Shurtleff v. City of Boston
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
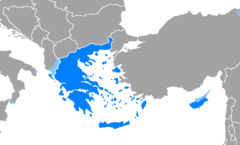
Artikel ini menjelaskan secara umum. Untuk bentuk bahasa yang dituturkan pada tahap tertentu, lihat Pra-Helenik, Proto-Helenik, Yunani Mikenai, Yunani Kuno, Yunani Koine, Yunani Pertengahan, dan Yunani Modern. Cari artikel bahasa Cari berdasarkan kode ISO 639 (Uji coba) Kolom pencarian ini hanya didukung oleh beberapa antarmuka Halaman bahasa acak Bahasa Yunani Ἑλληνική/ΕλληνικάHellēnikḗ/Ellinika Pengucapan[hel.lɛː.ni.ke] atau [eliniˈka]Dituturkan diYun...

Kereta rel listrik Tokyo Metro 05 (東京地下鉄05系 Tōkyō Chikatetsu 05-kei) adalah kereta rel listrik buatan Jepang dan kini beroperasi di lintas Commuter Jabodetabek. KRL ini didatangkan ke Indonesia pada tahun 2010 hingga tahun 2012. KRL ini diproduksi oleh Nippon Sharyo, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Hitachi, Kinki Sharyo, dan Tokyu Car Corporation pada tahun 1988 hingga tahun 2004 dalam berbagai generasi, dan antar generasi tersebut memiliki perbedaan yang cukup terlihat. KRL Tokyo Me...
Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article présente des problèmes à corriger. Vous pouvez aider à l'améliorer ou bien discuter des problèmes sur sa page de discussion. Certaines informations devraient être mieux reliées aux sources mentionnées dans la bibliographie ou les liens externes. Améliorez sa vérifiabilité en les associant par des références. (Marqué depuis février 2014) Il a une forme trop académique, ce qui le fait r...

Julio IglesiasInformasi latar belakangNama lahirJulio IglesiasLahir23 September 1943 (umur 80) Madrid, SpanyolAsal Madrid, SpanyolGenrePop, LatinPekerjaanPenyanyi, penulis laguTahun aktif1968 - sekarangLabelSony, ColumbiaSitus webhttp://www.julioiglesias.com Julio Iglesias (lahir 23 September 1943) adalah seorang penyanyi legendaris berkebangsaan Spanyol. Ia mencapai popularitas di kancah internasional pada era 1970-an dan 1980-an sebagai penyanyi ballad romantis. Julio telah merilis tak...

Chuck McCann (2013) Charles John Thomas Chuck McCann (2 September 1934 – 8 April 2018)[1] adalah seorang tokoh kebugaran Amerika, aktor, dan komedian. Catatan ^ Chuck McCann. IMDb. Diakses tanggal March 7, 2008. Pranala luar Chuck McCann di IMDb (dalam bahasa Inggris) (Inggris) http://www.chuckmccann.net Diarsipkan 2018-04-10 di Wayback Machine. Wikimedia Commons memiliki media mengenai Chuck McCann.

此條目介紹的是2012年在上海创办的一家民营新闻媒体。关于1946年在上海创刊的一份周刊,请见「观察 (杂志)」。关于2013年在上海创办、原名「上海觀察」的网络应用程序,请见「上觀新聞」。关于“观察者”的其他含义,请见「观察者」。 此條目過於依赖第一手来源。 (2021年1月17日)请補充第二手及第三手來源,以改善这篇条目。 观察者网观察者网首页在2019年7月...

1991 studio album by Cliff Richard Together with Cliff RichardStudio album by Cliff RichardReleased18 November 1991GenreChristmasLabelEMIProducerPaul MoesslCraig PruessCliff RichardCliff Richard chronology From a Distance: The Event(1990) Together with Cliff Richard(1991) The Album(1993) Singles from Together with Cliff Richard Scarlet RibbonsReleased: 14 October 1991(Europe, New Zealand only) We Should Be TogetherReleased: 25 November 1991 This New YearReleased: 30 December 1991 Professi...
NFL team season 1993 Detroit Lions seasonOwnerWilliam Clay Ford Sr.General managerChuck SchmidtHead coachWayne FontesHome fieldPontiac SilverdomeResultsRecord10–6Division place1st NFC CentralPlayoff finishLost Wild Card Playoffs(vs. Packers) 24–28 ← 1992 Lions seasons 1994 → The 1993 season was the Detroit Lions' 64th season in the National Football League (NFL), their 60th In Detroit, and their fifth under the head coach Wayne Fontes.The Lions improved upon the...

Large crustal block in North America The Superior Craton is a stable crustal block covering Quebec, Ontario, and southeast Manitoba in Canada, and northern Minnesota in the United States. It is the biggest craton among those formed during the Archean period.[1] A craton is a large part of the Earth's crust that has been stable and subjected to very little geological changes over a long time.[2] The size of Superior Craton is about 1,572,000 km2.[3] The craton unde...

