Speech coding
|
Read other articles:

Kabupaten TrenggalekKabupatenTranskripsi bahasa daerah • Hanacarakaꦠꦽꦔ꧀ꦒꦭꦺꦏ꧀ • Pegonترڠڬالَيك • Bentuk nonformal JawangGalekSearah jarum jam: Pantai Blado, Gua Kumbokarno, Pantai Prigi, dan lahan sawah berlatar belakang Gunung Wilis LambangEtimologi: Teranging galihGaplekJulukan: Penghasil GaplekMotto: Jwalita praja karana(Jawa) Cemerlang karena rakyatPetaKabupaten TrenggalekPetaTampilkan peta JawaKabupaten Trenggal...

Biografi ini tidak memiliki sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak dapat dipastikan. Bantu memperbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan sumber tepercaya. Materi kontroversial atau trivial yang sumbernya tidak memadai atau tidak bisa dipercaya harus segera dihapus.Cari sumber: Al-Mu'tashim Billah – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) Biografi ini memerlukan lebih banyak cata...

Isoprena Isoprena adalah nama umum (nama trivial) dari 2-metilbuta-1,3-diena. Senyawa ini biasa digunakan dalam industri, penyusun berbagai senyawa biologi penting, serta dapat berbahaya bagi lingkungan dan beracun bagi manusia bila terpapar secara berlebihan. Dalam suhu ruang isoprena berwujud cairan bening yang sangat mudah terbakar dan terpantik. Bila tercampur dengan udara sangat mudah meledak dan sangat reaktif bila dipanaskan. Pengangkutan isoprena memerlukan penanganan khusus. Secara i...

الممثل الدائم للمغرب لدى الأمم المتحدة عمر هلال عن المنصب المعين محمد السادس بن الحسن تأسيس المنصب 1956 الموقع الرسمي الموقع الرسمي تعديل مصدري - تعديل يتولى السفير والممثل الدائم للمغرب لدى الأمم المتحدة مهمة رئاسة الوفد المغربي لدى الأمم المتحدة في نيويو...

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Пт�...

Bakteri lipofilik adalah sejenis bakteri yang memiliki lipofilisitas, dapat berkembang biak dalam lipid (zat lemak yang tidak larut dalam air, tetapi umumnya larut dalam alkohol dan eter). Risiko kesehatan Kebanyakan material/perlengkapan di laboratorium dan pusat kesehatan memiliki sejumlah kecil lipid pada permukaan bakteri ini dan dengan demikian dapat mendukung proliferasi bakteri lipofilik,[1] tetapi karena bakteri ini tidak patogenik,[2] hal tersebut bukan merupakan suat...

Untuk film Denmark 2011, lihat ID A. IdaPoster filmSutradaraPaweł PawlikowskiProduser Eric Abraham Piotr Dzięcioł Ewa Puszczyńska Ditulis oleh Rebecca Lenkiewicz Paweł Pawlikowski Pemeran Agata Kulesza Agata Trzebuchowska Dawid Ogrodnik Penata musikKristian Eidnes AndersenSinematografer Łukasz Żal Ryszard Lenczewski PenyuntingJarosław KamińskiPerusahaanproduksi Canal+ Polska Institut Film Denmark Eurimages Distributor Solopan (Polandia) Memento Films (Prancis) Artificial Eye (U...
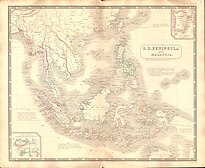
1841–1946 kingdom on northern Borneo Kingdom of Sarawak redirects here. For the former sultanate, see Sultanate of Sarawak. Raj of SarawakKerajaan Sarawak1841–1946 Flag Coat of arms Motto: Latin: Dum Spiro Spero[1][2](While I breathe, I hope)[2]Anthem: Gone Forth Beyond the Sea The Raj in the 1920sStatusIndependent sovereign state (1841–1888)Independent Protected State[3] (1888–1946)CapitalKuchingCommon languagesEnglish, Iban, Melanau, Bi...
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会波兰代表團波兰国旗IOC編碼POLNOC波蘭奧林匹克委員會網站olimpijski.pl(英文)(波兰文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員206參賽項目24个大项旗手开幕式:帕维尔·科热尼奥夫斯基(游泳)和马娅·沃什乔夫斯卡(自行车)[1]闭幕式:卡罗利娜·纳亚(皮划艇)&#...
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会波兰代表團波兰国旗IOC編碼POLNOC波蘭奧林匹克委員會網站olimpijski.pl(英文)(波兰文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員206參賽項目24个大项旗手开幕式:帕维尔·科热尼奥夫斯基(游泳)和马娅·沃什乔夫斯卡(自行车)[1]闭幕式:卡罗利娜·纳亚(皮划艇)&#...

