St Thomas' Church, Erfurt
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Sebuah kolek Kolek pengaman. Kolek adalah sejenis perahu kecil, yang sering dibawa atau ditarik oleh kapal yang lebih besar untuk digunakan sebagai perahu layan . [1] Kolek utilitas biasanya berupa perahu dayung atau memiliki motor tempel . Beberapa di antaranya dilengkapi untuk berlayar tetapi berbeda dengan kolek layar, yang dirancang pertama dan terutama untuk berlayar. Kegunaan utama kolek adalah untuk berpindah dari kapal yang lebih besar, terutama bila kapal yang lebih besar tid...

العلاقات الفنزويلية الناوروية فنزويلا ناورو فنزويلا ناورو تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الفنزويلية الناوروية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين فنزويلا وناورو.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقار...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Néso. Néso Neptune XIII Vue d'artiste Type Satellite naturel de Neptune Caractéristiques orbitales (Époque 10/06/2003, JJ 2452801.5[1]) Demi-grand axe 48 387 000 km[1] Périapside 24 435 000 km[2] Apoapside 72 339 000 km[2] Excentricité 0,495[1] Période de révolution 9 737 d[1] (26,66 a) Inclinaison 132,6°[1] (par rapport à l'écliptique) Caractéristiques physiques Dimension...

Christophe Vincent Lens versus AC Ajaccio (2015)Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Christophe VincentTanggal lahir 8 November 1992 (umur 31)Tempat lahir PrancisTinggi 1,78 m (5 ft 10 in)Posisi bermain GelandangInformasi klubKlub saat ini SC BastiaNomor 23Karier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2011– SC Bastia 5 (0) * Penampilan dan gol di klub senior hanya dihitung dari liga domestik dan akurat per 20 Juli 2012 Christophe Vincent (lahir 8 November 1992) adalah seorang pemai...

Armor Holdings, Inc.Company typeSubsidiaryIndustryDefenseFoundedJanuary 1, 1996HeadquartersJacksonville, Florida, United StatesOwnerBAE SystemsParentBAE Systems Land and ArmamentsDivisionsacquired vehicle division of Stewart & StevensonWebsitewww.armorholdings.com Armor Holdings, Inc. was an American manufacturer of military, law enforcement, and personnel safety equipment. It was acquired by BAE Systems on July 31, 2007[1] and renamed BAE Systems Mobility & Protection Systems...

Catholic Church Synod This article relies excessively on references to primary sources. Please improve this article by adding secondary or tertiary sources. Find sources: Third Extraordinary General Assembly of the Synod of Bishops – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Third Extraordinary General Assembly of the Synod of BishopsDate5–19 October 2014Convoked byPope Franc...

4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid Names Preferred IUPAC name 3-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-2-oxopropanoic acid Other names 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvatep-Hydroxyphenylpyruvic acidp-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Identifiers CAS Number 156-39-8 Y 3D model (JSmol) Interactive image ChEBI CHEBI:15999 Y ChEMBL ChEMBL607712 Y ChemSpider 954 Y DrugBank DB07718 Y ECHA InfoCard 100.005.322 IUPHAR/BPS 6629 KEGG C01179 Y PubChem CID 979 UNII 0YP1694WNQ Y CompTox Dashboard (EPA) DTXSID80166017 InCh...

Bread dish primarily from Spanish and Portuguese cuisine For other uses, see Rosca (disambiguation). Not to be confused with the Roscas and Rosquillos cookies in the Philippine cuisine RoscaRosca from Madrid, SpainAlternative namesKa'akeTypeBread, bagel, doughnutRegion or stateMexico, South America, and other areasCreated bySpanish and PortugueseMain ingredientsFlour, salt, sugar, butter, yeast, water, and seasonings Media: Rosca Rosca (ring or bagel) is a Spanish and Portuguese[...

ХристианствоБиблия Ветхий Завет Новый Завет Евангелие Десять заповедей Нагорная проповедь Апокрифы Бог, Троица Бог Отец Иисус Христос Святой Дух История христианства Апостолы Хронология христианства Раннее христианство Гностическое христианство Вселенские соборы Н...

Genus of ants Not to be confused with Myrmecia (ant) or Myrmica. Myrmecina Myrmecina graminicola worker from Japan Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Class: Insecta Order: Hymenoptera Family: Formicidae Subfamily: Myrmicinae Tribe: Crematogastrini Genus: MyrmecinaCurtis, 1829 Type species Myrmecina latreilliiMayr, 1855 Diversity[1] 53 species Synonyms Archaeomyrmex Mann, 1921 Myrmecina is a genus of ants in the subfamily Myrmicinae.[2&...

