Red-lipped batfish
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Maret 2016. Danau Paya Kuda, adalah satu danau yang berada di Desa Kempawa, Kecamatan Tanah Pinem, Kabupaten Dairi, Provinsi Sumatera Utara. Meski danau ini tidak seluas Danau Toba yang sudah terkenal sampai keluar negeri. Namun Danau Paya Kuda yang hanya memiliki l...

Learned society in Victoria, Australia The Royal Society of Victoria's historic headquarters, designed by Joseph Reed, purpose-built in 1859. The Royal Society of Victoria (RSV) is the oldest scientific society in Victoria, Australia. Foundation In 1854 two organisations formed with similar aims and membership, these being the Philosophical Society of Victoria (founded 15 June, 1854, inaugural president Andrew Clarke) and the Victorian Institute for the Advancement of Science (founded 12 Augu...
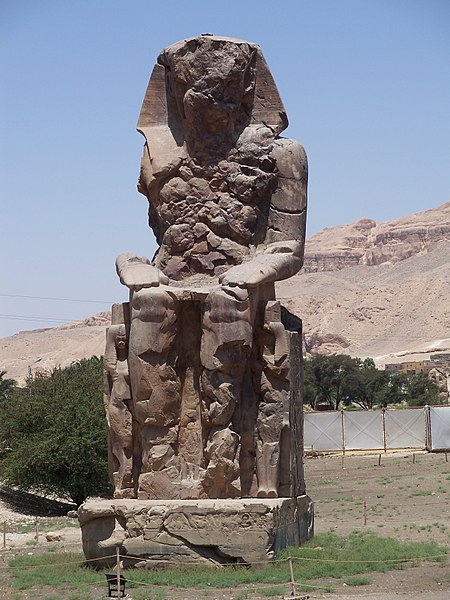

La XXIV dinastia egizia, penultima del Terzo periodo intermedio dell'Egitto, comprende solamente due sovrani, uno solo dei quali, Boccori, è citato come tale dalle liste manetoniane. EgittoDati amministrativiLingue parlateAntico egizio CapitaleSais PoliticaForma di governoMonarchia assoluta Nascita732 a.C. Fine720 a.C. Territorio e popolazioneReligione e societàReligione di StatoReligione egizia Evoluzione storicaPreceduto daRegno d'Egitto (XXIII dinastia) Succeduto daRegno d'Egitto (XXV di...

Beechcraft T-6 Texan II adalah sebuah pesawat bermesin turboprop tunggal sayap rendah (low wing) dibangun oleh Raytheon Aircraft Company (yang menjadi Hawker Beechcraft dan sekarang Beechcraft Corporation). Berdasarkan Pilatus PC-9, T-6A digunakan oleh Angkatan Udara Amerika Serikat untuk pelatihan pilot dasar dan oleh Angkatan Laut Amerika Serikat untuk Dasar dan Menengah Bersama Naval Flight Officer (NFO) dan pelatihan Angkatan Udara Combat Systems Officer (CSO). Pesawat bermesin turboprop...

South African cricketer Dale SteynSteyn in 2009Personal informationFull nameDale Willem SteynBorn (1983-06-27) 27 June 1983 (age 40)Phalaborwa, Transvaal Province, South AfricaBattingRight-handedBowlingRight-arm fastRoleBowlerInternational information National sideSouth Africa (2004–2020)Test debut (cap 297)17 December 2004 v EnglandLast Test21 February 2019 v Sri LankaODI debut (cap 82)17 August 2005 v Asia XILast ODI13 March 2019&#...

Constituency of Bangladesh's Jatiya Sangsad Lalmonirhat-1Constituencyfor the Jatiya SangsadDistrictLalmonirhat DistrictDivisionRangpur DivisionElectorate318,112 (2018)[1]Current constituencyCreated1984PartyAwami LeagueMember(s)Motahar Hossain← Seat no. 15Seat no. 16Seat no.17 → Lalmonirhat-1 is a constituency represented in the Jatiya Sangsad (National Parliament) of Bangladesh since 2001 by Motahar Hossain of the Awami League. Boundaries The constituency encompasses Hatibandha an...

Railway Station in Odisha, India Rupra RoadIndian Railways stationGeneral informationLocationRupra Road, OdishaIndiaCoordinates20°05′05″N 83°19′53″E / 20.084687°N 83.331392°E / 20.084687; 83.331392Owned byMinistry of Railways, Indian RailwaysLine(s)Jharsuguda–Vizianagaram linePlatforms3Tracks3ConstructionStructure typeStandard (on ground)ParkingNoOther informationStatusFunctioningStation codeRPRD Zone(s) East Coast Railway Division(s) SambalpurHistoryElec...

This article is about the album. For the title track, see Just a Little More Love (song). For the song by Liberty X, see Just a Little (Liberty X song). 2002 studio album by David GuettaJust a Little More LoveStudio album by David GuettaReleased10 June 2002 (2002-06-10)Recorded2000–01GenreHouseelectro houseFrench houseLength49:06LabelVirginGum ProdProducerJoachim GarraudDavid GuettaDavid Guetta chronology Just a Little More Love(2002) Guetta Blaster(2004) Singles...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Boulevard de Sébastopol – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Boulevard de Sébastopolboulevard de Sébastopol todayShown within ParisNamesakeSiege of SevastopolLength1,332 m (4,370&...

