Online Safety Amendment
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

La Paz Municipio Escudo Mapa interactivoCoordenadas 24°07′00″N 110°43′00″O / 24.116666666667, -110.71666666667Capital La PazEntidad Municipio • País México • Estado Baja California Sur • Cabecera La PazPresidenta municipal Milena Paola Quiroga Romero[1] (2021-2024)Eventos históricos • Fundación 3 de mayo de 1535 (Hernán Cortés)Superficie • Total 20274.98 km²Altitud • Media 1234 m ...

GabumonRookiePenampilan perdanaDigimon Adventure Episode 1[1]PartnerYamato IshidaEvolusi dariTsunomonBerevolusi menjadiGarurumon Tingkatan evolusiGabumon Level In-Training Tsunomon Level Rookie Gabumon Level Champion Garurumon Level Ultimate WereGarurumon Level Mega MetalGarurumon DigiDestined: Yamato Ishidalbs Gabumon adalah salah satu digimon yang menjadi pemeran utama dalam Digimon Adventure dan Digimon Adventure 02. Gabumon merupakan digimon berbentuk reptil dengan kulit hewan mam...

Richard SorgeRichard Sorge tahun 1940JulukanRamsayLahir4 Oktober 1895Baku, Kekaisaran RusiaMeninggal7 November 1944(1944-11-07) (umur 49)Tokyo, Kekaisaran JepangPengabdian German Empire (sampai 1918) USSR (mulai 1920)Dinas/cabangAngkatan Darat Kekaisaran JermanAngkatan Darat Soviet (GRU)Lama dinasJerman 1914–1916, Uni Soviet 1920–1941PenghargaanPahlawan Uni SovietOrdo LeninSalib Besi, kelas II (untuk kampanye Perang Dunia I)PasanganChristiane Gerlach (1921–1929) Rich...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Treize-Avril. Éphémérides Avril 1er 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 13 mars 13 mai Chronologies thématiques Croisades Ferroviaires Sports Disney Anarchisme Catholicisme Abréviations / Voir aussi (° 1852) = né en 1852 († 1885) = mort en 1885 a.s. = calendrier julien n.s. = calendrier grégorien Calendrier Calendrier perpétuel Liste de calendriers Naissances du jour mod...

Empat negara pendiri Aliansi Pasifik (hijau, dari atas ke bawah): Meksiko, Kolombia, Peru dan Chili. Aliansi Pasifik adalah sebuah organisasi yang dibentuk pada Juni 2012 oleh empat negara dalam kawasan Amerika Latin. Keempat negara pendirinya ialah Peru, Chili, Kolombia, dan Meksiko. Pembentukan Aliansi Pasifik merupakan hasil dari penandatanganan Deklarasi Lima oleh keempat negara tersebut pada April 2011. Aliansi Pasifik didirikan dengan tujuan untuk memperkuat kerja sama negara-negara Ame...

Volleyballat the Games of the XXVIII Olympiad Pictograms for indoor (left) and beach volleyball (right)VenuePeace and Friendship Stadium (indoor)Faliro Olympic Beach Volleyball Centre (beach)Dates14 – 29 August 2004Competitors384 (192 men, 192 women) from 31 nations← 20002008 → Indoor Volleyball at Peace and Friendship Stadium. Volleyball at the 2004 Summer Olympics consisted of indoor volleyball held at the Peace and Friendship Stadium and beach volleyball ...

Opening folio of Genesis A in Bodleian Libraries, Junius 11. Genesis A (or Elder Genesis) is an Old English poetic adaptation of the first half or so of the biblical book of Genesis. The poem is fused with a passage known today as Genesis B, translated and interpolated from the Old Saxon Genesis. Genesis A (and B) survive in the Junius Manuscript, which has been held in the Bodleian Library at the University of Oxford since 1677. Lacunae The sole manuscript containing Genesis A is incomplete,...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento militari statunitensi non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. I generali degli Stati Confederati d'America erano collocati gerarchicamente in quattro livelli. Il grado più elevato era quello di general (generale): il termine però, oltre ad essere specifico di...

National Fire and Rescue Administration国家消防救援局Operational areaCountryChinaAgency overviewEstablished2018CommissionerMinister of Emergency ManagementFire chiefWang Yupu Fire and rescue commissionerWebsite119.gov.cn National Fire and Rescue Administration (国家消防救援局) is the state emergency service force for firefighting and rescue in China, which is part of the civil service and is administered by the Ministry of Emergency Management (MEM). China Fire and Rescue Force ...

Sceaux 行政国 フランス地域圏 (Région) イル=ド=フランス地域圏県 (département) オー=ド=セーヌ県郡 (arrondissement) アントニー郡小郡 (canton) 小郡庁所在地INSEEコード 92071郵便番号 92330市長(任期) フィリップ・ローラン(2008年-2014年)自治体間連合 (fr) メトロポール・デュ・グラン・パリ人口動態人口 19,679人(2007年)人口密度 5466人/km2住民の呼称 Scéens地理座標 北緯48度4...

2023 video game 2023 video gameThe InvincibleDeveloper(s)Starward IndustriesPublisher(s)11 Bit StudiosDirector(s)Marek MarkuszewskiComposer(s)Brunon LubasEngineUnreal Engine 4Platform(s)Microsoft WindowsPlayStation 5Xbox Series X/SReleaseNovember 6, 2023Genre(s)AdventureMode(s)Single-player The Invincible is an adventure video game developed by Starward Industries and published by 11 Bit Studios. It is an adaptation of the 1964 Polish novel The Invincible. The game was released for Microsoft ...

