing Conjuration Cryptozoology Demonic possession Demonology Ectoplasm Electronic voice phenomenon Exorcism Extrasensory per...

South Korean daily newspaper For other uses, see Munhwa. Munhwa IlboTypeDaily newspaperFormatPrint, onlineOwner(s)Munhwa Ilbo Co.Founded1991Political alignmentConservative[1]LanguageKoreanWebsitehttp://www.munhwa.com/Munhwa IlboHangul문화일보Hanja文化日報Revised RomanizationMunhwa IlboMcCune–ReischauerMunhwa IlboLiterally, Culture Daily This article is part of a series onConservatismin South Korea Schools Authoritarian Ilminism Corporate Cultural Fiscal Libertarian Moderate ...

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 数字の大字(だいじ)は、漢数字の一種。通常用いる単純な字形の漢数字(小字)の代わりに同じ音の別の漢字を用いるものである。 概要 壱万円日本銀行券(「壱」が大字) 弐千円日本銀行券(「弐」が大字) 漢数字には「一」「二」「三」と続く小字と、「壱」「�...

HMCS Protecteur di Pearl Harbor pada 2009 Her Majesty's Canadian Ship (HMCS) Protecteur (AOR 509) adalah kapal perang dari Angkatan Laut Kerajaan Kanada. Kapal tersebut adalah unit angkatan laut Kanada pertama yang memakai nama Protecteur Pranala luar Media terkait IMO 6900678 di Wikimedia Commons Protecteur-class homepage Diarsipkan 2022-02-11 di Wayback Machine.

Voce principale: Krefelder Fußball-Club Uerdingen 05. Fußballclub Bayer 05 UerdingenStagione 1977-1978Sport calcio SquadraKrefelder Fußballclub Uerdingen 05 Allenatore Klaus Quinkert (1ª-4ª) Siegfried Melzig (5ª-38ª) 2. Bundesliga7º posto Coppa di GermaniaSecondo turno Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Brinkmann, Funkel (38)Totale: Brinkmann, Funkel (40) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Funkel (25)Totale: Funkel (25) StadioGrotenburg Stadion Maggior numero di spettatori9 000 vs. Preussen...
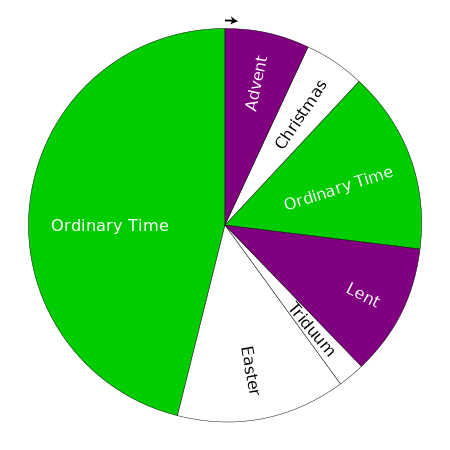
Pemberkatan Krisma pada Kamis Putih di Basilika Lateran. Ditandatangani P. Villanueva, sekitar tahun 1900 Misa Krisma adalah ibadah spesial yang dilakukan di Gereja Katolik, Lutheran dan Anglikan.[1][2] Misa Krisma merupakan salah satu liturgi yang paling khusyuk dan penting dalam kalender liturgi Kekristenan. Tradisi Kerasulan Kristen kuno (200 M) menggambarkan Misa Krisma sebagai upacara yang berlangsung selama Malam Paskah di mana dua minyak suci diberkati dan satu dikudusk...

Lynching of James Harvey and Joe JordanPart of Jim Crow EraDateJuly 1, 1922LocationLiberty County, GeorgiaParticipantsA white mob of 50 people lynched in Liberty County, GeorgiaDeaths2 Part of a series on theNadir of Americanrace relationsViolence in the 1906 Atlanta race massacre Historical background Reconstruction era Voter suppression Disfranchisement Redeemers Compromise of 1877 Jim Crow laws Segregation Anti-miscegenation laws Convict leasing Practices Common actions Expulsions of Afri...

American sculptor (1844–1907) Edmonia LewisWildfireBornMary Edmonia LewisJuly 4, 1844Town of Greenbush, Rensselaer County, New York, USDiedSeptember 17, 1907(1907-09-17) (aged 63)London, UKNationalityAmerican, MississaugaEducationNew-York Central College, OberlinKnown forSculptureMovementLate NeoclassicismPatron(s)Numerous patrons, American and European Mary Edmonia Lewis, also known as Wildfire (c. July 4, 1844 – September 17, 1907), was an American sculptor. Born in Upstate Ne...

Calculating tool Abaci redirects here. For the Turkish Surname, see Abacı. For the medieval book, see Liber Abaci. For other uses, see Abacus (disambiguation). Bi-quinary coded decimal-like abacus representing 1,352,964,708 An abacus (pl.: abaci or abacuses), also called a counting frame, is a hand-operated calculating tool which was used from ancient times in the ancient Near East, Europe, China, and Russia, until the adoption of the Arabic numeral system.[1] An abacus consists of a...

Russian military district For the Swedish commands, see Southern Military District (Milo S) and Southern Military District (MD S). You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Ukrainian. (October 2019) Click [show] for important translation instructions. View a machine-translated version of the Ukrainian article. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors a...

D 90د ٩٠ Negara: Uni Emirat Arab (UEA) Nama lain: Jalan Al Satwa, Jalan Mankhool, Jalan Al Mussallah Jenis rute: D Panjang: 4.6 mi (7 km) Arah: Timur-Barat Persimpangan Utama: Dubai D 73 (Jalan Lingkar Al Satwa) Perempatan Utama: Dubai D 75 (Jalan Sheikh Rashid), D 73 (Jalan Al Dhiyafa), D 71 (Jalan Al Safa) Kota: Dubai D 90 (bahasa Arab: د ٩٠), juga dikenal sebagai Jalan Al Satwa, Jalan Al Mussallah atau Jalan Mankhool merupakan sebuah rute di Dubai, Uni Emirat Arab. Jalan ...

Giuseppe Spataro Ministro dei trasportiDurata mandato26 luglio 1960 –21 febbraio 1962 PresidenteAmintore Fanfani PredecessoreMario Ferrari Aggradi SuccessoreBernardo Mattarella Ministro dell'internoDurata mandato25 marzo 1960 –26 luglio 1960 PresidenteFernando Tambroni PredecessoreAntonio Segni SuccessoreMario Scelba Ministro della marina mercantileDurata mandato1º luglio 1958 –15 febbraio 1959 PresidenteAmintore Fanfani PredecessoreGennaro Cas...


