Shirley Scott
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

2017 video gameYonder: The Cloud Catcher ChroniclesDeveloper(s)Prideful SlothPublisher(s)WW: Prideful SlothWW: Merge Games (Physical)JP: Nippon Ichi Software (Physical)Designer(s)Cheryl VanceEngineUnity[1]Platform(s)PlayStation 4PlayStation 5Microsoft WindowsNintendo SwitchXbox OneXbox Series X/SReleasePlayStation 4, Microsoft Windows18 July 2017Nintendo Switch17 May 2018Xbox One27 February 2019PlayStation 527 July 2021Xbox Series X/S5 August 2021Genre(s)AdventureMode(s)Single-player...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Januari 2016. Koordinat: 24°4′42.05″N 039°9′41.43″E / 24.0783472°N 39.1615083°E / 24.0783472; 39.1615083 (Ber Arrawha) Ar-Rauha (Arab: الروحاءcode: ar is deprecated ) adalah sebuah stasiun peristirahatan kafilah dan...

Stroberi Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Plantae Divisi: Magnoliophyta Kelas: Magnoliopsida Ordo: Rosales Famili: Rosaceae Subfamili: Rosoideae Genus: Fragaria Spesies: F. × ananassa Nama binomial Fragaria × ananassaDuchesne Stroberi atau tepatnya stroberi kebun (juga dikenal dengan nama arbei, dari bahasa Belanda aardbei) adalah sebuah varietas stroberi yang paling banyak dikenal di dunia. Seperti spesies lain dalam genus Fragaria (stroberi), buah ini berada dalam keluarga Rosaceae. Sec...
PemberitahuanTemplat ini mendeteksi bahwa artikel bahasa ini masih belum dinilai kualitasnya oleh ProyekWiki Bahasa dan ProyekWiki terkait dengan subjek. Terjadi [[false positive]]? Silakan laporkan kesalahan ini. 17.20, Jumat, 29 Maret, 2024 (UTC) • hapus singgahan Sebanyak 1.305 artikel belum dinilai Artikel ini belum dinilai oleh ProyekWiki Bahasa Cari artikel bahasa Cari berdasarkan kode ISO 639 (Uji coba) Kolom pencarian ini hanya didukung oleh beberapa antarmuka Hala...

Peruvian football club Football clubSomos AduanasFull nameAsociación Deportiva Somos AduanasFounded1996GroundEstadio Miguel Grau, CallaoCapacity15,000LeagueCopa Perú Home colours Asociación Deportiva Somos Aduanas is a Peruvian football club, playing in the city of Bellavista, Callao, Lima. History The Asociación Deportiva Somos Aduanas was founded in 1996. In the 2001 Copa Perú, Somos Aduanas classified to the National Stage, but was eliminated by C.D. Universidad Nacional de Ucayali. T...

Voies navigables de FranceLogo de Voies navigables de FranceLe siège de Voies navigables de France à BéthuneHistoireFondation 29 décembre 1990[1]Prédécesseur Office national de la navigationCadreSigle VNFType EPAForme juridique Établissement public national à caractère administratifDomaine d'activité Administration publique (tutelle) des activités économiquesSiège 175 rue Ludovic Boutleux 62400 BéthunePays FranceOrganisationEffectif 4 350 employés (2022)Président La...

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang Rhineland sebagai sebuah wilayah. Untuk periode sejarah dari 1822 sampai 1946, lihat Provinsi Rhine. Lambang Rhineland Rhineland (Jerman: Rheinlandcode: de is deprecated , Prancis: Rhénanie) adalah nama yang digunakan untuk kawasan yang kurang terdefinisi di Jerman bagian barat di sepanjang Sungai Rhine, terutama bagian tengahnya. Istilah Provinsi Rhine (hijau) pada 1830 disertai dengan batas-batas modern. Pada zaman dahulu, Rhineland[1] merujuk...

هذه المقالة عن الكلية الحربية بمصر. لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع الكلية الحربية (توضيح). الأكاديمية العسكرية المصريةالكلية الحربية شعار الكلية الحربية (مصر)الشعار الشعار الواجب . الشرف . الوطن معلومات المؤسس محمد علي باشا التأسيس 1811 (منذ 213 سنة) تتبع جامعة الأكاديمية العسكرية ال...

Provinsi Dataran Tinggi Barat Western Highlands ProvinceProvinsi BenderaNegara Papua NuginiIbukotaMount HagenPemerintahan • GubernurPaias Wingti (2012-)Luas • Total3,200 sq mi (8.288 km2)Populasi • Total440.000 • Kepadatan140/sq mi (53/km2)Zona waktuUTC+10 Provinsi Dataran Tinggi Barat adalah salah satu dari 21 provinsi di Papua Nugini . Provinsi ini mempunyai luas 8.288 km ² dengan jumlah penduduk lebih dari 440.0...