Portuguese painter (1768–1837) Domingos SequeiraSelf-Portrait by Domingos SequeiraBornDomingos António de Sequeira(1768-03-10)10 March 1768Lisbon, Kingdom of PortugalDied8 March 1837(1837-03-08) (aged 68)Rome, Papal StatesNationalityPortugueseKnown forFine PaintingMovementNeoclassicism Domingos António de Sequeira (Lisbon; 10 March 1768 – Rome; 8 March 1837) was a famous Portuguese painter at the Royal Court of King John VI of Portugal. Biography He was born in Be...
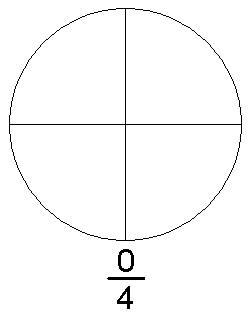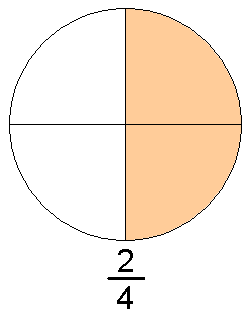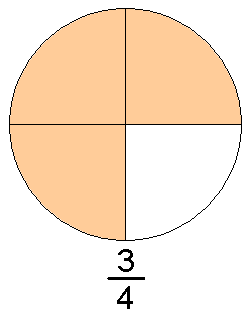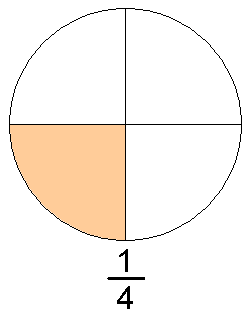
عدد كسريمعلومات عامةصنف فرعي من عدد قابل للإنشاءعدد حقيقيعدد تقاربي بتردد p جزء من مجموعة الأعداد الكسرية يدرسه rational number theory (en) تعريف الصيغة a b ∈ Q ⇔ a ∈ Z , b ∈ N {\displaystyle {\frac {a}{b}}\in \mathbb {Q} \Leftrightarrow a\in \mathbb {Z} ,b\in \mathbb {N} } الرموز في الصيغة Q {\displaystyle \mathbb {Q} } Z {\displaystyle \mathbb {Z}...

Series of Canadian satellites Launch of Anik B1 in December 1978 The Anik satellites are a series of geostationary communications satellites launched for Telesat Canada for television, voice and data in Canada and other parts of the world, from 1972 through 2013. Some of the later satellites in the series remain operational in orbit, while others have been retired to a graveyard orbit. The naming of the satellite was determined by a national contest, and was won by Julie-Frances Czapla of Sai...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (مايو 2019) الهجمات الإلكترونية على سريلانكا هي سلسلة من الهجمات الإلكترونية القوية التي استهدفت 10 مواقع إلكترونية سريلانكا على الأقل وبالتحديد مواقع ملكية عامة تشمل (lk...

Cette page contient des caractères spéciaux ou non latins. S’ils s’affichent mal (▯, ?, etc.), consultez la page d’aide Unicode. Onciale Codex Bezae vers 380-420 (Université de Cambridge). Caractéristiques Direction Gauche à droite Historique Époque IIIe – IXe siècle modifier L’onciale est une graphie particulière des alphabets latin, grec et copte utilisée du IIIe au VIIIe siècle, caractérisé par des liaisons entre les lettres ma...

伊恩·胡禮Ian Wright 個人信息本名 Ian Edward Wright[2]出生日期 (1963-11-03) 1963年11月3日(60歲)[1]出生地點 英国英格蘭伍利奇[1]位置 中鋒職業俱乐部*年份 球隊 出场 (进球)1985 Greenwich Borough(英语:Greenwich Borough F.C.) 1985–1991 水晶宫 225 (90)1991–1998 阿森纳 221 (128)1998–1999 西汉姆联 22 (9)1999 → 诺丁汉森林 (租借) 10 (5)1999–2000 凯尔特人 8 (3)2000 伯恩利 15 (4)�...

Abū Jaʿfar al-Ṭūsī, Shaykh al-Ṭāʾifa (in farsi شیخ توسی; Ṭūs, 996 – Najaf, 2 dicembre 1067), è stato un giurista e teologo persiano sciita duodecimano, fondatore della Ḥawza di Najaf[1]. Noto come sceicco Ṭūsī, Abū Jaʿfar Muḥammad ibn Ḥasan Ṭūsī (in Farsi ابوجعفر محمد بن حسن توسی), era soprannominato Shaykh al-Ṭāʾifa (in arabo شيخ الطائفة), che significa sceicco della branca e fu un importante studioso musu...

東白龍 雅士 基礎情報四股名 白石 雅仁 → 東白龍 雅士本名 白石 雅仁愛称 シラ、ハクリュー生年月日 (1996-04-17) 1996年4月17日(28歳)出身 日本・東京都墨田区身長 182.0cm体重 132.0kgBMI 39.9所属部屋 玉ノ井部屋得意技 突き、押し、叩き成績現在の番付 東十両10枚目最高位 東前頭15枚目生涯戦歴 200勝197敗11休(32場所)幕内戦歴 5勝10敗(1場所)優勝 三段目優勝1回データ初土�...

Città metropolitana di Palermocittà metropolitana Città metropolitana di Palermo – VedutaPalazzo Comitini, sede istituzionale LocalizzazioneStato Italia Regione Sicilia AmministrazioneCapoluogo Palermo Sindaco metropolitanoRoberto Lagalla (UdC) dal 20-6-2022 Data di istituzione4 agosto 2015 TerritorioCoordinatedel capoluogo38°06′56″N 13°21′41″E38°06′56″N, 13°21′41″E (Città metropolitana di Palermo) Superficie5 009,28 km² Abitanti1 1...