Raising a fluid by introducing bubbles of gas into the outlet tube This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Gas lift – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) A gas lift or bubble pump is a type of pump that can raise fluid between eleva...

English territorial police force Law enforcement agency Cheshire ConstabularyMottoBe safe, feel safeAgency overviewFormed20 April 1857; 167 years ago (20 April 1857)Employees2,088 Police Officers[1]168 PCSOs[1]Annual budget£169.8 million (2018–19)Jurisdictional structureOperations jurisdictionCheshire, EnglandMap of police areaSize905 square miles (2,340 km2)Population1.1 millionLegal jurisdictionEngland and WalesGoverning bodyCheshire Police and Crime Com...

1976 television film directed by Marvin J. Chomsky Victory at EntebbeTheatrical film release poster of Victory at EntebbeGenre Action Drama History Thriller Written byErnest KinoyDirected byMarvin J. ChomskyStarring Helmut Berger Linda Blair Kirk Douglas Richard Dreyfuss Helen Hayes Anthony Hopkins Burt Lancaster Christian Marquand Elizabeth Taylor Theodore Bikel David Groh Jessica Walter Theme music composerCharles FoxCountry of originUnited StatesOriginal languageEnglishProductionExecutive ...

ضريح درويش علم بازيمعلومات عامةنوع المبنى ضريحالمكان بابل[1] المنطقة الإدارية مقاطعة بابل البلد إيرانالاستعمال ضريح الصفة التُّراثيَّةتصنيف تراثي المعالم الوطنية الإيرانية[1] (2001 – ) تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات ضريح درويش علم بازي (بالفارسية: آرامگا�...

Swiss linguist and philosopher (1857–1913) Ferdinand de SaussureBorn(1857-11-26)26 November 1857Geneva, SwitzerlandDied22 February 1913(1913-02-22) (aged 55)Vufflens-le-Château, Vaud, SwitzerlandEducationUniversity of GenevaLeipzig University (Ph.D, 1880)University of BerlinEra19th-century philosophyRegionWestern philosophySchoolStructuralism, linguistic turn,[1] semioticsInstitutionsEPHEUniversity of GenevaMain interestsLinguisticsNotable ideasStructural linguisticsSemiologyL...

Art museum in Oakland, California Oakland Museum of CaliforniaLocation within Oakland, CaliforniaShow map of Oakland, CaliforniaOakland Museum of California (California)Show map of CaliforniaOakland Museum of California (the United States)Show map of the United StatesEstablished1969Location1000 Oak St, Oakland, CA 94607Coordinates37°47′55″N 122°15′49″W / 37.7986°N 122.2636°W / 37.7986; -122.2636TypeArt, History, Natural ScienceDirectorLori FogartyPublic tra...

This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (December 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) 52nd Air Defense Artillery RegimentCoat of armsActive1917Country United StatesBranchArmyRoleAir defense artillerySizeRegimentGarrison/HQFort BlissMotto(s)Semper Paratus (Always Prepared)ColorsScarletMascot(s)OozlefinchEquipmentMIM-104 PatriotInsigni...

American satellite and space systems manufacturer This article is about the satellite and space system manufacturer formerly named Loral. For other uses of SSL, see SSL (disambiguation). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: SSL company – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 20...
Protection of wilderness areas in the U.S. The Wilderness Act protects exceptionally undisturbed natural areas and scenery, such as in the Ansel Adams Wilderness. The National Wilderness Preservation System (NWPS) of the United States protects federally managed wilderness areas designated for preservation in their natural condition. Activity on formally designated wilderness areas is coordinated by the National Wilderness Preservation System. Wilderness areas are managed by four federal land ...

Last Tango in Paris Logotipo de la película.Título El último tango en ParísFicha técnicaDirección Bernardo BertolucciProducción Alberto GrimaldiGuion Bernardo BertolucciFranco ArcalliMúsica Gato BarbieriFotografía Vittorio StoraroMontaje Franco ArcalliRoberto PerpignaniProtagonistas Marlon BrandoMaria SchneiderJean Pierre LéaudMassimo GirottiMaria MichiCatherine AllegretGiovanna Galletti Ver todos los créditos (IMDb)Datos y cifrasPaís ItaliaFranciaAño 1972Género DramaDuración 1...

Dieser Artikel beschreibt die Jungtiere von Vögeln und Nagetieren. Für den Pilz Nidularia deformis siehe Nestlinge, für den Felsen siehe Nestling Rock. Drei Vogelnestlinge beim Sperren Neugeborene Farbmäuse haben noch embryonale Merkmale: Nesthocker. Als Nestlinge werden Jungtiere bezeichnet, die als so genannte Nesthocker noch im Nest ihrer Eltern leben. Der Begriff Nestling wird sowohl auf den Nachwuchs der Vögel[1] angewandt als auch auf den Nachwuchs von Nagetieren, also zum...
