Southern red muntjac
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

This article is about needle-like growths in animals. For backbone, see Vertebral column. For other uses, see Spine (disambiguation). In a zoological context, spines are hard, needle-like anatomical structures found in both vertebrate and invertebrate species. The spines of most spiny mammals are modified hairs, with a spongy center covered in a thick, hard layer of keratin and a sharp, sometimes barbed tip. Occurrence Mammals The defensive spines on a porcupine Spines in mammals include the ...

Lake between Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan Aral SeaKarakalpak: Арал теңизи, Aral teńiziKazakh: Арал теңізі, Aral teñiziRussian: Аральское море, Aralskoye moreUzbek: Орол денгизи, Orol dengiziThe Aral Sea in 1989 (left) and 2014 (right)Aral SeaLocationCentral Asia(Kazakhstan – Uzbekistan)Coordinates45°N 60°E / 45°N 60°E / 45; 60TypeEndorheic, natural lake, reservoir (North)Primary inflowsNorth: Syr DaryaSouth: Groundwater ...

В Википедии есть статьи о других людях с именем Магнус. Магнус Эрикссоншвед. Magnus Eriksson Печать Магнуса Эрикссона Король Швеции 8 июля 1319 — февраль 1364 (под именем Магнус II) Коронация 21 июля 1336, Стокгольм Совместно с Эрик XII (1356 — 21 июня 1359) Предшественник Биргер Магн�...

هذه المقالة تحتاج للمزيد من الوصلات للمقالات الأخرى للمساعدة في ترابط مقالات الموسوعة. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة وصلات إلى المقالات المتعلقة بها الموجودة في النص الحالي. (فبراير 2024) هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة...

Seindah DirikuAlbum studio karya AlenaDirilisApril 2008GenrePopLabelNagaswaraKronologi Alena Alena(2002)Alena2002 Seindah Diriku (2008) Seindah Diriku merupakan sebuah album musik kedua karya Alena yang dirilis pada tahun 2008.[1] Daftar lagu Seindah diriku Lavender (為你存在) Perbedaan Tanpa Air Mata Maaf Awan Putih Hati Yang Bicara Cinta Yang Menepi Yi Xuan Le Ta Berbagi Cinta Terlanjur Memilih Dia Love To Last My Life Referensi ^ Seindah Diriku. nagaswara.co.id. 2008-07-15....

Indian physicist (born 1956) For the Indian politician, see Ashoke Kumar Sen. Ashoke SenSen in the Physics department of Scottish Church College in 2019Born (1956-07-15) 15 July 1956 (age 67)Kolkata, West Bengal, IndiaAlma materPresidency College, Kolkata (BSc)IIT Kanpur (MSc)Stony Brook University (PhD)Known forContributions to string field theoryS-dualitySen ConjectureSpouseSumathi RaoAwardsG.D. Birla Award for Scientific Research (1996)TWAS Prize (1997)Padma Shri (2001)Infos...

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Muaradua Kisam, Ogan Komering Ulu Selatan – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Muaradua KisamKecamatanNegara IndonesiaProvinsiSumatera SelatanKabupatenOgan Komering Ulu SelatanPemerin...

† Человек прямоходящий Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:Синапсиды�...

Student union in Arkansas, USAArkansas UnionThe University of Arkansas UnionLocation of the Arkansas Union in the state of ArkansasShow map of ArkansasArkansas Union (the United States)Show map of the United StatesAlternative namesThe Union or Student UnionGeneral informationTypeStudent unionLocationCampus of the University of ArkansasAddress435 N. Garland AvenueTown or cityFayetteville, ArkansasCountryUSACoordinates36°4′6″N 94°10′30″W / 36.06833°N 94.17500°W...

Ne doit pas être confondu avec Nemanjina. Nemanjina La rue Nemanjina Situation Coordonnées 44° 50′ 22″ nord, 20° 24′ 41″ est Pays Serbie Ville Belgrade Quartier(s) Zemun Début Avijatičarski trg, rues Nikolaja Ostrovskog et Miroslava Tirša Fin Rues Štrosmajerova et Svetosavska Morphologie Type Rue Géolocalisation sur la carte : Serbie modifier La rue Nemanjina (en serbe cyrillique : Немањина) est située à Belgrade, la ca...

Election in Georgia Main article: 1948 United States presidential election 1948 United States presidential election in Georgia ← 1944 November 2, 1948 (1948-11-02) 1952 → Nominee Harry Truman Strom Thurmond Thomas E. Dewey Party Democratic Dixiecrat Republican Home state Missouri South Carolina New York Running mate Alben Barkley Fielding L. Wright Earl Warren Electoral vote 12 0 0 Popular vote 254,646 85,055 76,691 Percentage 60...

