Strategic nuclear weapon
|
Read other articles:
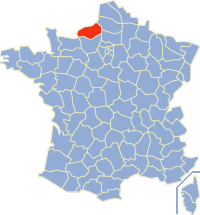
Lista das 745 comunas do departamento francês de Sena Marítimo.[1] INSEE Postal Comuna 76001 76190 Allouville-Bellefosse 76002 76640 Alvimare 76004 76550 Ambrumesnil 76005 76920 Amfreville-la-Mi-Voie (CAR) 76006 76560 Amfreville-les-Champs 76007 76710 Anceaumeville 76008 76370 Ancourt (CAD) 76009 76560 Ancourteville-sur-Héricourt 76010 76760 Ancretiéville-Saint-Victor 76011 76540 Ancretteville-sur-Mer 76012 76110 Angerville-Bailleul 76013 76540 Angerville-la-Martel 76014 76280 Anger...

Cycling race Cycling race 2017 Tour de Romandie2017 UCI World Tour, race 19 of 37Race detailsDates25–30 April 2017Stages6Distance682.98 km (424.4 mi)Winning time17h 16' 00[1]Results Winner Richie Porte (AUS) (BMC Racing Team) Second Simon Yates (GBR) (Orica–Scott) Third Primož Roglič (SLO) (LottoNL–Jumbo) Points Stefan Küng (SUI) (BMC Racing Team) Mountains Sander Armée (BEL) (Lotto–Soudal) Youth ...

American television personality Star JonesJones in 2011BornStarlet Marie Jones (1962-03-24) March 24, 1962 (age 61)Badin, North Carolina, U.S.Other namesStar Jones ReynoldsAlma mater American University (BA) University of Houston (JD) Occupations Lawyer journalist talk show host writer women's advocate fashion designer Years active1991–presentNotable credits The View (1997–2006) Star Jones (2007–2008) Spouses Al Reynolds (m. 2004; ...

The following is a timeline of the history of Lynn, Massachusetts, USA. This is a dynamic list and may never be able to satisfy particular standards for completeness. You can help by adding missing items with reliable sources. 17th-18th century 1629 - Saugus founded. [1] Among the founders — Edmund Ingalls 1637 - Saugus renamed to Lynn in honor of Reverend Samuel Whiting (Senior), Lynn's first official minister who arrived from King's Lynn.[2][1] 1642 - Saugus Iron W...

Львівська область Герб Львівської області Прапор Львівської області Основні дані Прізвисько: Галичина, Львівщина Країна: Україна Утворена: 4 грудня 1939 року Код КАТОТТГ: UA46000000000026241 Населення: 2 478 133 Площа: 21 831.97 км² Густота населення: 113,42 осіб/км² Поштові індекси 79000...

Districts of Montreal redirects here. Not to be confused with District of Montreal. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: List of neighbourhoods in Montreal – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Map of the Montreal neighbour...

College of West Bengal, India Dr. B.R. Ambedkar CollegeTypeUndergraduate college Public collegeEstablished1973; 50 years ago (1973)LocationBetai, West Bengal, 741163, India23°48′09″N 88°33′39″E / 23.80261°N 88.5608021°E / 23.80261; 88.5608021CampusUrbanAffiliationsUniversity of KalyaniWebsitebrambedkarcollegebetai.inLocation in West BengalShow map of West BengalDr. B.R. Ambedkar College (India)Show map of India Dr. B.R. Ambedkar College, e...

منهجية برينس2 لادارة المشروعات إن منهجية ادارة المشاريع برينس 2 (بالإنجليزية PRINCE2) (وهي اختصار Projects In Controlled Environments المشاريع في البيئات الخاضعة للتحكم، الإصدار 2) تشمل إدارة الجودة، ومراقبة وتنظيم المشروع مع الاتساق والمراجعة لتتماشى مع اهداف المشروع، وكذلك هي برنامج ل

「霹雳火 (电影)」重定向至此。關於同名的其它解釋,請見「霹靂火 (消歧義)」。 霹靂火Thunderbolt基本资料导演陳嘉上监制蔡瀾制片陳希文、羅秀慧编剧陳嘉上陳慶嘉郭偉鐘主演成龍袁詠儀楚原王敏德配乐梁邦彥摄影林國華劉鴻泉黃永恆關志勤陳廣鴻鄭兆強剪辑張耀宗張嘉輝吳宏雄陳祺合制片商嘉禾片长97分鐘产地 英屬香港语言粵語、英語、日語上映及发行上映日期 英屬

تاريخ اليابان الاقتصاديمعلومات عامةالمنطقة اليابان التأثيراتأحد جوانب اقتصاد اليابان — تاريخ اقتصادي فرع من تاريخ اليابانتاريخ الاقتصاد تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات جزء من سلسلة مقالات حولتاريخ اليابان خط زمني عصر حجري 35000–14000 ق.م. فترة جومون 14000–400 ق. م. فترة ي�...