1959 Christmas carol Cover of original 1959 edition of sheet music of Little Donkey Little Donkey is a popular Christmas carol, written by British songwriter Eric Boswell in 1959, which describes the journey by Mary the mother of Jesus to Bethlehem on the donkey of the title.[1] The first version to chart was by Gracie Fields, followed a fortnight later by The Beverley Sisters, who overtook her in the charts by Christmas. The song became No. 1 in the UK Sheet Music Chart[2] fr...

Species of flowering plant Penstemon barrettiae Conservation status Imperiled (NatureServe) Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae Clade: Tracheophytes Clade: Angiosperms Clade: Eudicots Clade: Asterids Order: Lamiales Family: Plantaginaceae Genus: Penstemon Species: P. barrettiae Binomial name Penstemon barrettiaeA.Gray Penstemon barrettiae is a species of flowering plant in the plantain family known by the common name Barrett's beardtongue or Barrett's penstemon. It is endemi...

Ancient Greek historian For other uses, see Polybius (disambiguation). PolybiusThe stele of Kleitor depicting Polybius, Hellenistic art, 2nd century BC, Museum of Roman Civilization[1]Bornc. 200 BCMegalopolis, ArcadiaDiedc. 118 BC (aged approx. 82)Roman GreeceNationalityGreekOccupationHistorianNotable workThe Histories (events of the Roman Republic, 220–146 BC)Main interestsHistory, philosophy of historyNotable ideasAnacyclosis Polybius (/pəˈlɪbiəs/; Greek: Πολύ�...

1930 film Sinkin' in the BathtubDirected byHugh Harman and Rudolf Ising (both uncredited)Story byIsadore Freleng (uncredited)Produced byHugh HarmanRudolf IsingAssociate producer:Leon SchlesingerStarringCarman MaxwellRochelle Hudson (both uncredited)Music byMusical Score and Direction by:Frank MarsalesAnimation byIsadore FrelengUncredited animators:Rollin HamiltonNorm BlackbornCarman MaxwellPaul J. SmithBen CloptonHugh HarmanRudolf IsingPainted and traced by:Robert McKimson (uncredited)Lay...

Inaugural ICC Women's World Twenty20 competition Cricket tournament 2009 ICC Women's World Twenty20Dates11 – 21 June 2009Administrator(s)International Cricket CouncilCricket formatWomen's Twenty20 InternationalTournament format(s)Group stage and KnockoutHost(s) EnglandChampions England (1st title)Runners-up New ZealandParticipants8Matches15Player of the series Claire TaylorMost runs Aimee Watkins (200)Most wickets Holly Colvin (9)2010 → South Africa in the field during ...

كارلو الثاني دوق بارما (بالإيطالية: Carlo II di Parma) معلومات شخصية الميلاد 22 ديسمبر 1799(1799-12-22)مدريد الوفاة 16 أبريل 1883 (83 سنة)نيس مواطنة إسبانيا الزوجة ماريا تيريزا أميرة سافوي (5 سبتمبر 1820–) الأولاد كارلو الثالث دوق بارما [لغات أخرى] الأب لويس الأول ملك إترو...

نهائي كأس إيطاليا 2021الحدثكأس إيطاليا 2020–21 أتالانتا يوفنتوس 1 2 التاريخ19 مايو 2021الملعبملعب مابي – تشيتا ديل تريكولوري، ريدجو إميليارجل المباراةفيديريكو كييزا (يوفنتوس)[1]الحكمدافيد ماسا[2]الحضور4.300[note 1] → 2020 2022 ← نهائي كأس إيطاليا 2021 (بالإيطالية: Finale Coppa Italia...

この記事には独自研究が含まれているおそれがあります。 問題箇所を検証し出典を追加して、記事の改善にご協力ください。議論はノートを参照してください。(2013年4月) クライマックスシリーズ > 2011年のパシフィック・リーグクライマックスシリーズ 2011年のパシフィック・リーグクライマックスシリーズ 2011マニュライフ生命クライマックスシリーズ パ MV...

Roman fort in Northern England VindolandaBardon Mill, Northumberland, U.K. Military bathhouse at VindolandaVindolandaCoordinates54°59′28″N 2°21′39″W / 54.9911°N 2.3608°W / 54.9911; -2.3608Grid referencegrid reference NY7766TypeRoman fortSite informationControlled byVindolanda TrustOpen tothe publicYesConditionDerelictWebsitehttp://www.vindolanda.com/ Vindolanda was a Roman auxiliary fort (castrum) just south of Hadrian's Wall in northern Engl...

Диакритические знаки со сходным начертанием: ˇ · ੱ · ◌ﬞЗапросы «Ĭ» и «Ĕ» перенаправляются сюда. На эти темы нужно создать отдельные статьи. Кратка ◌̆˘ Изображение ◄ ◌̂ ◌̃ ◌̄ ◌̅ ◌̆ ◌̇ ◌̈ ◌̉ ◌̊ ► ◄ ˔ ˕ ˖ ˗ ˘ ˙ ˚ ˛ ˜ ► Характеристики Название ◌̆: combining bre...