Artikel ini perlu diterjemahkan dari bahasa Inggris ke bahasa Indonesia. Artikel ini ditulis atau diterjemahkan secara buruk dari Wikipedia bahasa Inggris. Jika halaman ini ditujukan untuk komunitas bahasa Inggris, halaman itu harus dikontribusikan ke Wikipedia bahasa Inggris. Lihat daftar bahasa Wikipedia. Artikel yang tidak diterjemahkan dapat dihapus secara cepat sesuai kriteria A2. Jika Anda ingin memeriksa artikel ini, Anda boleh menggunakan mesin penerjemah. Namun ingat, mohon tidak men...

Islamic educational institute in Sahiwal, Pakistan This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article contains content that is written like an advertisement. Please help improve it by removing promotional content and inappropriate external links, and by adding encyclopedic content written from a neutral point of view. (July 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) The t...

Proposed NASA Mars communications satellite Not to be confused with the Earth Return Orbiter, an ESA Mars orbiter. Next Mars OrbiterThis proposed telecommunications orbiter features ion thrusters and improved solar arrays.NamesNeMO, Mars 2022 orbiter[1]Mission typeTelecommunications and reconnaissanceOperatorNASAMission durationPlanned: 6.5 years[1] Spacecraft propertiesLaunch mass1,900 kg (4,200 lb)[1]Dry mass1,300 kg (2,900 lb)[1]Payload m...

Le Lettere di Ignazio sono sette lettere attribuite al vescovo e martire Ignazio di Antiochia (107–110), detto L'Illuminatore, scritte in greco nei primi anni del II secolo. Dalla tradizione cristiana e dagli studiosi contemporanei sono ritenute autentiche.[1] Le epistole, di argomento teologico, furono scritte prima del martirio. Primo nella letteratura cristiana, Ignazio attribuì alla Chiesa l'appellativo di «cattolica», cioè «universale»: «Dove è Gesù Cristo, lì è la C...

A.C.F. Trani 80Calcio Segni distintiviUniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Terza divisa Colori sociali Bianco, azzurro Dati societariCittàTrani Nazione Italia ConfederazioneUEFA Federazione F.I.G.C.F. e F.I.G.C. Fondazione1979 Scioglimento1988StadioComunale di Trani(10 700 posti) Palmarès Trofei nazionali1 Coppe Italia Si invita a seguire il modello di voce L'Associazione Calcio Femminile Trani 80 era una società calcistica femminile con sede a Trani attiva tra il 1979 e il 1988. ...

Quarter of Hamburg in GermanyWellingsbüttel Quarter of Hamburg Former school (1888–1974) in Wellingsbüttel, now a health and advice centre and branch of the public libraries.Location of Rahlstedt in the city of Hamburg Wellingsbüttel Show map of GermanyWellingsbüttel Show map of HamburgCoordinates: 53°38′N 10°5′E / 53.633°N 10.083°E / 53.633; 10.083CountryGermanyStateHamburgCityHamburg BoroughWandsbek Population (2020-12-31)[1] •&#...
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会波兰代表團波兰国旗IOC編碼POLNOC波蘭奧林匹克委員會網站olimpijski.pl(英文)(波兰文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員206參賽項目24个大项旗手开幕式:帕维尔·科热尼奥夫斯基(游泳)和马娅·沃什乔夫斯卡(自行车)[1]闭幕式:卡罗利娜·纳亚(皮划艇)&#...

Boeing Model 203 adalah biplan pelatih tiga kursi dibangun oleh Boeing pada akhir tahun 1920 dan digunakan di sekolah pelatihan perusahaan. 203 adalah biplan daya rendah yang dirancang untuk bersaing dengan pesawat latih standar lainnya. Kokpit depan ditampung 2 penumpang side-by-side, atau 1 siswa dengan set kedua kontrol. Pesawat yang sedang dilas pipa baja (pesawat Boeing terakhir dibangun dengan cara ini) dan sayapnya terbuat dari kayu solid spar dan tulang rusuk kayu lapis. Secara fisik ...

Jaroslav Popovyč Jaroslav Popovyč allo Scheldeprijs 2015 Nazionalità Ucraina Altezza 175[1] cm Peso 71[1] kg Ciclismo Specialità Strada Termine carriera 2016 CarrieraSquadre di club 2000-2001Zoccorinese-Vellutex2002-2004 Landbouwkrediet2005-2007 Discovery Channel2008 Silence-Lotto2009 Astana2010-2011 RadioShack2012-2013 RadioShack2014-2016 TrekNazionale 2002-2013 UcrainaPalmarès Mondiali su strada Argento Plouay 2000 In line...

Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation SONY and Sony Corporation redirect here. For the U.S. subsidiary, see Sony Corporation of America. For other uses, see Sony (disambiguation). Not to be confused with Sany. Sony Group CorporationHeadquarters in Minato, TokyoNative nameソニーグループ株式会社Romanized nameSonī Gurūpu Kabushiki-gaishaFormerly Tokyo Tsushin Kogyo K.K. (1946–1957) Sony Corporation (1958–2021)[a][1] Company typePublicTraded as TYO: 6758...

For pre-1919 Prussian Ministers of War, see List of war ministers of Prussia. Federal Minister of DefenceBundesminister der VerteidigungCoat of armsState flagIncumbentBoris Pistoriussince 19 January 2023Federal Ministry of DefenceReports toThe Federal ChancellorAppointerThe President, upon advice of the Federal ChancellorFormation13 February 1919First holderGustav Noske (Weimar Republic)Theodor Blank (Federal Republic of Germany)Websitebmvg.de The Federal Minister of Defence (German: Bu...



