Mycosphaerella coffeicola
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
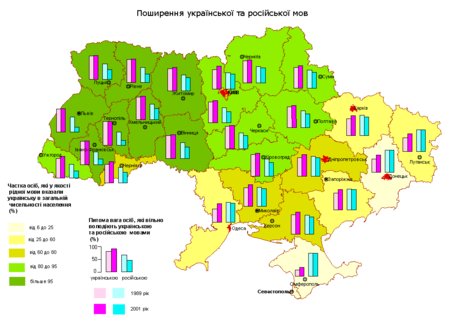
Языки Украины Жёлтый — украинский языкСветло-зелёный, голубой — относительно преобладает украинский Тёмно-зелёный — абсолютно преобладает русский язык Официальные украинский Языки меньшинств армянский, белорусский, болгарский, венгерский, гагаузский, идиш, караимск...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Provincia di Mantova (disambigua). Provincia di Mantovaprovincia Provincia di Mantova – VedutaPalazzo della Cervetta, sede della Provincia LocalizzazioneStato Italia Regione Lombardia AmministrazioneCapoluogoMantova PresidenteCarlo Bottani (lista civica di centro-destra) dal 18-12-2021[1] Data di istituzione1786 TerritorioCoordinatedel capoluogo45°10′N 10°48′E / 45.166667°N 10.8...

Sketsa dari Portugis untuk Isakhar. Suku Isakhar (bahasa Ibrani: שבט יִשָּׂשׁכָר, Modern Shevet Yissakhar Tiberias Šḗḇeṭ Yiśśâḵār; Inggris: Tribe of Issacharcode: en is deprecated ) adalah salah satu dari suku-suku Israel menurut Alkitab Ibrani, keturunan dari Isakhar, anak Yakub. Pembagian tanah suku-suku Israel Wilayah Suku Isakhar menerima daerah kepunyaan mereka berdasarkan undian ke-4 pada zaman Yosua. Daerah mereka ialah Yizreel, Kesulot, Sunem, Hafa...

Special Air ServiceLambang Special Air ServiceAktif22 Juli 1941Negara Britania RayaCabangAngkatan Darat Britania RayaTipe unitPasukan khususPeranOperasi khusus, anti-terorisme, intelijen, pengintaian khusus, aksi langsung, penyelamatan sandera, perang gunungJumlah personel3 Resimen: 21 S.A.S 22 S.A.S 23 S.A.S MarkasHereford, Britania Raya21 S.A.S: London22 S.A.S: Hereford23 S.A.S: BirminghamJulukanBlades, The RegimentMotoWho Dares WinsSiapa yang berani, menang Special Air Service (SAS) a...

تاريخ المهاتفة المرئيةمعلومات عامةالبداية عقد 1920 التأثيراتأحد جوانب مهاتفة فيديوية فرع من تاريخ الاتصالات تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات يغطي تاريخ المهاتفة المرئية التطور التاريخي للعديد من التقنيات التي أتاحت استخدام الفيديو المباشر بالإضافة إلى الاتصالات ال...

v · mGouvernement Lionel Jospin (2 juin 1997 – 6 mai 2002) jusqu'au remaniement du 20 mars 2000 Sous la présidence de Jacques Chirac Emploi et Solidarité Martine Aubry Ministre délégué à la Ville (2) : Claude Bartolone (2) Secrétaire d'État à la Santé puis ministre délégué à la Santé et à la Solidarité (5) : Bernard Kouchner (dém) (8) puis Dominique Gillot (9) Secrétaire d'État à la Formation professionnelle (2) puis s...

Championnats du monde de cyclisme sur route 2018 Généralités Sport Cyclisme sur route Organisateur(s) Union cycliste internationale Édition 85e Lieu(x) Innsbruck Date Du 22 au 30 septembre 2018 Épreuves 12 Navigation Bergen 2017 Yorkshire 2019 modifier Innsbruck Les championnats du monde de cyclisme sur route 2018, quatre-vingt-cinquième édition des championnats du monde de cyclisme sur route, ont lieu du 22 au 30 septembre 2018 à Innsbruck, en Autriche. C'est la troisième fois que ...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant une personnalité américaine. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Pour les articles homonymes, voir Porter. Peter Buell PorterFonctionsSecrétaire à la Guerre des États-Unis23 mai 1828 - 9 mars 1829James BarbourJohn EatonReprésentant des États-UnisNew York's 21st congressional district (en)4 mars 1815 - 23 janvier 1816Samuel M. Hopkins (en)Archibald S...

Loïc Mbe Soh Mbe Soh nel 2019 con la maglia del Paris Saint-Germain Nazionalità Camerun Altezza 187 cm Peso 104 kg Calcio Ruolo Difensore Squadra Almere City Carriera Giovanili 2009-2012 Pontoisienne2012-2013 Courbevoie2013-2018 Paris Saint-Germain Squadre di club1 2018-2019 Paris Saint-Germain 220 (0)2019-2020 Paris Saint-Germain3 (0)2020-2023 Nottingham Forest9 (1)2023→ Guingamp14 (1)2023-→ Almere City0 (0) Nazionale 2016-2017 Francia U-169...

