Rodolphus Agricola
|
Read other articles:

Peta Peloponnesia. Peloponnesia atau Peloponnesos (Greek: Πελοπόννησοςcode: el is deprecated , Pelopónnisos) adalah sebuah semenanjung yang luas dan merupakan daerah di Yunani Selatan. Selama akhir Abad pertengahan dan masa Turki Ustmani, semenanjung ini dikenal sebagai Morea (Yunani: Μωρέας), nama yang masih sering digunakan dalam percakapan sehari-hari. Semenanjung ini menjadi sebuah pulau sejak pembangunan Terusan Korintus tahun 1893. Semenanjung ini dibagi menjadi tiga ...

العلاقات البوتسوانية الكورية الجنوبية بوتسوانا كوريا الجنوبية تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات البوتسوانية الكورية الجنوبية (بالكورية: 보츠와나-대한민국 관계) هي العلاقات الثنائية بين بوتسوانا وكوريا الجنوبية. أقام البلدان علاقات دبلوماسية بتاريخ 18 أبريل عام 1968...

Esta página cita fontes, mas que não cobrem todo o conteúdo. Ajude a inserir referências. Conteúdo não verificável pode ser removido.—Encontre fontes: ABW • CAPES • Google (N • L • A) (Julho de 2022) Campeonato Brasileiro de 2010 - Série D Brasileirão 2010 - Série D Dados Participantes 40 Organização CBF Período 18 de julho – 14 de novembro Gol(o)s 436 Partidas 164 Média 2,66 gol(o)s por partida Campeão Guarany...

Piala FA 2006–2007Negara Inggris WalesJumlah peserta687Juara bertahanLiverpoolJuaraChelsea(gelar ke-4)Tempat keduaManchester UnitedPencetak gol terbanyakFrank Lampard (6 gol)← 2005–2006 2007–2008 → Piala FA 2006–2007 adalah edisi ke-126 dari penyelenggaraan Piala FA, turnamen tertua dalam sepak bola di Inggris. Edisi ini dimenangkan oleh Chelsea setelah mengalahkan Manchester United pada pertandingan final dengan skor 1–0. Final Artikel utama: Final Piala FA 2007 Chels...

Operazione diabolicaAntiochus Wilson (Rock Hudson) guarda una foto del suo vecchio sé (Arthur Hamilton/John Randolph)Titolo originaleSeconds Lingua originaleInglese Paese di produzioneStati Uniti d'America Anno1966 Durata107 min Dati tecniciB/Nrapporto: 1,66:1 Generethriller, fantascienza, drammatico RegiaJohn Frankenheimer Soggettodal romanzo Istituto di bella morte di David Ely SceneggiaturaLewis John Carlino ProduttoreEdward Lewis Casa di produzioneParamount Pictures, Joel Product...
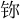
Artikel ini sebagian besar atau seluruhnya berasal dari satu sumber. Diskusi terkait dapat dibaca pada the halaman pembicaraan. Tolong bantu untuk memperbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan rujukan ke sumber lain yang tepercaya. Artikel ini memuat Teks Tionghoa. Tanpa bantuan render yang baik, anda mungkin akan melihat tanda tanya, kotak-kotak, atau simbol lainnya bukannya Karakter Tionghoa. Nama untuk unsur kimia dalam bahasa Asia Timur, bersama dengan beberapa senyawa kimia (kebanyakan ...

Not to be confused with Granivore. A graminivore is a herbivorous animal that feeds primarily on grass,[1] specifically true grasses, plants of the family Poaceae (also known as Graminae). Graminivory is a form of grazing. These herbivorous animals have digestive systems that are adapted to digest large amounts of cellulose, which is abundant in fibrous plant matter and more difficult to break down for many other animals. As such, they have specialized enzymes to aid in digestion and ...

Railway station in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England CottinghamGeneral informationLocationCottingham, East Riding of YorkshireEnglandCoordinates53°46′54″N 0°24′23″W / 53.781702°N 0.406376°W / 53.781702; -0.406376Grid referenceTA051328Managed byNorthern TrainsPlatforms2Other informationStation codeCGMClassificationDfT category F1HistoryOpened6 October 1846Passengers2018/19 0.211 million2019/20 0.219 million2020/21 40,2182021/22 0.162 million2022/23 0.211...

flybmi IATA ICAO Kode panggil BM[1][2] BMR[3] MIDLAND[3] Didirikan1987 (dengan nama Business Air)Berhenti beroperasi16 Februari 2019PenghubungBandar Udara AberdeenBandar Udara ManchesterProgram penumpang setiaBMI Diamond ClubLounge bandaraLounge Diamond ClubAliansiStar AllianceArmada15Perusahaan indukBritish Midland Airways Ltd.Kantor pusatAberdeen, Skotlandia, Britania RayaTokoh utamaStewart AdamsSitus webhttp://www.flybmi.com Embraer ERJ 145 Flybmi, ditulis s...

