Podocnemididae
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

SMA Negeri 1 SawahluntoInformasiDidirikan15 Oktober 1959JenisNegeriAkreditasiANomor Pokok Sekolah Nasional10303691Kepala SekolahDrs. Jafrizal, M.Pd.Jumlah kelas7 kelas setiap tingkatJurusan atau peminatanIlmu alam, Ilmu sosial dan Ilmu bahasaRentang kelasX-XIIKurikulumKurikulum Tingkat Satuan PendidikanStatusNegeri (Rintisan SMA Kategori Mandiri)AlamatLokasiJalan Sudirman No. 7, Kubang Sirakuak Selatan, Lembah Segar, Sawahlunto 27417, Sumatera Barat, IndonesiaTel./Faks.(0754) - 6100...

BunderDesaKantor Desa BunderPeta lokasi Desa BunderNegara IndonesiaProvinsiJawa TimurKabupatenBanyuwangiKecamatanKabatKode pos68461Kode Kemendagri35.10.14.2002 Luas... km²Jumlah penduduk... jiwaKepadatan... jiwa/km² Bunder adalah sebuah nama desa di wilayah Kabat, Kabupaten Banyuwangi, Provinsi Jawa Timur, Indonesia. Pembagian Wilayah Desa Bunder terdiri dari 5 dusun Dusun Kelir Dusun Krajan Dusun Mulyosari Dusun Sangkur Dusun Sruni Galeri Gerbang Desa Bunder Pranala luar Situs resmi P...

بلومينغبورغ الإحداثيات 41°33′15″N 74°26′22″W / 41.5542°N 74.4394°W / 41.5542; -74.4394 [1] تقسيم إداري البلد الولايات المتحدة[2] التقسيم الأعلى نيويورك خصائص جغرافية المساحة 0.3 ميل مربع ارتفاع 515 قدم عدد السكان عدد السكان 1032 (1 أبريل 2020)[3 ...

العلاقات الأرمينية المالطية أرمينيا مالطا أرمينيا مالطا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الأرمينية المالطية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين أرمينيا ومالطا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارنة أ�...

This article is about the region. For the local government area in New South Wales, see City of Canterbury-Bankstown. This article uses bare URLs, which are uninformative and vulnerable to link rot. Please consider converting them to full citations to ensure the article remains verifiable and maintains a consistent citation style. Several templates and tools are available to assist in formatting, such as reFill (documentation) and Citation bot (documentation). (August 2022) (Learn how and whe...

Chronologie de la France ◄◄ 1770 1771 1772 1773 1774 1775 1776 1777 1778 ►► Chronologies Le bosquet des bains d’Apollon à Versailles, Hubert Robert. Tableau exposé au salon de 1777 avec les vues des jardins de Versailles, dans le temps qu’on abattait les arbres.Données clés 1771 1772 1773 1774 1775 1776 1777Décennies :1740 1750 1760 1770 1780 1790 1800Siècles :XVIe XVIIe XVIIIe XIXe XXeMillénaires :-Ier Ier IIe ...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (أبريل 2019) رحمت ميا معلومات شخصية الميلاد 8 ديسمبر 1999 (25 سنة) الطول 1.70 م (5 قدم 7 بوصة) مركز اللعب مدافع الجنسية بنغلاديش معلومات النادي النادي الحالي Abaha...
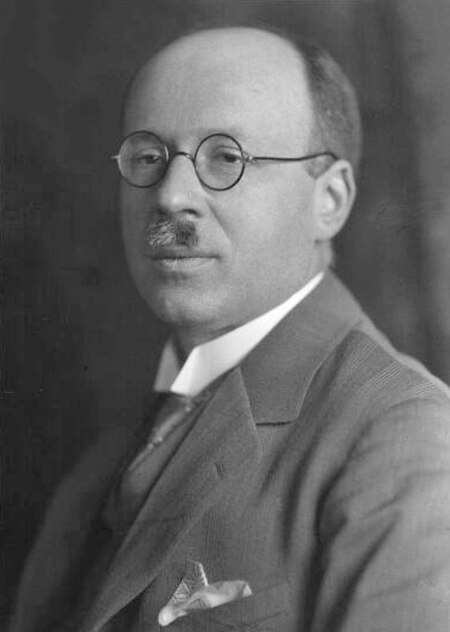

Leopold Ruzicka Lavoslav (Leopold) Stjepan Ružička (l. Vukovar, Austria-Hungaria (kini Kroasia), 13 September 1887 - † Zürich, 26 September 1976) adalah kimiawan dan profesor di Universitas Swiss yang dianugerahi Penghargaan Nobel dalam Kimia pada 1939. Biografi Ia menghadiri SD program klasik di Osijek (Kroasia), mengubah cita-citanya dari pendeta untuk belajar ilmu teknik. Memilih kimia, mungkin karena ia mengharap mendapat kedudukan di pabrik gula yang baru dibangun di Osijek. Namun i...

1998 studio album by KatatoniaDiscouraged OnesStudio album by KatatoniaReleased27 April 1998 (1998-04-27)RecordedJuly–August 1997StudioSunlight Studios[1]GenreGothic metal[2]Length46:57LabelAvantgarde MusicProducerKatatoniaKatatonia chronology Saw You Drown(1998) Discouraged Ones(1998) Tonight's Decision(1999) Professional ratingsReview scoresSourceRatingAllMusic[3]Chronicles of Chaos9/10[4] Discouraged Ones (stylized discøuraged øne...

