Raphe nuclei
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

1993 single by Dionne WarwickWhere My Lips Have BeenSingle by Dionne Warwickfrom the album Friends Can Be Lovers Released1993Length4:35LabelAristaSongwriter(s) Robert Charles Burns Sandy Knox Don Huber Producer(s)Barry EastmondDionne Warwick singles chronology Sunny Weather Love (1993) Where My Lips Have Been (1993) Friends Can Be Lovers (1993) Where My Lips Have Been is a song recorded by American singer Dionne Warwick. It was written by Robert Charles Burns, Sandy Knox, and Don Huber fo...
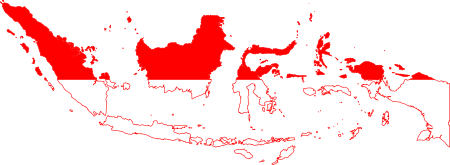
Teluk SemangkaLetakAsia TenggaraJenis perairanTelukTerletak di negaraIndonesiaReferensiTeluk Semangka: Indonesia National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, Bethesda, MD, USA Teluk Semangka adalah teluk besar yang berada di ujung selatan Pulau Sumatra. Di ujung selatan Sumatra terdapat dua teluk besar, Teluk Semangka adalah yang terletak di bagian barat. Di sisi timur teluk ini membentang Kabupaten Tanggamus, dengan ibu kota Kotaagung yang berada di ujung utara teluk ini. Artikel bertopik geogra...

Season of television series Season of television series ScrubsSeason 9DVD coverCountry of originUnited StatesNo. of episodes13ReleaseOriginal networkABCOriginal releaseDecember 1, 2009 (2009-12-01) –March 17, 2010 (2010-03-17)Season chronology← PreviousSeason 8 List of episodes The ninth and final season of the American comedy television series Scrubs (also known as Scrubs: Med School) premiered on ABC on December 1, 2009, and concluded on March 17, 2010, and consists ...

Partai Komunis Ukraina Nama dalam bahasa UkrainaКомунiстична Партiя УкраïниNama dalam bahasa RusiaКоммунистическая партия УкраиныPendiriVladimir LeninDibentuk17 Juli 1918 (1918-07-17)Dilarang30 Agustus 1991; 32 tahun lalu (1991-08-30)Didahului olehPartai Buruh Demokrat Sosial Rusia (Bolshevik) – Demokrat-Sosial UkrainaDiteruskan olehPartai Sosialis UkrainaPartai Komunis Ukraina (1993)Partai Kebangkitan Demokratik Ukrain...

Isidoro Diéguez DueñasInformación personalNacimiento 12 de enero de 1909 Puertollano (España) Fallecimiento 21 de enero de 1942 (33 años)cementerio de La Almudena (España) Causa de muerte Herida por arma de fuego Nacionalidad EspañolaInformación profesionalOcupación Político Partido político Partido Comunista de España [editar datos en Wikidata] Isidoro Diéguez Dueñas (Puertollano, 19 de enero de 1909 – Madrid, 21 de enero de 1942) fue un político comunista español...

?Негрито патагонський Самець патагонського негрито Самиця патагонського негрито Охоронний статус Найменший ризик (МСОП 3.1)[1] Біологічна класифікація Домен: Еукаріоти (Eukaryota) Царство: Тварини (Animalia) Тип: Хордові (Chordata) Клас: Птахи (Aves) Ряд: Горобцеподібні (Passeriformes) Род�...

Helmi HasanWali Kota Bengkulu ke-14PetahanaMulai menjabat 24 September 2018PendahuluBudiman Ismaun (Pj.)Masa jabatan21 Januari 2013 – 21 Januari 2018PendahuluAhmad KanediPenggantiBudiman Ismaun (Pj.)Anggota DPRD Provinsi BengkuluMasa jabatan2009 – 2013Anggota DPRD Kota BengkuluMasa jabatan2004 – 2009 Informasi pribadiLahir29 November 1979 (umur 44)Pisang, Penengahan, Lampung Selatan, LampungKebangsaanIndonesiaPartai politikPartai Amanat NasionalSu...

Guilty Pleasures, buku pertama dari seri Anita Blake: Vampire Hunter Anita Blake: Vampire Hunter adalah seri novel fantasi karangan Laurell K. Hamilton. Seri ini berlatar di semesta paralel dari Saint Louis dan menceritakan tentang dunia yang dihuni oleh vampir. Tokoh utama dalam novel ini bernama Anita Blake. Buku Guilty Pleasures (1993) ISBN 0-515-13449-X The Laughing Corpse (1994) ISBN 0-425-19200-8 Circus of the Damned (1995) ISBN 0-515-13448-1 The Lunatic Cafe (1996) ISBN 0-425-20137-6 B...

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang seri permainan video. Untuk permainan video pertama dari seri tersebut, lihat Deus Ex (video game). Untuk the dramatic device from which its title is derived, lihat Deus ex machina. Deus ExAliranPeran laga, first-person shooter, stealthPengembangPrimerIon Storm (2000–2003)Eidos Montréal (2011–)Lain-lainN-Fusion Interactive (2013)Square Enix Montreal (2016)Feral Interactive (Mac OS, Linux)PenerbitEidos Interactive (2000–2003)Square Enix (2011–)Feral ...

