Suma people
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
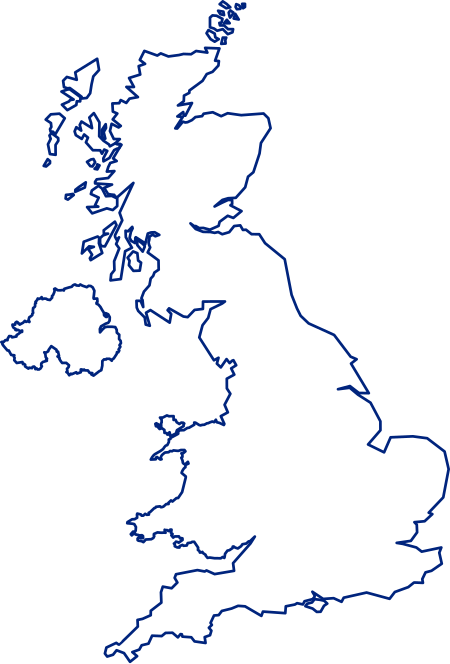
Lokasi Southampton di Inggris Southampton merupakan kota pelabuhan yang terletak di Inggris bagian selatan. Penduduknya berjumlah 222.000 jiwa (2005). Kota ini terletak di county Hampshire. Kota ini memiliki luas wilayah 49,84 km². Kota ini memiliki kepadatan penduduk sebesar 4.454 jiwa/km². Pranala luar Wikimedia Commons memiliki media mengenai Southampton. Situs web resmi Artikel bertopik geografi atau tempat Britania Raya ini adalah sebuah rintisan. Anda dapat membantu Wikipedia den...

العلاقات الكندية الليسوتوية كندا ليسوتو كندا ليسوتو تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الكندية الليسوتوية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين كندا وليسوتو.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارنة كندا ليس...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Januari 2016. Chuvashia Airlines IATA ICAO Kode panggil CBK Didirikan1993Berhenti beroperasi2009Pusat operasiBandar Udara CheboksaryKantor pusatCheboksary, Chuvashia, Rusia Chuvashia Airlines adalah maskapai penerbangan yang berbasis di Cheboksary, Chuvashia, Rusia....
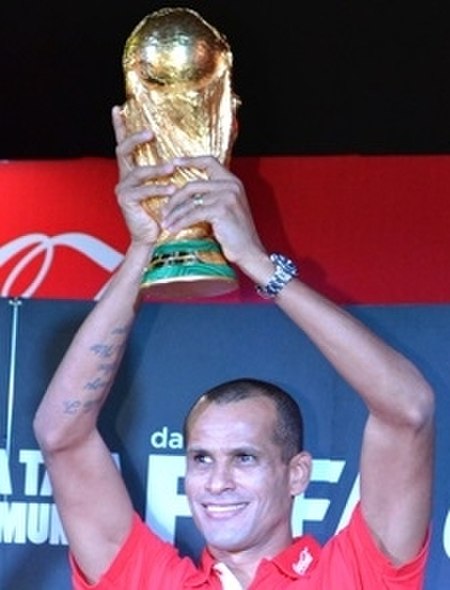

Rivaldo, vincitore del Pallone d'oro 1999 L’edizione 1999 del Pallone d'oro, 44ª edizione del premio calcistico istituito dalla rivista francese France Football, fu vinta dal brasiliano Rivaldo (Barcellona). I giurati che votarono furono 51, provenienti da Albania, Andorra, Armenia, Austria, Azerbaigian, Belgio, Bielorussia, Bosnia ed Erzegovina, Bulgaria, Cipro, Croazia, Danimarca, Estonia, Finlandia, Francia, Galles, Georgia, Germania, Grecia, Inghilterra, Irlanda, Irlanda del Nord, Isla...

Benjamin Nathan Cardozo Hakim Mahkamah Agung Amerika SerikatMasa jabatan14 Maret 1932 – 9 Juli 1938 Informasi pribadiKebangsaanAmerika SerikatProfesiHakimSunting kotak info • L • B Benjamin Nathan Cardozo adalah hakim Mahkamah Agung Amerika Serikat. Ia mulai menjabat sebagai hakim pada mahkamah tersebut pada tanggal 14 Maret 1932. Masa baktinya sebagai hakim berakhir pada tanggal 9 Juli 1938.[1] Referensi ^ Justices 1789 to Present. Washington, D.C.: Mahkamah ...

† Человек прямоходящий Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:Синапсиды�...

Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat Daerah Kabupaten Lombok BaratDewan Perwakilan RakyatKabupaten Lombok Barat2019-2024JenisJenisUnikameral Jangka waktu5 tahunSejarahSesi baru dimulai14 Agustus 2019PimpinanKetuaHj. Nur Hidayah (Gerindra) sejak 24 September 2019 Wakil Ketua IHj. Nurul Adha (PKS) sejak 24 September 2019 Wakil Ketua IIImam Kafali (Golkar) sejak 24 September 2019 Wakil Ketua IIIAhmad Suparman (PPP) sejak 24 September 2019 KomposisiAnggota45Partai & kursi PDI-P ...

سباق طواف فرنسا 1970 الاسم سباق طواف فرنسا 1970 السلسلة سوبر برستيج بيرنود 1970 التاريخ 27 يونيو - 19 يوليو، 1970 التاريخ بداية:27 يونيو 1970 نهاية:19 يوليو 1970 عدد المراحل 23+Prologue, including five split stages عدد الرياضيين 150 (نقطة البداية)، و100 (نقطة النهاية) المسافة 4366 الزمن 119 ساعة و31 د�...

