Sinclair Radionics
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Radio station in Toronto This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: CHUM-FM – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) CHUM-FMToronto, OntarioBroadcast areaGreater Toronto AreaFrequency104.5 MHz (FM)BrandingCHUM 104.5ProgrammingFormatHo...

Kaisar Taizu dari JinKaisar Dinasti JinBerkuasa28 Januari 1115 – 19 September 1123PenerusKaisar Taizong dari JinInformasi pribadiKelahiran1 Agustus 1068Kematian19 September 1123 (usia 55)Nama lengkapWanyan Min (nama sinifikasi)Aguda (nama Jurchen)Shouguo (收國; 1115–1116)Tianfu (天輔; 1117–1123)Nama anumertaKaisar Yingqian Yuyun Zhaode Dinggong Renming Zhuangxiao Dasheng Wuyuan (應乾興運昭德定功仁明莊孝大聖武元皇帝)Nama kuilTaizu (太祖)AyahHeliboIbuLady NalanPasa...

You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in French. (June 2018) Click [show] for important translation instructions. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the English Wikipedia. Do not translate text that appears unreliable or low-qu...

Para otros usos de este término, véase Piamonte (desambiguación). PiamontePiemonte RegiónBanderaEscudo Coordenadas 45°15′00″N 7°55′00″E / 45.25, 7.9166666666667Capital TurínIdioma oficial Italiano y piamontésEntidad Región • País Italia • Zona Italia noroccidental, Italia septentrional • Municipios 1206Presidente Alberto Cirio(FI-CDX)Subdivisiones AlessandriaAstiBiellaCuneoNovaraTurínVerbano-Cusio-OssolaVercelliSuperficie &#...
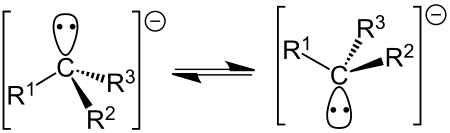
Karbanion Karbanion adalah sejenis anion dari karbon yang memiliki satu pasangan elektron menyendiri. Karbanion memiliki geometri trigonal piramida dan secara formal merupakan konjugat basa dari asam karbon: R3C-H + B− → R3C− + H-B dengan B merujuk pada basa. Karbanion merupakan salah satu dari beberapa zat antara reaktif kimia organik. Teori Karbanion merupakan sejenis nukleofil. Stabilitas dan reaktivitas karbanion ditentukan oleh beberapa faktor, yaitu: Efek induktif. Atom-atom elekt...
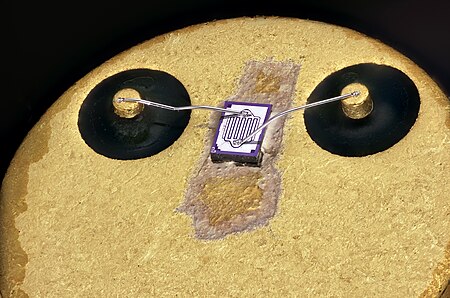
Technique used to connect a microchip to its package Gold wire ball-bonded on a silicon die Aluminium wires wedge-bonded to a BC160 transistor die The interconnections in a power package are made using thick (250 to 400 μm), wedge-bonded, aluminium wires. Inside a wire-bonded BGA package. This package has an Nvidia GeForce 256 GPU. Wire bonding is a method of making interconnections between an integrated circuit (IC) or other semiconductor device and its packaging during semiconductor device...

1961 film by Paul Wendkos Angel BabyDirected byPaul WendkosHubert Cornfield (uncredited)Written byOrin BorstenPaul MasonSamuel RoecaBased onJenny Angel1954 novelby Elsie Oakes BarberProduced byThomas F. WoodsStarringSalome JensGeorge HamiltonMercedes McCambridgeCinematographyJack MartaHaskell WexlerEdited byBetty J. LaneMusic byWayne ShanklinProductioncompanyMadera ProductionsDistributed byAllied Artists Pictures CorporationRelease date May 14, 1961 (1961-05-14) Running time97 ...

Potez 630 Constructeur SNCAN Rôle Avion de chasse Statut Retiré du service Premier vol 25 avril 1936 Mise en service 1938 Date de retrait 1947 Équipage 3 personnes Motorisation Moteur Hispano-Suiza 14Ab Nombre 2 Type 14 cylindres en étoile refroidis par air Puissance unitaire 590 ch n°1 à 48 640 ch n° 49 et suivants Dimensions Envergure 16,00 m Longueur 11,07 m Hauteur 3,62 m Surface alaire 32,70 m2 Masses Maximale 3 845 kg Performances Vitesse ...

2017 presidential campaign of Marine Le Pen Marine Le Pen during her presidential campaign in Lille, on 26 March 2017. Marine Le Pen, as leader of the National Front ran for President of France in the 2017 French presidential election, receiving 21.30% of the vote in the first round, and 33.90% in the second round, losing to Emmanuel Macron of La République En Marche!.[1] Background Le Pen ran an unsuccessful campaign in 2012. Campaign Le Pen launched her presidential campaign on 5 F...

