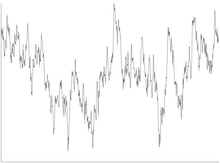
Noise (electronics)
|
Read other articles:

BouleJenisBentuk rotiTempat asalPrancisSunting kotak info • L • BBantuan penggunaan templat ini Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Boule. Boule, dari bahasa Prancis yang berarti bola, adalah bentuk roti Prancis tradisional yang menyerupai bola remas. Bentuk roti ini dapat dibuat dengan tepung jenis apapun. Sebuah boule dapat dikembangkan dengan ragi komersial, pengembang kimia, atau adonan asam ragi liar. Pranala luar How to shape a boule Diarsipkan 2010-09-11 di Wayback Machine. lbsRot...

Fritz PreglLahir(1869-09-03)3 September 1869Laibach, Austria-HungariaMeninggal13 Desember 1930(1930-12-13) (umur 61)Graz, AustriaWarga negaraAustria-Hungaria,kemudian AustriaAlmamaterKarl-Franzens-Universität GrazDikenal atasanalisis mikroelemenPenghargaanNobel Kimia (1923)Karier ilmiahBidangKimia, kedokteranPembimbing doktoralWilhelm OstwaldEmil FischerAlexander Rollett Fritz Pregl (3 September 1869 – 13 Desember 1930) ialah seorang dokter dan kimiawan Austria-Slovenia. Ia memenangk...

Opera by Gian Carlo Menotti The TelephoneComic opera by Gian Carlo MenottiThe composer in 1944LibrettistMenottiLanguageEnglishPremiereFebruary 18, 1947 (1947-02-18)Heckscher Theater, New York City The Telephone, or L'Amour à trois is an English-language comic opera in one act by Gian Carlo Menotti, both words and music. It was written for production by the Ballet Society and was first presented on a double bill with Menotti's The Medium at the Heckscher Theater, New York City,...

Peta wilayah Haag (merah). Haag adalah kota yang terletak di Austria Hilir, Austria. Kota ini memiliki luas sebesar 54.77 km². Kota ini memiliki populasi sebesar 5.310 jiwa. Pranala luar Situs resmi Diarsipkan 2023-08-05 di Wayback Machine. lbsKota di distrik Amstetten Allhartsberg Amstetten Ardagger Aschbach-Markt Behamberg Biberbach Ennsdorf Ernsthofen Ertl Euratsfeld Ferschnitz Haag Haidershofen Hollenstein an der Ybbs Kematen an der Ybbs Neuhofen an der Ybbs Neustadtl an der Donau O...
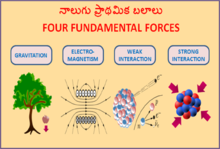
Pour les articles homonymes, voir Interaction. Les 4 forces fondamentales. Quatre interactions élémentaires sont responsables de tous les phénomènes physiques observés dans l'Univers, chacune se manifestant par une force dite force fondamentale. Ce sont l'interaction nucléaire forte, l'interaction électromagnétique, l'interaction faible et l'interaction gravitationnelle. En physique classique, les lois de la gravitation et de l'électromagnétisme étaient considérées comme axiomes...

2004 2011 Élections cantonales de 2008 en Lot-et-Garonne 20 des 40 cantons de Lot-et-Garonne 9 et 16 mars 2008 Type d’élection Élections cantonales Opposition départementale – Pierre Camani Liste PSDVGPCF Sièges obtenus 25 5 Majorité départementale – Michel Diefenbacher Liste UMPDVD Sièges obtenus 15 5 PCF : 1 siège PS : 19 sièges DVD : 5 sièges UMP : 10 sièges Président du Conseil général Sortant Élu Michel Diefe...

Radley MetzgerLahir(1929-01-21)21 Januari 1929[1]New York City, New York, U.S.Meninggal31 Maret 2017(2017-03-31) (umur 88)[2][3][4][5]New York City, New York, U.S.KebangsaanAmericanWarga negaraUnited StatesPendidikanB. A. degree in Dramatic ArtsAlmamaterCity College of New York;Columbia UniversityPekerjaanFilm directorTahun aktif1957–2010sDikenal atasArtistic, adult-oriented films and related works[2][6][7]Karya terk...

This article is about the township near Geelong. For the river in same area, see Little River (Greater Geelong). For other uses, see Little River. Town in Victoria, AustraliaLittle RiverVictoriaLittle RiverCoordinates37°55′59″S 144°30′00″E / 37.933°S 144.500°E / -37.933; 144.500Population1,353 (2021 census)[1]Established1840Postcode(s)3211Elevation22 m (72 ft)Location 44 km (27 mi) from Melbourne 31 km (19 mi) from...