Yanagawa 柳川市Kota BenderaLambangLocation of Yanagawa in Fukuoka PrefectureNegara JepangWilayahKyūshūPrefektur FukuokaPemerintahan • WalikotaKenji KanekoLuas • Total77,2 km2 (298 sq mi)Populasi (Oktober 1, 2015) • Total67.777 • Kepadatan877,9/km2 (22,740/sq mi)Zona waktuUTC+9 (Waktu Standar Jepang)Simbol • PohonSalix• BungaIris ensata Wisteria floribundaAlamatHonmachi 87-1, Yanagawa-shi, Fukuoka-...

Closed United States Air Force General Surveillance Radar station This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (December 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Cambria Air Force Station Part of Air Defense Command (ADC)Cambria AFSLocation of Cambria AFS, CaliforniaCoordinates35°31′20″N 121°03′49″W / 35.52222°N ...

Neanderthal fossil discovered in the early 19th-century in modern day Belgium Engis 2Lateral view of juvenileCommon nameEngis 2SpeciesNeanderthalAge35,350 years (aged c. 3)Place discoveredFlemalle, Liege, BelgiumDate discovered1829Discovered byPhilippe-Charles SchmerlingEngis 2 refers to part of an assemblage, discovered in 1829 by Dutch physician and naturalist Philippe-Charles Schmerling in the lower of the Schmerling Caves. The pieces that make up Engis 2 are a partially preserved calvaria...

Chronologies Données clés 1886 1887 1888 1889 1890 1891 1892Décennies :1850 1860 1870 1880 1890 1900 1910Siècles :XVIIe XVIIIe XIXe XXe XXIeMillénaires :-Ier Ier IIe IIIe Chronologies géographiques Afrique Afrique du Sud, Algérie, Angola, Bénin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroun, Cap-Vert, République centrafricaine, Comores, République du Congo, République démocratique du Congo, Côte d'Ivoire, Djibouti, Égyp...

v · mArmées françaises Révolution française Armée des Alpes composition Armée d'Allemagne Armée d'Angleterre Armée des Ardennes Armée de Belgique Armée du Centre Armée des côtes de Brest Armée des côtes de Cherbourg Armée des côtes de La Rochelle Armée du Danube Armée de Hollande Armée de l'Intérieur Armée d'Italie composition Armée de Mayence Armée du Midi Armée de la Moselle composition Armée de Naples Armée du Nord composition Armée d’Orient Armée de l'...

2005 live album by Grateful DeadDick's Picks Volume 35Live album by Grateful DeadReleasedJune 17, 2005RecordedAugust 7, 1971 August 24, 1971 August 6, 1971GenreRockLength290:56LabelGrateful Dead RecordsGrateful Dead chronology Grateful Dead Download Series Volume 2(2005) Dick's Picks Volume 35(2005) Grateful Dead Download Series Volume 3(2005) Professional ratingsReview scoresSourceRatingAllmusic [1]The Music Box [2]TheBestOfWebsiteB+ [3] Dick's Picks Volume 35...

Charity Shield FA 1912TurnamenCharity Shield FA Blackburn Rovers Queens Park Rangers 2 1 Tanggal4 Mei 1912StadionWhite Hart Lane, LondonPenonton7.100← 1911 1913 → Charity Shield FA 1912 adalah pertandingan sepak bola antara Blackburn Rovers dan Queens Park Rangers yang diselenggarakan pada 4 Mei 1912 di White Hart Lane, London. Pertandingan ini merupakan pertandingan ke-5 dari penyelenggaraan Charity Shield FA. Pertandingan ini dimenangkan oleh Blackburn Rovers dengan skor 2–1.&...

Auto race track in Mexico City, Mexico Autódromo Hermanos RodríguezThe Autódromo Hermanos Rodríguez Grand Prix circuit (2015–2019, 2021–present)The Autódromo Hermanos Rodríguez Formula E circuit (2023)LocationMexico City, MexicoTime zoneUTC−6 / UTC−5 (DST)Coordinates19°24′22″N 99°5′33″W / 19.40611°N 99.09250°W / 19.40611; -99.09250Capacity110,000FIA Grade1 (GP)3E (Formula E)Broke ground1959Opened20 November 1959; 64 years ago ...

سفارة لبنان في المملكة المتحدة لبنان المملكة المتحدة الإحداثيات 51°30′29″N 0°11′31″W / 51.5081°N 0.192083°W / 51.5081; -0.192083 البلد المملكة المتحدة المكان لندن الاختصاص المملكة المتحدة، وجمهورية أيرلندا[1] تعديل مصدري - تعديل سفارة لبنان في المملكة المتحد...

Political party in Eswatini People's United Democratic Movement Insika Yenkhululeko YemaswatiAbbreviationPUDEMOPresidentMlungisi MakhanyaSecretary-GeneralPenuel MalingaFounded7 July 1983 (1983-07-07)Youth wingSwaziland Youth CongressIdeologyDemocratic socialismPolitical positionLeft-wingInternational affiliationProgressive Alliance[1]Socialist International (consultative)Colours Green, Orange, Red and BlackParty flagWebsitewww.pudemo.netPoli...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir NRF. Force de réaction de l'OTAN NATO Response Force (NRF) Emblème de la NRF Création 2002 Allégeance OTAN Type Force multi-nationale Rôle Force de déploiement rapide Effectif 40 000 (300 000+ en état d'alerte) Fait partie de Grand Quartier général des puissances alliées en Europe Garnison JFC Brunssum, Pays-BasJFC Naples, Italie(rotation annuelle) Surnom NRF modifier La Force de réaction de l'OTAN (en anglais : NATO Response ...
