USA-177
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Taman Panahan Internasional Sydney Taman Panahan Internasional Sydney (Inggris: Sydney International Archery Parkcode: en is deprecated ) dirancang khusus untuk panahan selama Olimpiade Musim Panas 2000. Stadion ini terletak di Sydney Olympic Park.[1] Dirancang oleh Stutchbury and Pape.[2] Pusat Panahan terletak di seberang Waterfront Apartments di Bennelong Parkway, dan berjarak sekitar 3 km dari pusat kota Sydney Olympic Park. Tempat ini menyelenggarakan berbagai acara,...

Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori italiani è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Giampaolo Piaceri Nazionalità Italia Calcio Ruolo Allenatore (ex attaccante) Termine carriera 1973 - giocatore1997 - allenatore Carriera Giovanili Camaiore Squadre di club1 1955-1958 Camaiore? (?)1958-1959 Talmone Torino5 (2)1959-1960 Cagliari19 (3)1960-1962 Anconitana58 (19)1...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Desember 2023. Yasuhiro YoshidaInformasi pribadiNama lengkap Yasuhiro YoshidaTanggal lahir 14 Juli 1969 (umur 54)Tempat lahir Prefektur Hiroshima, JepangPosisi bermain GelandangKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)1992-1994 Kashima Antlers 1995 Shimizu S-Pulse 1...

Sporting event delegationIndia at the2010 Asian Beach GamesIOC codeINDNOCIndian Olympic Associationin MuscatCompetitors102 in 10 sportsMedalsRanked 6th Gold 3 Silver 0 Bronze 1 Total 4 Asian Beach Games appearances20082010201220142016 India participated in the 2010 Asian Beach Games in Muscat, Oman from 8 to 16 December 2010. Medalists Medal[1] Name Sport Event Date Gold Hc. Jaswinder Singh Tent pegging Individual Sword 10 December Gold India Beach kabaddi Women 16 Decemb...
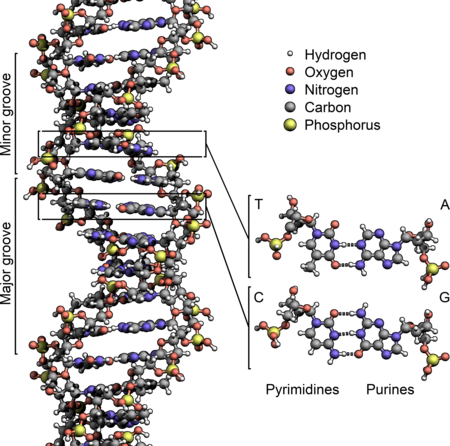
Biological process DNA replication: The double helix is un'zipped' and unwound, then each separated strand (turquoise) acts as a template for replicating a new partner strand (green). Nucleotides (bases) are matched to synthesize the new partner strands into two new double helices. In molecular biology,[1][2][3] DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule.[4] DNA replication occurs in all l...

Independent motion picture distributor Momentum PicturesCompany typePublicIndustryFilm distributionFounded1996; 28 years ago (1996) (Original)2015; 9 years ago (2015) (Relaunch)Defunct2013; 11 years ago (2013) (Original)2023; 1 year ago (2023) (Relaunch)FateAbsorbed by Entertainment One in 2013; relaunched in 2015; reabsorbed in 2023SuccessorsLionsgate FilmsHeadquartersToronto, Ontario, CanadaProductsMotion picturesParent...

2017 single by ASAP Ferg Plain JaneSingle by ASAP Fergfrom the album Still Striving ReleasedJune 13, 2017Recorded2017GenreHip hopLength2:54LabelRCASongwriter(s)Darold Ferguson, Jr.Kirlan LabarriePaul BeauregardJordan HoustonProducer(s)Kirk KnightASAP Ferg singles chronology Look at Us Now (2017) Plain Jane (2017) Nasty (Who Dat) (2017) Music videoPlain Jane on YouTubeRemixCover art of the official remix featuring Nicki Minaj. Nicki Minaj singles chronology The Way Life Goes (Remix)(2017) ...
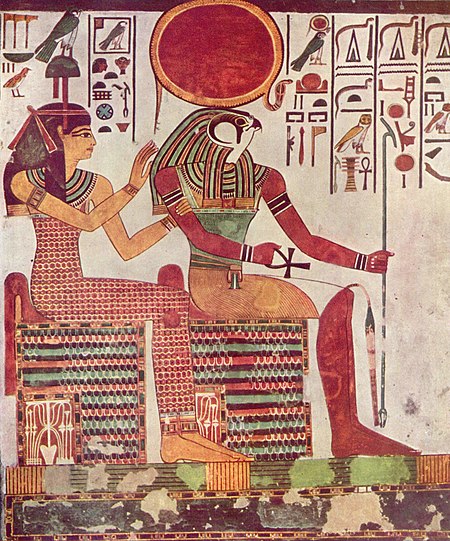

Imentet saluta il faraone Horemheb nella sua tomba. Imentet e Ra, tomba di Nefertari. Imentet o Amentit è una divinità egizia appartenente alla religione dell'antico Egitto, nella quale rappresentava le necropoli occidentali del Nilo. In geroglifico traslitterato ỉmntt È raffigurata come una donna che indossa come copricapo il geroglifico indicante l'Occidente oppure lo ha al posto del capo con al braccio i simboli di vita, stabilità e potenza.[1] Era rappresentata spesso sul fo...