Annual science fiction convention held in Chattanooga, Tennessee ChattaconStatusActiveGenreScience fictionVenueDoubleTree by HiltonLocation(s)Chattanooga, TennesseeCountryUnited StatesInaugurated1976Attendance1,200+ (2014)[1]Organized byChattanooga Speculative Fiction Fans, Inc.Filing status501(c)(3)Websitehttp://www.chattacon.org/ Chattacon is an annual science fiction convention held in Chattanooga, Tennessee.[2] The convention is organized by the nonprofit Chattanooga ...

Bupati Bangka TengahLambang Kabupaten Bangka TengahPetahanaAlgafry Rahman, S.T.sejak 26 Februari 2021KediamanPendapa Kabupaten Bangka TengahMasa jabatan5 tahunDibentuk24 Mei 2003Pejabat pertamaAbu HanifahSitus webbangkatengahkab.go.id Berikut ini adalah Daftar Bupati Bangka Tengah dari masa ke masa. No Bupati Mulai Jabatan Akhir Jabatan Prd. Ket. Wakil Bupati 1 Drs. H.Abu Hanifah 24 Mei 2003 1 Februari 2005 1 [Ket. 1] 2 Drs. Iskandar Zulkarnaen 1 Februari 2005 2005 2 [Ket. 2&...

Laws of nationality in Cuba Cuban Citizenship ActParliament of Cuba Long title An Act relating to Cuban citizenship Territorial extentCubaEnacted byGovernment of CubaRelated legislationConstitution of CubaStatus: Current legislation Cuban nationality law is regulated by the Constitution of Cuba, currently the 2019 Constitution, and to a limited degree upon Decree 358 of 1944.[1][2] These laws determine who is, or is eligible to be, a citizen of Cuba. The legal means to ac...

Protestant Wesleyan Christian denomination Global Methodist ChurchAbbreviationGM ChurchClassificationEvangelicalOrientationMethodistTheologyWesleyanGovernanceConnectionalism[1] (modified episcopal polity)OriginMay 1, 2022 (2022-05-01)[2]Separated fromUnited Methodist Church (2022)AbsorbedEvangelical Methodist Church in Croatia (2022)[3]Congregations4,495[4][5]Ministers4,504[4]Official websiteglobalmethodist.org The Global Methodis...

Horse racing venue in Bribane, Queensland, Australia DoombenLocationAscot, QueenslandCoordinates27°25′34.75″S 153°4′33.72″E / 27.4263194°S 153.0760333°E / -27.4263194; 153.0760333Owned byBrisbane Racing ClubDate opened1933Race typeFlat racingCourse typeOval, kikuyu turf trackNotable racesDoomben 10,000Doomben CupBTC Cup Doomben Racecourse is a horse racing venue in Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. It is located in the suburb of Ascot, 7 kilometres nort...

UN-led inspections of Iraq This article's lead section may be too short to adequately summarize the key points. Please consider expanding the lead to provide an accessible overview of all important aspects of the article. (November 2022) United Nations Special Commission (UNSCOM) was an inspection regime created by the United Nations to ensure Iraq's compliance with policies concerning Iraqi production and use of weapons of mass destruction after the Gulf War.[1] Between 1991 and 1997...

Cemetery in York, England York CemeteryDetailsEstablished1837LocationYorkCountryEnglandCoordinates53°57′N 1°04′W / 53.950°N 1.067°W / 53.950; -1.067TypePublicOwned byThe York Cemetery TrustSize24 acres (97,000 m2)No. of graves28,000+Find a GraveYork Cemetery York Cemetery is a cemetery located in the city of York, England. Founded in 1837, it now encompasses 24 acres (97,000 m2) and is owned and administered by The York Cemetery Trust with support of the F...
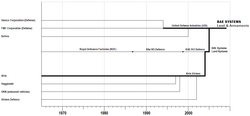
This article's factual accuracy may be compromised due to out-of-date information. The reason given is: BAE sold their 75% stake to Denel in April 2015. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (June 2017) Evolution of the land systems division of BAE Systems, 1970s to Land & Armaments formation BAE Systems Land Systems South Africa is a South African defence company and a subsidiary of BAE Systems Land Systems, itself part of BAE Systems La...

Questa voce sull'argomento cantoni della Costa Rica è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Cantone di AguirrecantoneCantón de Aguirre LocalizzazioneStato Costa Rica Provincia Puntarenas AmministrazioneCapoluogoQuepos TerritorioCoordinatedel capoluogo9°27′N 84°09′W9°27′N, 84°09′W (Cantone di Aguirre) Altitudine36 m s.l.m. Superficie543,77[1] km² Abitanti20 188[2] (2000) Densità37,13...





