Saskatchewan Human Rights Commission
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Francisco de Melo Dom Francisco de Melo (1597 – 18 Desember 1651) merupakan seorang bangsawan dan jenderal Portugis. Melo lahir di Estremoz, Portugal. Ia adalah marquess Tor de Laguna, comte Assumar, dan dari 1641 hingga 1644, gubernur sementara Belanda Selatan. Ketika Francisco de Melo datang ke Belanda Selatan, ia telah memiliki karier politik yang menakjubkan. Dari tahun 1632 hingga 1636 ia berada di Spanyol sebagai duta besar Republik Genova. Pada tahun 1638 ia ditunjuk sebagai viceroy ...

Mosque in Kazan, Tatarstan, Russia This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (January 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Märcani MosqueMärcani Mosque, 2016ReligionAffiliationIslamDistrictTatarstanStatusActiveLocationLocationKazan, RussiaGeographic coordinates55°46′47″N 49°07′03″E&#...

Ethem Servet Boral1315-P. 16[1]Ethem Servet BoralBorn1876 (1876)Caucasus, Russian EmpireDied21 September 1956(1956-09-21) (aged 79–80)?, TurkeyBuriedState CemeteryAllegiance Ottoman Empire TurkeyYears of serviceOttoman: January 1900-1920Turkey: July 1, 1920-February 25, 1931RankMiralayCommands heldCommissariat of the Greek Border, 14th RegimentCommittee of the Purchase of Minister of National Defense, Supply General Command, 2nd Cavalry Division, Department ...

C/1995 O1 (Hale–Bopp)Komet Hale–Bopp, tidak lama setelah melewati perihelion pada April 1997PenemuanDitemukan oleh:Alan HaleThomas BoppDitemukan tanggal:23 Juli 1995Nama lain:Komet Besar 1997,C/1995 O1Karakteristik orbit AEpos:2022-Sep-15(JD 2459837.5)Tipe orbitKomet periode lamaAphelion:354 AU[1]Perihelion:0.914 AU[1]Sumbu semi-mayor:186 AUEksentrisitas orbit:0.995086Periode orbit:2520[2]–2533[1] thn(Barisentrum 2391 thn)[3]Inklinasi:89.4°Dimens...

2014 single by Chris Brown LoyalCover artwork for the album versionSingle by Chris Brown featuring Lil Wayne and Tygafrom the album X ReleasedDecember 19, 2013 (2013-12-19) (East and West Coast versions)March 24, 2014 (2014-03-24) (album version)Recorded2013StudioGlenwood Place (Burbank, California)[1]GenreHip hopR&Bpop[2]Length4:24 (West Coast, East Coast, and album versions)6:02 (extended remix)LabelRCASongwriter(s)Christopher BrownTyrone Gr...

† Человек прямоходящий Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:Синапсиды�...

1962 film by John Frankenheimer Birdman of AlcatrazTheatrical release poster by Saul BassDirected byJohn FrankenheimerScreenplay byGuy TrosperBased onBirdman of Alcatraz1955 bookby Thomas E. GaddisProduced byHarold HechtStuart MillarGuy TrosperStarringBurt LancasterKarl MaldenThelma RitterNeville BrandEdmond O'BrienTelly SavalasCinematographyBurnett GuffeyEdited byEdward MannMusic byElmer BernsteinProductioncompanyNorma ProductionsDistributed byUnited ArtistsRelease date July 3, 196...
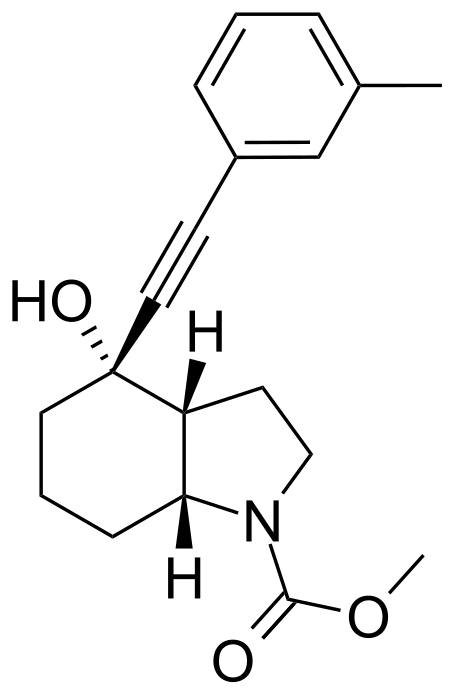
Mavoglurant Names Preferred IUPAC name Methyl (3aR,4S,7aR)-4-hydroxy-4-[(3-methylphenyl)ethynyl]octahydro-1H-indole-1-carboxylate Other names AFQ056 Identifiers CAS Number 543906-09-8 Y 3D model (JSmol) Interactive image ChemSpider 8102466 ECHA InfoCard 100.219.728 IUPHAR/BPS 7586 PubChem CID 9926832 UNII GT0I9SV4F6 CompTox Dashboard (EPA) DTXSID30202777 InChI InChI=1S/C19H23NO3/c1-14-5-3-6-15(13-14)8-11-19(22)10-4-7-17-16(19)9-12-20(17)18(21)23-2/h3,5-6,13,16-17,22H,4,7,9-10,12H2,1-2H3...