American college basketball season 2022–23 Mississippi State Bulldogs women's basketballNCAA Tournament, Round of 32ConferenceSoutheastern ConferenceRecord22–11 (9–7 SEC)Head coachSam Purcell (1st season)Assistant coaches Murriel Page Corry Irvin Gabe Lazo Home arenaHumphrey ColiseumSeasons← 2021–222023–24 → 2022–23 SEC women's basketball standings vte Conf Overall Team W L PCT W L PCT No. 1 South Carolina† 16 – 0...

Борис Миколайович Лятошинський Борис Миколайович ЛятошинськийІм'я при народженні Борис Миколайович ЛятошинськийНародився 22 листопада (4 грудня) 1894[4][5]Житомир, Російська імперія[1]Помер 15 квітня 1968(1968-04-15)[1][2][…] (73 роки)Київ, Українська РСР, СРСР[1]...

American punk band Dead KennedysDead Kennedys performing in 2019Background informationOriginSan Francisco, California, USGenresPunk rockhardcore punkDiscographyDead Kennedys discographyYears active 1978–1986 2001–present LabelsCherry RedFaulty ProductsAlternative TentaclesManifesto/DecayMembers East Bay Ray Klaus Flouride Ron Skip Greer Steve Wilson Past members Jello Biafra 6025 Ted D. H. Peligro Brandon Cruz Jeff Penalty Dave Scheff Greg Reeves Santi Guardiola Websitedeadkennedys.c...
International basketball competition 1998 FIBA World Championshipfor Women13th FIBA World Championship for WomenTournament detailsHost countryGermanyDatesMay 26 – June 7Teams16Venue(s)7 (in 7 host cities)Final positionsChampions United States (6th title)Tournament statisticsTop scorer Arcain (20.2)Top rebounds Ferazzoli (11.8)Top assists Chun (6.2)Official website1998 FIBA World Championship for Women← 1994 2002 → The 1998 FIBA Women's World Championship (Ger...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018) 1998 في أستراليامعلومات عامةالسنة 1998 البلد أستراليا 1997 في أستراليا 1999 في أستراليا تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعد�...

American technology company General MagicIndustryPersonal digital assistantsSoftwareFoundedMay 1990 (1990-05)[1]FoundersBill AtkinsonAndy HertzfeldMarc Porat[1]DefunctSeptember 17, 2002 (2002-09-17)[2]HeadquartersMountain View, California, United States[1]ProductsTelescriptMagic Cap General Magic was an American software and electronics company co-founded by Bill Atkinson, Andy Hertzfeld,[1] and Marc Porat. Based in Mountain Vie...

American psychologist (1936–2022) Clyde HendrickBorn(1936-07-13)July 13, 1936Reed, Oklahoma, U.S.[1]DiedAugust 6, 2022(2022-08-06) (aged 86) Clyde Hendrick was a Horn Professor of Psychology at Texas Tech University. He received his doctorate degree from University of Missouri in 1967 in Psychology. His main research interests included close relationships. During the past decade his primary focus was around love and sex attitudes. In collaboration with doctoral students. Hendri...

Trade of sexual slaves This article is written like a personal reflection, personal essay, or argumentative essay that states a Wikipedia editor's personal feelings or presents an original argument about a topic. Please help improve it by rewriting it in an encyclopedic style. (July 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) The business model for sex trafficking as described by Swedish anti-sex work activists Sex and the law Social issues Consent Reproductive rights Homophobia (Crimin...

Traditional parade This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (March 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message)This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Cava...

PT Bank Pembangunan Daerah Kalimantan SelatanJenisBUMDIndustriJasa keuanganDidirikanBanjarmasin, Indonesia (1964)KantorpusatBanjarmasin, IndonesiaTokohkunciHanawijaya Direktur UtamaPendapatanRp 1,47 Trilyun (2021)Laba bersihRp 219,25 Milyar (2021)Situs webwww.bankkalsel.co.id Bank Kalsel adalah salah satu bank di Indonesia dengan nama usaha PT Bank Pembangunan Daerah Kalimantan Selatan, yang berlokasi di Provinsi Kalimantan Selatan. Sejarah Bank Pembangunan Daerah Kalimantan Selatan didirikan...

Một tháp semaphore Chappe gần Saverne, Pháp Đối với các định nghĩa khác, xem Semaphore (định hướng). Semaphore hay optical telegraph (tạm dịch: truyền tin thị giác) là một công cụ dùng để truyền tin qua phương tiện tín hiệu nhìn thấy được với tháp cao cùng với các phiến quay quanh trục (pivoting blades) hay các cánh quạt (paddles), các cửa chớp (shutters) trong một hình thể ma trận (matrix), hoặc là các c...

For other towers with the same name, see Centennial Tower. Centennial TowerLocation in Rizal ParkShow map of Rizal ParkLocation in ManilaShow map of ManilaLocation in Metro ManilaShow map of Metro ManilaLocation in LuzonShow map of LuzonLocation in the PhilippinesShow map of PhilippinesGeneral informationStatusNever builtAddressAgrifina Circle, Rizal Park, Ermita(original site)Julia Vargas Avenue cor. Meralco Avenue(final site)Town or cityManila (original site)Pasig (final site)CountryPhilipp...