هاملت أو نهاية الليل الطويل Hamlet oder Die lange Nacht غلاف الطبعة الأولى للرواية معلومات الكتاب المؤلف ألفرد دوبلن البلد ألمانيا اللغة ألمانية الناشر Rütten & Loening, East Berlin تاريخ النشر 1956 النوع الأدبي رواية الموضوع أدب، وعلاقة الوالدين بالابناء [لغات أخرى]، وزواج، &...

العلاقات البليزية البوتسوانية بليز بوتسوانا بليز بوتسوانا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات البليزية البوتسوانية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين بليز وبوتسوانا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقار�...

Malaysia United Nations membershipRepresented by Federation of Malaya (1957–1963) MembershipFull memberSince17 September 1957 (1957-09-17)UNSC seatNon-permanentPermanent RepresentativeH.E. Dato’ Dr. Ahmad Faisal bin Muhamad Malaysia became the 82nd member of the United Nations on 17 September 1957 (when it was then known as the Federation of Malaya).[1] Malaysia has held a rotational non-permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council for four terms, and has p...

Subsidiary manufacturer of HVAC systems This article is about the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning system manufacturer. For the holding company, see Trane Technologies. Trane Inc.Former Trane Company headquarters in La Crosse, WisconsinTypeSubsidiaryIndustryEquipment manufacturingFounded1913; 110 years ago (1913) as The Trane Company in La Crosse, Wisconsin, U.S.FounderJames TraneReuben TraneHeadquartersSwords, Dublin, IrelandProductsHeating, ventilation and air co...

2022 NCAA Division I women's soccer rankingsSeason2022NCAA Tournament2022Preseason No. 1Florida StateNCAA Tournament ChampionsUCLA NCAA Division I women's soccer rankings ← 2021 2023 → Two major human polls made up the 2022 NCAA Division I women's soccer rankings: United Soccer Coaches and Top Drawer Soccer. Legend Increase in ranking Decrease in ranking New to rankings from previous week Italics Number of first place votes (#–#) Win-loss rec...

Title in the Peerage of Scotland This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (October 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) For the 1833 steam locomotive Earl of Airlie, see Earl of Airlie (locomotive). Earldom of AirlieCreation date2 April 1639Created byKing Charles IPeeragePeerage of ScotlandFirst holderJames Ogilv...

5th episode of the 2nd season of RuPaul's Drag Race All Stars Revenge of the QueensRuPaul's Drag Race All Stars episodeEpisode no.Season 2Episode 5Original air dateSeptember 15, 2016 (2016-09-15)Running time42 minutesGuest appearance Ross Matthews Episode chronology ← PreviousDrag Movie Shequels Next →Drag Fish Tank RuPaul's Drag Race All Stars (season 2)List of episodes Revenge of the Queens is the fifth episode of the second season of the American reality c...

Restaurant in Portland, Oregon, U.S. Cadillac CafeThe restaurant's exterior in 2022Restaurant informationStreet address1801 NE BroadwayCityPortlandCountyMultnomahStateOregonPostal/ZIP Code97232CountryUnited StatesCoordinates45°32′07″N 122°38′51″W / 45.5352°N 122.6475°W / 45.5352; -122.6475Websitecadillaccafepdx.com Cadillac Cafe is a restaurant in Portland, Oregon's Irvington neighborhood, in the United States. Description Cadillac Cafe is a restaurant alon...

British theologian (born 1946) Richard BauckhamFRSE FBABorn (1946-09-22) 22 September 1946 (age 77)London, EnglandTitleRetired Professor of New Testament Studies and Bishop Wardlaw Professor in the University of St AndrewsParent(s)John Robert Bauckham (1911–1980) and Stephiana Lilham (Lilian) (1911–1998)Academic backgroundAlma materClare College, University of CambridgeThesis (1972)Academic workInstitutionsRidley Hall, CambridgeMain interestsNew Testament Christology and the...

You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in German. (March 2022) Click [show] for important translation instructions. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the English Wikipedia. Do not translate text that appears unreliable or low-q...
