Miklós Wesselényi
| |||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Nuvoton Technology Corp.新唐科技股份有限公司JenisKorporasiIndustriSemikonduktorDidirikan2008KantorpusatHsinchu Science and Industrial Park, TaiwanTokohkunciArthur Yu-Cheng Chiao, PemilikProdukMikrokontroler Aplikasi IC, Audio Aplikasi IC, Clo...

Uppslagsordet ”WHO” leder hit. För andra betydelser, se Who. منظمة الصحة العالمية (arabiska) 世界卫生组织 (kinesiska) World Health Organization (engelska) Organización Mundial de la Salud (spanska) Organisation mondiale de la santé (franska) Всемирная организация здравоохранения (ryska) Världshälsoorganisationens flaggaOrganisationstypfackorganFörkortningarWHOOMSGeneraldirektörTedros Adhanom, Director-General...
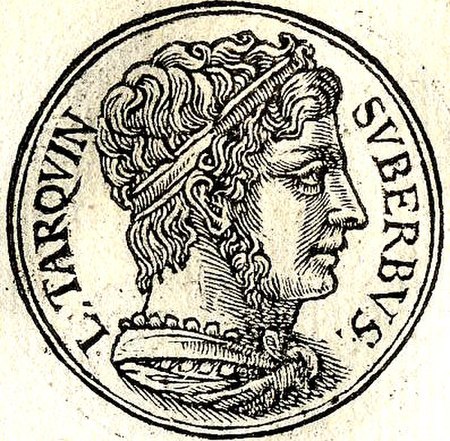

Lucius Tarquinius Superbus Lucius Tarquinius Superbus (tidak diketahui - 496 SM) adalah Raja ketujuh Roma, yang memerintah dari tahun 535 SM sampai terjadi pemberontakan pada tahun 509 SM yang mengarah pada pembentukan Republik Romawi. Dia lebih dikenal dengan nama Tarquinius Superbus dan merupakan bagian dari Dinasti Etruska. Dikatakan bahwa Superbus menjadi raja setelah membunuh raja sebelumnya, Servius Tullius. Ayah Superbus, Lucius Tarquinius Priscus, adalah Raja kelima Roma yang memerint...
PrvaLiga SloveniaBadan yang mengaturAsosiasi Sepak Bola SloveniaNegaraSloveniaKonfederasiUEFADibentuk1991; 33 tahun lalu (1991)Jumlah tim10Tingkat pada piramida1Degradasi ke2. SNLPiala domestikSlovenia CupPiala internasionalUEFA Champions LeagueUEFA Europa Conference LeagueJuara bertahan ligaOlimpija Ljubljana (3 gelar) (2022–23)Klub tersuksesMaribor (16 gelar)Pencetak gol terbanyakMarcos Tavares (159)Televisi penyiarSportklubŠport TVSitus webprvaliga.si 2023–24 Slovenian PrvaLiga P...

Энциклопедия Криворожьяукр. Енциклопедія Криворіжжя Автор сост. В. Ф. Бухтияров Жанр энциклопедия Язык оригинала украинский Оригинал издан 2005 Оформление формат: 60x90 1/8 Издатель Явва Носитель книга ISBN 966-96328-1-1 Внешние изображения Редакция газеты «Червоный го...

1890–91 series of paintings by Claude Monet This article is about a series of paintings by Claude Monet. For the English hill, see Haystacks (Lake District). Wheatstacks (End of Summer)ArtistClaude MonetYear1890–91MediumOil on canvasDimensions60 cm × 100 cm (23+5⁄8 in × 39+3⁄8 in)LocationArt Institute of Chicago, Chicago Haystacks is the common English title for a series of impressionist paintings by Claude Monet. The principal subje...

Eurasia This is a list of the extreme points of Eurasia, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location on the continent. Some of these locations are open to debate, owing to the diverse definitions of Europe and Asia. Mainland Eurasia is entirely located within the northern hemisphere and mostly within the eastern hemisphere, yet it touches the western hemisphere on both extremes. Thus, both the easternmost and westernmost points of Eurasia are in the western...

Province of Thailand Province in ThailandTrat ตราดProvince FlagSealMotto(s): เมืองเกาะครึ่งร้อย พลอยแดงค่าล้ำ ระกำแสนหวาน หลังอานหมาดี ยุทธนาวีเกาะช้าง สุดทางบูรพา (The city of half a hundred islands. Precious rubies. Sweet salacca. Fine Thai ridgeback dogs. The Naval Battle of Ko Chang. The far end in the East.Map of Th...

Railway station in North Yorkshire, England CommondaleGeneral informationLocationCommondale, ScarboroughEnglandCoordinates54°28′52″N 0°58′30″W / 54.4812048°N 0.9749156°W / 54.4812048; -0.9749156Grid referenceNZ665100Owned byNetwork RailManaged byNorthern TrainsPlatforms1Tracks1Other informationStation codeCOMClassificationDfT category F2HistoryOriginal companyNorth Eastern RailwayPre-groupingNorth Eastern RailwayPost-grouping London and North Eastern Railwa...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Halévy. Pour les autres membres de la famille, voir Famille Halévy. Ludovic HalévyLudovic Halévy photographié par Paul Nadar en 1896.FonctionFauteuil 22 de l'Académie française4 décembre 1884 - 7 mai 1908Joseph d’HaussonvilleEugène BrieuxBiographieNaissance 1er janvier 1834Ancien 10e arrondissement de ParisDécès 7 mai 1908 (à 74 ans)1er arrondissement de ParisSépulture Cimetière de MontmartreNationalité françaiseFormation Lycée L...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento guerra è priva o carente di note e riferimenti bibliografici puntuali. Sebbene vi siano una bibliografia e/o dei collegamenti esterni, manca la contestualizzazione delle fonti con note a piè di pagina o altri riferimenti precisi che indichino puntualmente la provenienza delle informazioni. Puoi migliorare questa voce citando le fonti più precisamente. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. 7º Reggimento BersaglieriStemma araldico del R...