† Стеллерова корова Муляж стеллеровой коровы в Лондонском музее естествознания Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:Челюстно�...

River in Norfolk, England This article uses bare URLs, which are uninformative and vulnerable to link rot. Please consider converting them to full citations to ensure the article remains verifiable and maintains a consistent citation style. Several templates and tools are available to assist in formatting, such as reFill (documentation) and Citation bot (documentation). (June 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) ThetRiver Thet at BrettenhamLocation of the river mouth within Norfo...

Iraq-US relations Further information: Saddam–al-Qaeda conspiracy theory, Timeline of Saddam–al-Qaeda conspiracy allegations, and Criticism of the war on terror On 19 March 2003, President George W. Bush addressed the nation from the Oval Office, announcing the beginning of Operation Iraqi Freedom. The people of the United States and our friends and allies will not live at the mercy of an outlaw regime that threatens the peace with weapons of mass murder. The Senate committee found that m...

烏克蘭總理Прем'єр-міністр України烏克蘭國徽現任杰尼斯·什米加尔自2020年3月4日任命者烏克蘭總統任期總統任命首任維托爾德·福金设立1991年11月后继职位無网站www.kmu.gov.ua/control/en/(英文) 乌克兰 乌克兰政府与政治系列条目 宪法 政府 总统 弗拉基米尔·泽连斯基 總統辦公室 国家安全与国防事务委员会 总统代表(英语:Representatives of the President of Ukraine) 总...

ヨハネス12世 第130代 ローマ教皇 教皇就任 955年12月16日教皇離任 964年5月14日先代 アガペトゥス2世次代 レオ8世個人情報出生 937年スポレート公国(中部イタリア)スポレート死去 964年5月14日 教皇領、ローマ原国籍 スポレート公国親 父アルベリーコ2世(スポレート公)、母アルダその他のヨハネステンプレートを表示 ヨハネス12世(Ioannes XII、937年 - 964年5月14日)は、ロ...

Part of a series on theCulture of Canada History Canadians Ethnicity Folklore Free expression Identity Immigration Holidays Languages Multiculturalism Symbols Royal Protectionism Women Values Topics Architecture Art Comics Quebec Crime Cuisine Festivals Humour Law Literature Media Cinema Television Radio Newspapers Internet Video games Music Peacekeeping Politics Religion Sports Theatre Research Bibliography HistoriographyHistorians Surveys Canada portalvteThe maple leaf is the symbol mo...

Highway authority in Northern Ireland This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: DfI Roads – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2014)...

Tropical cyclone 2003 Sri Lanka cyclone Satellite image of the tropical storm on May 13Meteorological historyFormedMay 10, 2003DissipatedMay 20, 2003Very severe cyclonic storm3-minute sustained (IMD)Highest winds140 km/h (85 mph)Lowest pressure980 hPa (mbar); 28.94 inHgTropical storm1-minute sustained (SSHWS/JTWC)Highest winds110 km/h (70 mph)Lowest pressure980 hPa (mbar); 28.94 inHgOverall effectsFatalities260 totalDamage$135 m...

Peta infrastruktur dan tata guna lahan di Komune Autreville. = Kawasan perkotaan = Lahan subur = Padang rumput = Lahan pertanaman campuran = Hutan = Vegetasi perdu = Lahan basah = Anak sungaiAutreville, Vosges merupakan sebuah komune di departemen Vosges yang terletak pada sebelah timur laut Prancis. Lihat pula Komune di departemen Vosges Referensi INSEE lbsKomune di departemen Vosges Les Ableuvenettes Ahéville Aingeville Ainvelle Allarmont Amb...

Modern pentathlon at the Olympics Modern pentathlonat the Games of the XXVIII OlympiadVenueOlympic Modern Pentathlon CentreDates26 – 27 August 2004Competitors64 from 26 nations← 20002008 → Modern pentathlon at the2004 Summer OlympicsEventsmenwomenvte Final segment of the men's event The modern pentathlon at the 2004 Summer Olympics was held from 26 to 27 August 2004, at the Olympic Modern Pentathlon Centre at the Goudi Olympic Complex. The men's and women's e...

Dedi Nurhadiman Dansatinduk Bais TNIPetahanaMulai menjabat 2 Oktober 2023PendahuluI Wayan SuarjanaPenggantiPetahana Informasi pribadiLahir0 Juli 1967 (umur 57)IndonesiaAlma materAkademi Militer (1991)Karier militerPihak IndonesiaDinas/cabang TNI Angkatan DaratMasa dinas1991—SekarangPangkat Brigadir Jenderal TNISatuanArtileri MedanSunting kotak info • L • B Brigadir Jenderal TNI Dedi Nurhadiman, S.I.P. (lahir Juli 1967) adalah seorang perwira tinggi TNI-AD ya...