School in New York City Main building at 225 East 43rd Street Lyceum Kennedy International School is an international school occupying two buildings in Midtown Manhattan, New York City.[1] It serves preschool through grade 12.[2] The school was named after President of the United States John F. Kennedy.[3] Founded in 1964, Lyceum Kennedy French American school serves the needs of French and francophone families living in New York. It has a French language K-12 day scho...

National park in California, United States This article is about the national park in the United States. For Kings Canyon in Australia, see Kings Canyon (Northern Territory). Kings Canyon National ParkIUCN category II (national park)[1]View of Kings Canyon, looking south from Paradise Valley. The Sphinx centered.Location in CaliforniaShow map of CaliforniaLocation in the United StatesShow map of the United StatesLocationFresno and Tulare counties, CaliforniaNearest cityFresnoCoor...

This article uses bare URLs, which are uninformative and vulnerable to link rot. Please consider converting them to full citations to ensure the article remains verifiable and maintains a consistent citation style. Several templates and tools are available to assist in formatting, such as reFill (documentation) and Citation bot (documentation). (September 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Developer(s)Steve Lime originally, now a project of the OSGeo foundationInitial release19...

Port in PortugalPort of LisbonPorto de LisboaClick on the map for a fullscreen viewLocationCountryPortugalUN/LOCODEPTLIS[1]StatisticsWebsiteOfficial Website The Port of Lisbon (Portuguese: Porto de Lisboa) is the third-largest port in Portugal, mainly on the north sides of the Tagus's large natural harbour that opens west, through a short strait, onto the Atlantic Ocean. Each part lies against central parts of the Portuguese capital Lisbon. Due to its strategic site between Europe, Af...

مطار طنجة ابن بطوطة الدولي إياتا: TNG – ايكاو: GMTT موجز نوع المطار عام المشغل المكتب الوطني للمطارات يخدم جهة طنجة تطوان البلد المغرب[1] الموقع طنجة، المغرب الارتفاع 19 م؛ 62 قدم إحداثيات 35°43′37″N 5°55′01″W / 35.726916666667°N 5.9168888888889°W / 35.726916666667; -5.9168888888889 الخ�...

Zuid-Korea op de Olympische Spelen Land Zuid-Korea IOC-landcode KOR NOC Korean Olympic Committee(ko) (en) externe link Olympische Zomerspelen 1996 in Atlanta Vlaggendrager Choi Cheon-Sik Aantal deelnemers 302 Aantal disciplines 25 MedaillesRang: 10 goud7 zilver15 brons5 totaal27 Zuid-Korea op de Zomerspelen 1948 · 1952 · 1956 · 1960 · 1964 · 1968 · 1972 · 1976 · 1980 · 1984 · 1988 · 1992 · 1996 · 2000 · 2004 · 2008 · 2012 · 2016 · 2020 · 2024 Zuid-Korea op de Winters...

Vous lisez un « article de qualité » labellisé en 2007. Pour les articles homonymes, voir Besançon (homonymie). Pour l’article ayant un titre homophone, voir Bezançon. Besançon De haut en bas et de gauche à droite : le quartier Saint-Jean, l'hôtel de ville, le palais Granvelle, le quai Vauban, les rives du Doubs et la citadelle. Blason Logo Administration Pays France Région Bourgogne-Franche-Comté (siège) Département Doubs (préfecture) Arrondissement Besançon(...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant un film français. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les conventions filmographiques. Cet article concerne le film de Max de Rieux. Pour le film de Desmond Mac Anuff, voir La Cousine Bette. Pour les articles homonymes, voir La Cousine Bette (homonymie). La Cousine Bette, affiche de G. Elisabeth. La Cousine Bette est un film français réalisé par Max de Rieux, sorti en 1927, adapté de la nouvelle La ...
776 ← 777 → 778素因数分解 3×7×37二進法 1100001001三進法 1001210四進法 30021五進法 11102六進法 3333七進法 2160八進法 1411十二進法 549十六進法 309二十進法 1IH二十四進法 189三十六進法 LLローマ数字 DCCLXXVII漢数字 七百七十七大字 七百七拾七算木 777(七百七十七、七七七、ななひゃくななじゅうなな)は、自然数また整数において、776の次で778の前の数である。 7と並んで幸...

كينيتاتقسيم إداريالبلد اليونان التقسيم الأعلى Megara Municipality (en) — Commune of Kineta, W. Attiki (en) خصائص جغرافيةالارتفاع 5 م السكانعدد السكان القائمة ... 1٬651 وفق resident population of Greece (en) (2021)1٬433 وفق resident population of Greece (en) (2001)1٬090 وفق resident population of Greece (en) (1991)1٬446 وفق resident population of Greece (en) (2011)110[1] وفق d...

Scholar of Second Temple period Jewish history Daniel R. Schwartz in 2022 Daniel R. Schwartz (born 1952; Hebrew: דניאל שוורץ) is a professor of Jewish History at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem.[1] He is a scholar of Hellenistic Judaism, Flavius Josephus, the Second Temple Period, and the book 2 Maccabees. Background Daniel Schwartz was born in the United States in 1952. He immigrated to Israel (aliyah) in 1971. He earned a Ph.D in Jewish History from the Hebrew Universit...