For other uses, see Lauriston (disambiguation). Private, single-sex, day school in Armadale, Victoria, AustraliaLauriston Girls' SchoolLocationArmadale, VictoriaAustraliaCoordinates37°51′6″S 145°1′32″E / 37.85167°S 145.02556°E / -37.85167; 145.02556InformationTypeprivate, single-sex, day schoolMottoLatin: Sancte Sapienter Strenue(Holiness, Wisdom, Strength)DenominationNon-denominationalEstablished1901[1]FoundersMargaret and Lilian IrvingChairmanElsp...

For its historical development, see Spherical Earth. For its determination, see Arc measurement. Distance from the Earth surface to a point near its center Earth radiusCross section of Earth's InteriorGeneral informationUnit systemastronomy, geophysicsUnit ofdistanceSymbolR🜨, R E {\displaystyle R_{E}} , R e E N {\displaystyle {\mathcal {R}}_{\mathrm {eE} }^{\mathrm {N} }} Conversions 1 R🜨 in ...... is equal to ... SI base unit 6.3781×...

Cognitive bias Homicide rate in the United States (blue line): it may be seen that the homicide rate today is similar to that of the 1950s, and much lower than it was in the 1970s–80s. Nevertheless, most people imagine crime rates to be worse.[1] Homicide rate in Western Europe since 1300: again, a precipitous decline is seen. Mean world syndrome is a proposed cognitive bias wherein people may perceive the world to be more dangerous than it is. This is due to long-term moderate to h...

For the Mississippi county, see Pontotoc County, Mississippi. For other uses, see Pontotoc (disambiguation). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Pontotoc, Mississippi – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this message) City in Mississippi, United ...

1ª Divisão 1951 Competizione 1ª Divisão Sport hockey su pista Edizione 13ª Organizzatore FPP Date dal 13 maggioal 10 dicembre 1951 Luogo Portogallo Partecipanti 17 Formula Due gironi eliminatori + girone finale Risultati Vincitore Benfica(1º titolo) Retrocessioni Colegio Militar Cronologia della competizione 1950 1952 Manuale La 1ª Divisão 1951 è stata la 13ª edizione del torneo di primo livello del campionato portoghese di hockey su pista. La manifestazio...

Location of Badakhshan, divided between Tajikistan in the north and Afghanistan in the south. Badakhshan is a region of Tajikistan and Afghanistan with a unique musical heritage, especially that of the remote Pamiri Ismailis. Badakhshan's unique folk scene is said to be characteristed by the use of many chromatized tones (especially in falak) in a narrow melodic range, and the use of a characteristic minor-like scale [1]. Instrumentation Lutes are an extremely important part of Badakhshani m...

Questa voce sull'argomento parchi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Giardino di Palazzo Gonzaga-AcerbiUbicazioneStato Italia LocalitàCastel Goffredo IndirizzoPiazza Gonzaga CaratteristicheTipogiardino InaugurazionePrima metà del Cinquecento Aperturanon visitabile IngressiPiazza Gonzaga Luoghi d'interesseLoggia di palazzo Gonzaga-Acerbi RealizzazioneAppaltatoreAloisio Gonzaga Proprietariofamiglia Acerbi Mappa di localizzazione Modi...
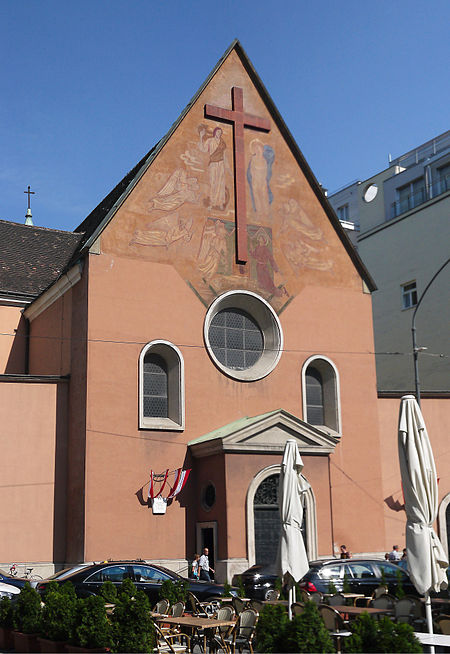

Burial chamber beneath the Capuchin Church and monastery in Vienna, Austria The Capuchin Church in Vienna, Austria, which houses the Imperial Crypt The Imperial Crypt (‹See Tfd›German: Kaisergruft), also called the Capuchin Crypt (Kapuzinergruft), is a burial chamber beneath the Capuchin Church and monastery in Vienna, Austria. It was founded in 1618 and dedicated in 1632, and located on the Neuer Markt square of the Innere Stadt, near the Hofburg Palace. Since 1633, the Imperial Crypt se...

1973 manifesto This article relies excessively on references to primary sources. Please improve this article by adding secondary or tertiary sources. Find sources: Humanist Manifesto II – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Humanist Manifesto II, written in 1973 by humanists Paul Kurtz and Edwin H. Wilson, was an update to the previous Humanist Manifesto published in 1933, and the seco...