Vaccine against Strep pneumoniae Pneumococcal conjugate vaccinePrevenar 13Vaccine descriptionTargetStreptococcus pneumoniaeVaccine typeConjugateClinical dataTrade namesPrevnar 20, Prevnar 13, Synflorix, others; discontinued Prevnar (PCV7)Other namesPCV, pneumococcal vaccine, capsular polysaccharides[1]AHFS/Drugs.comMonographMedlinePlusa607021License data US DailyMed: Pneumococcal Pregnancycategory AU: B1[2][3][4] Routes ofadministrationIntramuscu...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant l’art et une chronologie ou une date. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Chronologies Données clés 1795 1796 1797 1798 1799 1800 1801Décennies :1760 1770 1780 1790 1800 1810 1820Siècles :XVIe XVIIe XVIIIe XIXe XXeMillénaires :-Ier Ier IIe IIIe Chronologies géographiques Afrique Afrique du S...

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府...

American military general (1937–2023) Robert B. JohnstonBorn(1937-10-06)October 6, 1937Edinburgh, ScotlandDiedOctober 19, 2023(2023-10-19) (aged 86)AllegianceUnited StatesService/branchUnited States Marine CorpsYears of service1961–1995RankLieutenant GeneralCommands heldII Marine Expeditionary ForceMarine Forces EuropeFleet Marine Force, AtlanticCamp PendletonI Marine Expeditionary ForceOfficer Candidates School8th Marine Regiment2nd Battalion, 8th MarinesBattles/warsVietnam War...

Crash Landing on YouPoster promosiHangul사랑의 불시착 GenreKomedi romantis[1]PembuatStudio DragonDitulis olehPark Ji-eunSutradaraLee Jeong-hyoPemeranSon Ye-jinHyun BinKim Jung-hyunSeo Ji-hyeNegara asalKorea SelatanBahasa asliKoreaProduksiLokasi produksiKorea SelatanSwiss[2]Mongolia[3]Rumah produksiStudio DragonCulture DepotDistributortvNRilis asliJaringantvNFormat gambar1080i (HDTV)Format audioDolby DigitalRilis14 Desember 2019 (2019-12-14) –16 Febru...

Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne cite aucune source et peut contenir des informations erronées (signalé en septembre 2021). Si vous disposez d'ouvrages ou d'articles de référence ou si vous connaissez des sites web de qualité traitant du thème abordé ici, merci de compléter l'article en donnant les références utiles à sa vérifiabilité et en les liant à la section « Notes et références ». Trouver des sou...
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (August 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Méribel Ice Palace is an indoor ice hockey arena in Méribel, France. It was built in 1991 and held 8,000 people when it opened. The ice hockey games from the 1992 Winter Olympics were held at this arena. After the Olymp...

Food trucks in New Jersey, United States The Grease trucks at their long time College Avenue location, ending on August 15, 2013 The Grease trucks were a group of food trucks located on the College Avenue Campus of Rutgers University in New Brunswick, New Jersey. They were known for serving, among other things, Fat Sandwiches, a sub roll containing a combination of ingredients such as burgers, cheese, chicken fingers, french fries, falafel, and mozzarella sticks.[1] In August 2004, Ma...

モリブデン酸亜鉛[1] 識別情報 CAS登録番号 13767-32-3 PubChem 16213780 特性 化学式 ZnMoO4 モル質量 225.33 g/mol 外観 白色正方晶結晶 密度 4.3 g/cm3, 固体 融点 900 °C 水への溶解度 不溶 構造 結晶構造 正方晶系 危険性 EU分類 not listed NFPA 704 0 2 0 特記なき場合、データは常温 (25 °C)・常圧 (100 kPa) におけるものである。 モリブデン酸亜鉛(モリブデンさんあえん、英...
هذه المقالة بحاجة لصندوق معلومات. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة صندوق معلومات مخصص إليها. هذه المقالة تحتاج للمزيد من الوصلات للمقالات الأخرى للمساعدة في ترابط مقالات الموسوعة. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة وصلات إلى المقالات المتعلقة بها الموجودة في ال�...

You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in German. (February 2009) Click [show] for important translation instructions. View a machine-translated version of the German article. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the English Wikip...

Geographic region in Europe Northern Germany (‹See Tfd›German: Norddeutschland, pronounced [ˈnɔʁtdɔɪ̯tʃlant] ⓘ) is a linguistic, geographic, socio-cultural and historic region in the northern part of Germany which includes the coastal states of Schleswig-Holstein, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and Lower Saxony and the two city-states Hamburg and Bremen. It contrasts with Southern Germany, Western Germany and Eastern Germany. Language Uerdingen line: ich (I) and ik isogloss North...