Министерство природных ресурсов и экологии Российской Федерациисокращённо: Минприроды России Общая информация Страна Россия Юрисдикция Россия Дата создания 12 мая 2008 Предшественники Министерство природных ресурсов Российской Федерации (1996—1998)Министерство охраны...

Village in South Governorate, LebanonAin El Delb عين الدلبVillageAin El DelbLocation in LebanonCoordinates: 33°32′28″N 35°23′18″E / 33.541104°N 35.388272°E / 33.541104; 35.388272Country LebanonGovernorateSouth GovernorateDistrictSidon DistrictTime zoneUTC+2 (EET) • Summer (DST)UTC+3 (EEST) Ain El Delb (عين الدلب) is a small village in the Sidon District of the South Governorate in Lebanon. History In 1875 Victor Guérin foun...

Грамота Президії Верховної Ради УРСРГрамота Президії Верховної Ради Української РСР Країна УРСРТип Державна нагорода Української РСРВручається: громадяни, підприємства, установи, організації, трудові колективи, населені пункти, військові частиниВручає: Президія Вер�...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Final Fantasy (disambigua). «Non penso di essere bravo a creare giochi d'azione. Preferisco narrare storie.» (Hironobu Sakaguchi, creatore di Final Fantasy) Il bobi della serie. Final Fantasy (ファイナルファンタジー?, Fainaru Fantajī) è una serie di videogiochi di ruolo giapponese prodotti da Square (divenuta Square Enix nel 2003). Final Fantasy rappresenta uno dei più grandi marchi per il mondo del divertimento int...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article is an orphan, as no other articles link to it. Please introduce links to this page from related articles; try the Find link tool for suggestions. (April 2022) Some of this article's listed sources may not be reliable. Please help improve this article by looking for better, more reliable sources. Unreliable citations may be chall...

Не плутати з Домініканською Республікою. Співдружність Домінікиангл. Commonwealth of Dominicaфр. Commonwealth de Dominiqueкар. Wai‘tu kubuliдом. креольська Dominik Прапор Герб Девіз: «Après Bondie, C'est La Ter»Після Бога тільки земля Гімн: «Isle of Beauty, Isle of Splendour» Розташування Домініки Столиця(та найбільше місто) Р�...

For the club that was founded in 1918, see West Melbourne Football Club (1918). Australian rules football club West MelbourneNamesFull nameWest Melbourne Football ClubNickname(s)WestsClub detailsFounded1874Dissolved1908Colours Red WhiteCompetitionVictorian Football Association (1879–1880, 1899–1907)Premierships1906Ground(s)North Melbourne Recreation Reserve (1899–1906)East Melbourne Cricket Ground (1907)Uniforms Home The West Melbourne Football Club was an Australian rules ...

1966 film This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: The Plainsman 1966 film – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) The PlainsmanTheatrical release posterDirected byDavid Lowell RichWritten byMichael BlankfortProduced byRichard E. Lyons...

Arco della PaceLocalizzazioneStato Italia RegioneLombardia LocalitàMilano IndirizzoPiazza Sempione Coordinate45°28′32.51″N 9°10′20.67″E45°28′32.51″N, 9°10′20.67″E Informazioni generaliCondizioniIn uso Costruzione1807 - 1838 Inaugurazione1838 StileNeoclassicismo Usomonumento RealizzazioneArchitettoLuigi Cagnola ProprietarioComune di Milano Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale L'Arco della Pace (Arch del Sempion in dialetto milanese[1]) è un arco trio...
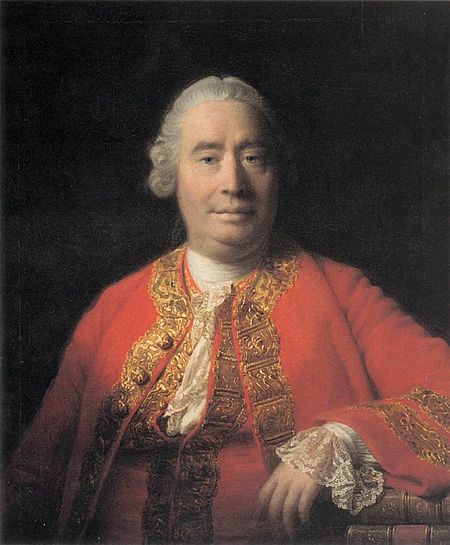

Philosophical problem articulated by David Hume David Hume raised the is–ought problem in his Treatise of Human Nature. The is–ought problem, as articulated by the Scottish philosopher and historian David Hume, arises when one makes claims about what ought to be that are based solely on statements about what is. Hume found that there seems to be a significant difference between positive (or descriptive) statements (about what is) and prescriptive or normative statements (about what ought ...