Kadim Al Sahirكاظم الساهرInformasi latar belakangNama lahirKadim Jabbar Al Samaraiكاظم جبار السامرائيLahir12 September 1957 (umur 66)Mosul, IrakGenreMusik ArabPekerjaanpenyanyiaktorpenulis lagukomposerInstrumenvokal, gitar, oudTahun aktif1980 – kiniLabelRotana Records Kadim Jabbar Al Samarai (Arab: كاظم جبار السامرائي; lahir 12 September 1957) atau lebih dikenal sebagai Kadim Al Sahir (Arab: كاظم الساهر) adalah seorang penya...
Human settlement in EnglandHorsingtonChurch of St John the Baptist, HorsingtonHorsingtonLocation within SomersetPopulation571 (2011)[1]OS grid referenceST702238Civil parishHorsingtonDistrictSouth SomersetShire countySomersetRegionSouth WestCountryEnglandSovereign stateUnited KingdomPost townTemplecombePostcode districtBA8Dialling code01963PoliceAvon and SomersetFireDevon and SomersetAmbulanceSouth Western UK ParliamentSomerton and Frome List of...

Currency of Oman Omani rialريال عماني (Arabic) Banknote of 10 Omani RialISO 4217CodeOMR (numeric: 512)Subunit0.001UnitSymbolر.ع. R.O or ﷼DenominationsSubunit 1⁄1000baisaBanknotes Freq. used100 baisa, 1⁄2, 1, 5, 10, 20, 50 rialsCoins Freq. used5, 10, 25, 50 baisaDemographicsUser(s) OmanIssuanceCentral bankCentral Bank of Oman Websitecbo.gov.omValuationInflation4.1% SourceThe World Factbook, 2011 est.Pegged withUS...

American economist Theodore Schulz redirects here. For the golfer, see Ted Schulz. Theodore SchultzBorn(1902-04-30)April 30, 1902Arlington, South Dakota, U.S.Died26 February 1998(1998-02-26) (aged 95)Evanston, Illinois, U.S.EducationSouth Dakota State UniversityUniversity of Wisconsin-MadisonAcademic careerInstitutionIowa State UniversityUniversity of ChicagoFieldAgricultural economicsSchool ortraditionChicago school of economicsAwardsNobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences (1979)...

Lake in the Bernese Oberland, SwitzerlandOeschinen LakeOeschinen Lake from Heuberg. View towards the Blüemlisalp and the Doldenhorn.Oeschinen LakeShow map of Canton of BernOeschinen LakeShow map of Canton of ValaisOeschinen LakeShow map of SwitzerlandOeschinen LakeShow map of AlpsLocationKandersteg, Bernese OberlandCoordinates46°29′54″N 07°43′37″E / 46.49833°N 7.72694°E / 46.49833; 7.72694Typeoligotrophic, holomicticPrimary inflowsBärglibach, Wyssbach, L�...

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府...

لييفة عضلية عضلة هيكلية، تظهر لييفة عضلية معلمة في أعلى الصورة إلى اليمين. تفاصيل ترمينولوجيا هستولوجيكا H2.00.05.0.00007 ن.ف.م.ط. A10.690.552.875، وA11.284.430.214.190.750.620، وA11.620.249.850، وA11.620.500.500 ن.ف.م.ط. D009210 [عدل في ويكي بيانات ] تعديل مصدري - تعديل رسم بياني لتركيب اللي�...

CesinaliKomuneComune di CesinaliLokasi Cesinali di Provinsi AvellinoNegaraItaliaWilayah CampaniaProvinsiAvellino (AV)Luas[1] • Total3,73 km2 (1,44 sq mi)Ketinggian[2]380 m (1,250 ft)Populasi (2016)[3] • Total2.472 • Kepadatan660/km2 (1,700/sq mi)Zona waktuUTC+1 (CET) • Musim panas (DST)UTC+2 (CEST)Kode pos83020Kode area telepon0825Situs webhttp://www.comune.cesinali.av.it Cesinali adalah...

Sărmașu NagysármásKota Lambang kebesaranNegara RumaniaCountyCounty MureşStatus[[Kota {{{1}}}|{{{1}}}]]Pemerintahan • Wali kotaIoan Mocean (PNL)Populasi (2011) • Total6.833Zona waktuUTC+2 (EET) • Musim panas (DST)UTC+3 (EEST) Sărmașu (bahasa Hongaria: Nagysármás; pelafalan Hungaria: [’nɒɟʃaːrmaːʃ] ) adalah sebuah kota yang terletak di County Mureș, Transilvania tengah, Rumania. Secara administratif di kota ini terdapat tujuh d...

County in West Virginia, United States For other uses, see Wayne County. This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) Some of this article's listed sources may not be reliable. Please help improve this article by looking for better, more reliable sources. Unreliable citations may be challenged and removed. (June 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) This article needs addit...

The Immaculate Collection Сборник Мадонны Дата выпуска 9 ноября 1990 Дата записи февраль 1983 — август 1990 Жанры Поп, данс Длительность 73:34 Продюсеры Мадонна, Стивен Брэй, Патрик Леонард, Джон Бенитэс, Регги Лукас, Найл Роджерс, Шэп Пэттибон, Ленни Кравиц Язык песен английский Лейблы Sire,...

Trading bloc with no internal barriers and common policies on regulation and trade Part of a series onWorld trade Policy Import Export Balance of trade Trade law Trade pact Trade bloc Trade creation Trade diversion Export orientation Import substitution Trade finance Trade facilitation Trade route Domestic trade Tax Restrictions Trade barriers Tariffs Non-tariff barriers Import quotas Tariff-rate quotas Import licenses Customs duties Export subsidies Technical barriers Bribery Exchange rate c...