Nord-Flyg IATA ICAO Kode panggil - NEF NORDEX Didirikan1952PenghubungBandar Udara EskilstunaArmada4Kantor pusatEskilstuna, SwediaSitus webhttp://www.nordflyg.se Nord-Flyg adalah maskapai penerbangan kargo dan sewaan penumpang Swedia yang berbasis di Eskilstuna, Swedia. [1] Maskapai penerbangan ini didirikan pada tahun 1955 sebagai operator taksi udara itu pelanggannya dimulai untuk konversi dari kargo dengan Bombardier Dash 8 Q400.[1] Armada Pada Mei 2009 armada Nord-Flyg terd...

Series of fantasy novels Septimus Heap seriesThe cover art for all seven main titles in the series Magyk Flyte Physik Queste Syren Darke Fyre AuthorAngie SageIllustratorMark ZugCountryUnited KingdomGenreJuvenile fantasyPublisherBloomsbury Publishing (UK)Katherine Tegen Books (US)Published23 September 2005 – 16 April 2013Media typePrint (hardback & paperback) Septimus Heap is a series of children's fantasy novels featuring a protagonist of the same name written by English author Angie Sa...

土库曼斯坦总统土库曼斯坦国徽土库曼斯坦总统旗現任谢尔达尔·别尔德穆哈梅多夫自2022年3月19日官邸阿什哈巴德总统府(Oguzkhan Presidential Palace)機關所在地阿什哈巴德任命者直接选举任期7年,可连选连任首任萨帕尔穆拉特·尼亚佐夫设立1991年10月27日 土库曼斯坦土库曼斯坦政府与政治 国家政府 土库曼斯坦宪法 国旗 国徽 国歌 立法機關(英语:National Council of Turkmenistan) ...

Species of eucalyptus Salt River gum Eucalyptus sargentii near Hyden Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae Clade: Tracheophytes Clade: Angiosperms Clade: Eudicots Clade: Rosids Order: Myrtales Family: Myrtaceae Genus: Eucalyptus Species: E. sargentii Binomial name Eucalyptus sargentiiMaiden[1] Flowers in Kings Park, PerthFruit in Kings Park Eucalyptus sargentii, commonly known as Salt River gum,[2] is a species of mallet, mallee or small tree that is endemic to Weste...

Untuk pemakaian istilah ini sebagai demonim, lihat Bangsa Gibraltar. Budaya Gibraltar Sejarah Bangsa Genoa Malta Bahasa Inggris Llanito Spanyol Andalusia Hidangan Agama Katolik Roma Judaisme Islam Hinduisme Musik dan seni pertunjukan Breed 77 Melon Diesel Taxi Olahraga Victoria Stadium Sepak bola di Gibraltar (Gibraltar Football Association Tim nasional sepak bola) Persatuan rugbi di Gibraltar Tim nasional kriket lbs Llanito atau Yanito (diucapkan [ʎaˈnito] atau [ʝaˈnito]) adalah bentuk b...

AllsvenskanSäsong2009Nya lag för säsongenIF Brommapojkarna Örgryte IS BK HäckenVinnareAIK(5:e allsvenska titeln)(11:e SM-titeln)NedflyttadeÖrgryte IS Hammarby IFChampions LeagueAIKEuropa LeagueIFK Göteborg IF Elfsborg Kalmar FFStatistikTotalt antal mål584 (2,43 per match)Bästa målgörareTobias Hysén (18) Wanderson (18)Största hemmavinst6 - 0 (IFKG - DIF)Största bortavinst1 - 5 (ÖIS - GAIS)Högsta åskådarantal26 241 (AIK - DIF)Lägsta åskåda...

Den här artikeln behöver fler eller bättre källhänvisningar för att kunna verifieras. (2011-07) Åtgärda genom att lägga till pålitliga källor (gärna som fotnoter). Uppgifter utan källhänvisning kan ifrågasättas och tas bort utan att det behöver diskuteras på diskussionssidan. Varningsskylt för bigård, Trädgårdsföreningen, Linköping. Biodling är hållandet av honungsbin som husdjur för att pollinera växter och för att utvinna honung och vax. Historik Traditionell b...

British politician and editor Susan LawrenceLawrence in 1920Member of Parliament for East Ham NorthIn office21 July 1926 – 27 October 1931Preceded byCharles Williamson CrookSucceeded byJohn MayhewIn office6 December 1923 – 28 October 1924Preceded byCharles Williamson CrookSucceeded byCharles Williamson Crook Personal detailsBornArabella Susan Lawrence(1871-08-12)12 August 1871Died24 October 1947(1947-10-24) (aged 76)NationalityBritishPolitical partyConservative then...

Electric power supply to trains by locomotives This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Head-end power – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) MBTA Commuter Rail car with U.S. standard head-end power electrical connection cables In rail t...

上大堀,是臺灣桃園市觀音區的一個傳統地域名稱,位於該區東南部。相較於今日行政區,其範圍大致包括上大里、藍埔里東側凸出部分的大堀溪以東及下草湖以南地區。 歷史 台灣清治末期至日治初期,上大堀地區為一街庄,稱為「上大堀庄」,隸屬於竹北二堡。該庄西北與下大堀庄為鄰,東北與崙坪庄為鄰,東南邊為過嶺庄,西南邊隔大堀溪與苦練腳庄、北勢庄為界[...

United States Army post in Alabama Buckner Hall at Fort McClellan in 2014. Fort McClellan, originally Camp McClellan, is a decommissioned United States Army post located adjacent to the city of Anniston, Alabama. During World War II, it was one of the largest U.S. Army installations, training an estimated half-million troops. After the war it became the home of the Military Police Corps, the Chemical Corps and the Women's Army Corps. From 1975 until it was closed in 1999, Fort McClellan was h...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。 出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: 国道122号 – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL (2012年9月) 一般国道 国道122号 地図 総延長 163.6 km 実延長 150.7...