Constituency of the Madhya Pradesh legislative assembly in India For constituency in other states, see Sagar, Karnataka Assembly constituency and Sagar, West Bengal Assembly constituency. SagarConstituency for the Madhya Pradesh Legislative AssemblyConstituency detailsCountryIndiaRegionCentral IndiaStateMadhya PradeshDistrictSagarLS constituencySagarReservationNoneMember of Legislative Assembly16th Madhya Pradesh Legislative AssemblyIncumbent Shailendra Jain PartyBharatiya Janata Party Sagar ...

2008 fad This article is about the lying down game. For the isometric exercise for the abdominal muscles, see Plank (exercise). Planking in a kitchen Planking (or the Lying Down Game) is an activity consisting of lying in a face down position, sometimes in an unusual or incongruous location. The palms of the hands are typically touching the sides of the body and the toes are typically touching the ground.[1] Some players compete to find the most unusual and original location in which ...

2007 video gameSSX BlurDeveloper(s)EA MontrealPublisher(s)EA Sports BIGDirector(s)Éric PlanteProducer(s)Alex HyderDesigner(s)Éric ChartrandProgrammer(s)Sergei SavchenkoArtist(s)David TaylorComposer(s)Junkie XLSeriesSSXPlatform(s)WiiReleaseNA: February 27, 2007AU: March 15, 2007EU: March 16, 2007Genre(s)Snowboarding, Skiing, RacingMode(s)Single-player, multiplayer SSX Blur is a snowboarding and skiing video game, published by Electronic Arts under the EA Sports BIG label and developed by EA ...

American sports radio personality (born 1983) Evan RobertsRoberts at Citi Field, 2012Born (1983-07-11) July 11, 1983 (age 40)CareerShow Carton and Roberts Joe & Evan (2007-2020) Station(s)WFANTime slotM-F 02:00 p.m. - 06:30 p.m. ETStyleSports radioCountryUnited States Websitewfan.radio.com/shows/joe-evan Evan Roberts (born July 11, 1983) is an American sports radio personality. He co-hosts the Evan and Tiki radio show, along with Tiki Barber, on the New York radio stations WFAN-AM an...

Walther Bringolf Walther Bringolf (1 August 1895 – 24 March 1981) was a former President of the National Council of Switzerland (1961/1962).[1] He was a member of the Social Democratic Party of Switzerland[2] and was a long-time mayor of Schaffhausen (1933–1968).[3] Communist activities A group of members of the International Bureau of Proletkult. Sitting (left to right): War Van Overstraeten, P. Lebedev-Polyansky (secretary). Anatoly Lunacharsky (chairman), Nicola...

Street in Hanoi, Vietnam Ngõ 224 Lê DuẩnThe street in 2017.LocationOld Quarter, Hanoi, Vietnam Ngõ 224 Lê Duẩn is a narrow alley in Hanoi’s Old Quarter, known as “The Train Street”, which sees a twice-daily train pass close to buildings on either side of the tracks (the railroad tracks take up nearly the entirety of the “train street”). [1] The track was built by the French in 1902 and is still an active rail line as of 2023. [2] The train passes at 3pm and 7...

Board game Advanced HeroQuestPublishersGames WorkshopPlayers1 to 5Playing timeca. 90 minutesChanceDice rolling Advanced HeroQuest is a board game published by Games Workshop in 1989, a sequel to HeroQuest. Description The original HeroQuest was an adventure board game created in 1989 by Milton Bradley in conjunction with the British company Games Workshop. Later the same year, Games Workshop released Advanced HeroQuest, a similar but more complex game. Changes from HeroQuest include more comp...

This article is about specific aspects of the history of Anzac Day in Queensland. For Anzac Day worldwide, see Anzac Day. Anzac Day parade on Dee Street, Mount Morgan, 25 April 1916 Anzac Day is a day of remembrance in Queensland, Australia. It is a public holiday held on 25 April each year. The date is significant as the Australian and New Zealand troops (the ANZACs) first landed at Gallipoli in World War I on 25 April 1915. Background Anzac Day observance in Australia did not begin as a gov...

Estonian musical group Malcolm LincolnMalcolm Lincoln with Manpower 4 in Oslo, 2010.Background informationOriginEstoniaGenresElectropopYears active2009 (2009)–2012LabelsUniversal Music, Mortimer SnerdPast membersRobin Juhkental Uku Kübar Märt Tomson Aap OdresMadis Kubu Jakob Juhkam Johan Alexander Petti Hans Kurvits Siim RaidmaMalcolm Lincoln was an Estonian band that formed in October 2009. The members are Robin Juhkental, Jakob Juhkam, Siim Raidma, Ott Adamson, Johan Alexander Pett...

Draft de la NBA de 2022Información generalFecha 23 de junio de 2022Hora 7:00 p.m. (EST)Ubicación Barclays Center Brooklyn, Nueva YorkTransmisión ESPNDrafts de la NBA 2021 2023 El Draft de la NBA de 2022 se celebró el jueves 23 de junio de 2022 en el Barclays Center de Brooklyn, Nueva York. Los equipos de la National Basketball Association (NBA) se turnaron para seleccionar a los jugadores del baloncesto universitario de los Estados Unidos y otros jugadores elegibles, incluyendo los jugado...

Ancien cimetière de WissousLocalisation Wissous, Essonne FranceCoordonnées 48° 43′ 56″ N, 2° 19′ 37″ EIdentifiantsSauvons nos tombes 45490modifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata L,ancien cimetière de Wissous est un cimetière situé à Wissous dans le département de l'Essonne, en France. Description L'entrée principale se trouve sur Charles-Legros. Historique Sa création est antérieure à 1838[1]. S'y trouvait autrefois le monument a...