Petróleos de Venezuela S.A.JenisState-owned enterpriseDidirikan1976KantorpusatCaracas, VenezuelaTokohkunciRafael Ramirez, PresidenProdukBahan bakar, gas alam dan petrokimia lainPendapatan $114 miliar (2013)[1]Laba bersih $15.8 miliar (2013)[1]Total aset $231.1 miliar (2013)[1]PemilikPemerintah VenezuelaAnakusahaPDV MarinaCVPPequivenCIEDPDVSA GasPDV (Deltaven)PalmavenElectricidad de Caracas, C.A. (93.62%)[2] Citgo (100%)[3]more…Situs webwww.pdvsa.com ...

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府...

Human-dominated ecosystems of the anthropocene era An aerial view of a human ecosystem. Pictured is the city of Chicago Human ecosystems are human-dominated ecosystems of the anthropocene era that are viewed as complex cybernetic systems by conceptual models that are increasingly used by ecological anthropologists and other scholars to examine the ecological aspects of human communities in a way that integrates multiple factors as economics, sociopolitical organization, psychological factors,...

Medication legally requiring a medical prescription before it can be dispensed Photo of the packaging of four medicines registered in the UK, showing their Product Licence Numbers and symbols denoting if they are Prescription Only Medicine (POM) or Pharmacy Medicine (P) A prescription drug (also prescription medication, prescription medicine or prescription-only medication) is a pharmaceutical drug that is permitted to be dispensed only to those with a medical prescription. In contrast, over-...

Mountain in the state of Colorado San Luis PeakSan Luis Peak viewed from the northeastHighest pointElevation14,014 ft (4273.8 m)[1]NAVD88Prominence3113 ft (949 m)[2]Isolation26.9 mi (43.4 km)[2]ListingNorth America highest peaks 58thUS highest major peaks 44thColorado highest major peaks 24thColorado fourteeners 49thCoordinates37°59′12″N 106°55′53″W / 37.9867757°N 106.9312578°W / 37.9867757; -106.9312578[1]GeographySan L...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Battle of Granville – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Battle of GranvillePart of the War in the VendéeThe burning of Granville by the Vendéens, painting by Jean-François HueDate14 Novembe...
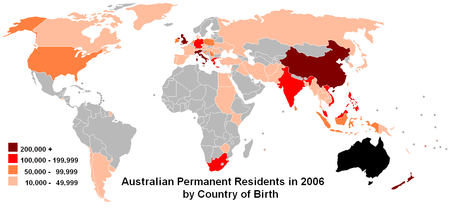
Imigrasi ke benua Australia diperkirakan telah dimulai sekitar 50.000 tahun yang lalu[1] ketika nenek moyang Aborigin Australia tiba di benua melalui pulau-pulau Kepulauan Melayu dan Nugini. Penduduk Eropa pertama mendarat tahun 1600-an dan 1700-an, tetapi kolonisasi baru dimulai tahun 1788. Seluruh tingkat imigrasi telah meningkat selama satu setengah dasawarsa terakhir. Migrasi luar negeri meningkat dari 30.042 tahun 1992-93[2] menjadi 177.600 tahun 2006-07.[3] Ini m...

此條目需要擴充。 (2018年3月3日)请協助改善这篇條目,更進一步的信息可能會在討論頁或扩充请求中找到。请在擴充條目後將此模板移除。 此條目没有列出任何参考或来源。 (2018年3月3日)維基百科所有的內容都應該可供查證。请协助補充可靠来源以改善这篇条目。无法查证的內容可能會因為異議提出而被移除。 埃及大洲联合会非洲排球联合会總教練Sherif El Shemerly球衣 ...

село Гарбузи Країна Україна Область Харківська область Район Богодухівський район Громада Богодухівська міська громада Облікова картка Гарбузи Основні дані Засноване 1918 рік Населення 12 осіб Площа 0,26 км² Густота населення 46 осіб/км² Поштовий індекс 62111 Тел�...

Keju casolèt Masakan Trentino Alto Adige (cucina trentina) adalah masakan yang berasal dari regione Trentino-Alto Adige, Italia Utara. Kawasan Trentino Alto Adige terletak di daerah lembah yang dibatasi dengan puncak-puncak pegunungan Alpen yang dinamakan dolomites. Tradisi kuliner daerah ini merupakan perpaduan antara Italia dan Jerman. Bahan-bahan utama yang dihasilkan adalah anggur, keju, madu, buah-buahan dan sayuran yang berkualitas bagus karena diproduksi di lahan yang masih alami. Sel...

American actor (1928–2014) This article is about the American actor. For other uses, see James Garner (disambiguation). James GarnerGarner as Maverick (1959)BornJames Scott Bumgarner(1928-04-07)April 7, 1928Denver, Oklahoma, now part of Norman, Oklahoma, U.S.DiedJuly 19, 2014(2014-07-19) (aged 86)Los Angeles, California, U.S.Alma materUniversity of OklahomaOccupation(s)Actor, producerYears active1954–2010Political partyDemocraticSpouse Lois Josephine Fleischman Clarke ̴...