Database management system This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Object–relational database – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) An object–relational database (ORD), or object–relational database management system (O...
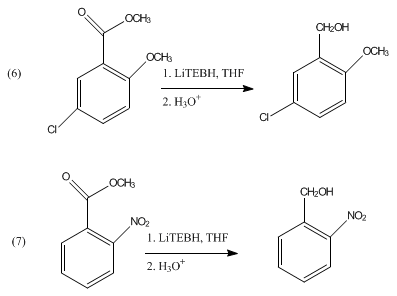
Superhydride redirects here. For the class of compounds sometimes known as superhydrides, see Polyhydride. Lithium triethylborohydride Names Preferred IUPAC name Lithium triethylboranuide Other names SuperhydrideLiTEBH Identifiers CAS Number 22560-16-3 Y 3D model (JSmol) Interactive image ChemSpider 2006168 Y ECHA InfoCard 100.040.963 EC Number 245-076-8 PubChem CID 23712863 UNII Q1ML638JFD Y CompTox Dashboard (EPA) DTXSID10897726 InChI InChI=1S/C6H16B.Li/c1-4-7(5-2)6-3;/h7H,4-...

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 数字の大字(だいじ)は、漢数字の一種。通常用いる単純な字形の漢数字(小字)の代わりに同じ音の別の漢字を用いるものである。 概要 壱万円日本銀行券(「壱」が大字) 弐千円日本銀行券(「弐」が大字) 漢数字には「一」「二」「三」と続く小字と、「壱」「�...

此條目介紹的是仇恨犹太人的思想与行为。关于反对犹太人建立民族国家的政治思想,请见「反锡安主义」。关于反对犹太教的宗教思想,请见「反犹太教主义」。关于基于宗教上的原因而仇恨犹太人,请见「宗教反犹主义」。 系列条目反犹太主义犹太人历史及歧視的一部分 历史(英语:History of antisemitism) 年表(英语:Timeline of antisemitism) 参考资料(英语:List ...

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目的语调或风格或許不合百科全書。 (2024年1月29日)請根據指南協助改善这篇条目,並在讨论页討論問題所在,加以改善。 此生者传记条目需要补充更多可供查證的来源。 (2024年1月29日)请协助補充可靠来源,无法查证的在世人物内容将被立即移除。 此条目页的主題是中华人民共和国现任国...

State affiliate of the Libertarian Party Libertarian Party of Alaska AbbreviationALPChairmanAlex CokerFounded1974; 50 years ago (1974)HeadquartersAnchorage, AlaskaMembership (2021)6,789[1]IdeologyLibertarianismColorsa shade of Blue; YellowSenate0 / 20House of Representatives0 / 40U.S. Senate0 / 2U.S. House of Representatives0 / 1Websitealaskalp.orgPolitics of United StatesPolitical partiesElections The Libertarian Party of Alaska is the affiliate of the Libertarian P...

BlackrockFormer station at Blackrock, photographed on 13 September 2005General informationLocationBlackrock, Cork, County CorkIrelandCoordinates51°53′46″N 8°25′10″W / 51.896166°N 8.419447°W / 51.896166; -8.419447HistoryOriginal companyCork, Blackrock and Passage RailwayPre-groupingCork, Blackrock and Passage RailwayPost-groupingGreat Southern RailwaysKey dates8 June 1850Station opens12 September 1932Station closes Blackrock railway station was on the Cork,...

Bias within the mass media This article needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (June 2023) Journalism News Writing style Ethics code of ethics Culture Objectivity News values Attribution Defamation Sensationalism Editorial independence Journalism school Index of journalism articles Areas Arts Business Data Entertainment Environment Fashion Medicine Music Politics Science Sports Technology Traffic War Weather World Genres A...

Swiss-French politician and writer (1767–1830) This article is about the European writer and politician. For other people and places, see Benjamin Constant (disambiguation). Benjamin ConstantPortrait by Hercule de Roche, c. 1820Member of the Chamber of DeputiesIn office14 April 1819 – 8 December 1830ConstituencySarthe (1819–24)Seine 4th (1824–27)Bas-Rhin 1st (1827–30)Member of the Council of StateIn office20 April 1815 – 8 July 1815Appointed byNapoleon IMember of...

آرنو بينزياس (بالإنجليزية: Arno Allan Penzias) معلومات شخصية الميلاد 26 أبريل 1933 [1][2] ميونخ[3] الوفاة 22 يناير 2024 (90 سنة) [4][5] سان فرانسيسكو[4][5] سبب الوفاة مرض آلزهايمر مواطنة ألمانيا (–1935)بدون جنسية (1935–1946) الولايات المتحدة (1946–) عض�...

1984 Indian filmPartyDirected byGovind NihalaniWritten byGovind NihalaniBased onPartyby Mahesh ElkunchwarProduced byNFDCStarringManohar SinghVijaya MehtaRohini HattangadiOm PuriNaseeruddin ShahCinematographyGovind NihalaniEdited byRenu SalujaRelease date 1984 (1984) Running time118 minutesCountryIndiaLanguageHindi Party is a 1984 Hindi-language film directed by Govind Nihalani. The film boasted an ensemble cast, including Vijaya Mehta, Manohar Singh, Om Puri, Naseeruddin Shah, and Rohin...
