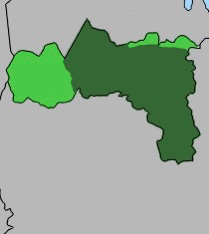
Tigray Defense Forces
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Toyota Yaris VersoInformasiProdusenToyotaJuga disebutToyota Fun CargoMasa produksi1999-2006PerakitanToyota City, JepangBodi & rangkaKelasMini MPVBentuk kerangka5-door vanTata letakMesin depan, penggerak roda depan4WDPenyalur dayaMesin1298 cc 2NZ-FE I4 (NCP20/22)1497 cc 1NZ-FE I4 (NCP21/25)1364 cc 1ND-TV td I4 (NLP20/22)KronologiPenerusToyota Ractis (Japan)Toyota Verso-S (Europe)Toyota Space Verso (Israel) Toyota Yaris Verso adalah MPV mini yang diproduksi Toyota M...

English actress For the British artist and sculptor, see Helen Margaret George. Helen GeorgeGeorge in 2015BornHelen Elizabeth George (1984-06-19) 19 June 1984 (age 39)Birmingham, West Midlands, England[1]OccupationActressYears active2006–presentSpouse Oliver Boot (m. 2011; div. 2015)PartnerJack Ashton (2016–2023)Children2 Helen Elizabeth George (born 19 June 1984) is an English actress, best known for playing Trixie Fra...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Desember 2023. Miss SupranationalTanggal pendirian2009TipeKontes kecantikanKantor pusatPanama City, PanamaPresidenTryny Marcela Yadar Lobón dari PanamaTokoh pentingWBASitus webwww.misssupranational.com Berikut ini adalah daftar penghargaan khusus yang diberikan pad...
2022 Itahari municipal elections ← 2017 13 May 2022 2027 → 102 seats to Itahari Sub Metropolitan City Council52 seats needed for a majority First party Second party Leader Hem Karna Paudel Party Nepali Congress+ CPN (UML) Seats before 43 58 Seats won 22 75 Seat change 21 17 Third party Fourth party Party Independent CPN (MC) Seats before 0 1 Seats won 5 0 Seat change 5 1 Results for ward chair by party Mayor befor...

Questa voce o sezione sugli argomenti unità militari e stati scomparsi non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Commento: Alcune sezioni non presentano fonti sufficienti, altre nemmeno una. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti dei progetti di riferimento 1, 2. Unione Sovietica (dettagli) (dettagli) Motto: (RU) Пролетарии всех стран, соеди...

British territory from 1953 to 1963 Not to be confused with the Central African Republic or British Central Africa Protectorate. Federation ofRhodesia and Nyasaland1953–1963 Flag Coat of arms Motto: Magni Esse MereamurLet Us Achieve GreatnessAnthem: God Save the QueenStatusColonyProtectorate and self-governing colonyCapitaland largest citySalisburyLanguagesEnglish, Shona, Tumbuka, Ndebele, Bemba, ChewaGovernmentFederal monarchyMonarch • 1953-1963 Elizabeth II Governor-...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、�...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、�...

Philippine indigenous people For the language, see Cotabato Manobo language. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Tasaday – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) TasadayThe Tasaday people in their homeland, the last primal rainfore...

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府...

Misi diplomatik Suriname di dunia. Berikut ini adalah daftar misi diplomatik Suriname, tidak termasuk konsulat kehormatan. Afrika Kedutaan Besar Suriname di Den Haag. Kedutaan Besar Suriname di Paris. Ghana Accra (kedutaan besar) Amerika Amerika Serikat Washington, D.C. (kedutaan besar) Miami (konsulat jenderal) Brasil Brasília (kedutaan besar) Guyana Georgetown (kedutaan besar) Kuba Havana (kedutaan besar) Trinidad dan Tobago Port of Spain (kedutaan besar...

1993 album This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Who Covers Who? – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2016) (Learn how and wh...

American politician (1877–1953) Senator Wagner redirects here. For other uses, see Senator Wagner (disambiguation). Not to be confused with Robert Wagner. Robert F. WagnerHarris & Ewing photo, Library of CongressUnited States Senatorfrom New YorkIn officeMarch 4, 1927 – June 28, 1949Preceded byJames W. Wadsworth Jr.Succeeded byJohn Foster DullesActing Lieutenant Governor of New YorkIn officeOctober 17, 1913 – December 31, 1914GovernorMartin H. GlynnPreceded byMarti...

この項目では、シロシビンを含むキノコについて説明しています。白い斑点の赤キノコ(マジックマッシュルームではない)については「ベニテングタケ」をご覧ください。 Psilocybe Semilanceataの定訳のための文献求。暫定として、俗に頻用されたと思われる用語「リバティーキャップ」とした。 メキシコでシャーマンが用いてきたシロシベ・メキシカーナ(英語版) Psi...

إلفسينا Ελευσίνα Elefsina (باليونانية: Ελευσίνα) الموقع الجغرافي تقسيم إداري البلد اليونان[1] عاصمة لـ أتيكا الغربية المنطقة الإدارية أتيكا أتيكا الغربية خصائص جغرافية إحداثيات 38°02′29″N 23°32′43″E / 38.04138889°N 23.54527778°E / 38.04138889; 23.54527778 المساحة 18.455 كي�...

Medical procedure to replace blood or immune stem cells Bone marrow transplant redirects here. For the journal abbreviated Bone Marrow Transplant, see Bone Marrow Transplantation (journal). Hematopoietic stem cell transplantationBone marrow transplantICD-9-CM41.0MeSHD018380MedlinePlus003009[edit on Wikidata] Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord bl...

Medication of the opioid type, patented 1972 Tramadol Clinical dataPronunciationtra' ma doll Trade namesUltram, Zytram, Ralivia, others[1]AHFS/Drugs.comMonographMedlinePlusa695011License data US DailyMed: Tramadol Pregnancycategory AU: C[2] DependenceliabilityLow–moderate[3]Routes ofadministrationBy mouth, intravenous (IV), intramuscular (IM), rectalDrug classOpioid analgesic[4]ATC codeN02AX02 (WHO) N02AJ13 (WHO)Legal status...

Virslīga 2017SynotTip Virslīga 2017 Competizione Virslīga Sport Calcio Edizione 43ª Organizzatore LFF Date dal 10 marzo 2017al 4 novembre 2017 Luogo Lettonia Partecipanti 8 Formula Girone all'italiana Risultati Vincitore Spartaks Jūrmala(2º titolo) Secondo Liepāja Retrocessioni Babīte Statistiche Miglior marcatore Evgenij Kozlov (13) Incontri disputati 84 Gol segnati 200 (2,38 per incontro) Cronologia della competizione 2016 2018 Manuale La Virslīga 2017 è s...

Prime Minister of Japan 1978 to 1980 This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Masayoshi Ōhira – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2007) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Masayoshi Ōhira大平 正芳Official portrait, 1978Prime Minister of JapanIn office7 December 1978&#...

VII Recopa Africana 1981 Fecha abril de 1981diciembre de 1981 Cantidad de equipos 32 Podio • Campeón• Subcampeón• Semifinalistas Union Douala Stationery Stores Djoliba AC Sekondi Hasaacas Partidos 47 Goles anotados 127 (2.70 por partido) La Recopa Africana 1981 es la sétima edición de este torneo de fútbol a nivel de clubes de África organizado por la CAF y que contó con la participación de 32 equipos campeones de copa de sus respectivos países, 4 más que en la ed...