Medical Renaissance
|
Read other articles:

Provinsi Iwami (石見国code: ja is deprecated , iwami no kuni) adalah provinsi lama Jepang yang berada di wilayah yang sekarang menjadi bagian barat prefektur Shimane. Iwami berbatasan dengan provinsi Aki, Bingo, Izumo, Nagato, dan provinsi Suo. Ibu kota berada di kota yang sekarang disebut Hamada. Di zaman Sengoku, wilayah Iwami dikuasai klan Mōri yang berkedudukan di provinsi tetangga Aki. lbsProvinsi lama Jepang Aki Awa (Kanto) Awa (Shikoku) Awaji Bingo Bitchu Bizen Bungo Buzen Chikugo...

RTH Petamanan, Kelurahan Petamanan, Kecamatan Panggungrejo Pada Tahun 2024 Tamanan, Bugulkidul, Pasuruan beralih ke halaman ini. Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Tamanan (disambiguasi). PetamananKelurahanNegara IndonesiaProvinsiJawa TimurKotaPasuruanKecamatanPanggungrejoKode Kemendagri35.75.04.1008 Kode BPS3575031001 Luas... km²Jumlah penduduk... jiwaKepadatan... jiwa/km² Petamanan atau Tamanan adalah sebuah kelurahan di wilayah Kecamatan Panggungrejo, Kota Pasuruan, Provinsi Jawa Timur.[...

Extinct genus of reptiles SinocyamodusTemporal range: Late Triassic (Tuvalian)~232–222 Ma PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N Fossil of Sinocyamodus xinpuensis in the Shandong Tianyu Museum of Nature Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Reptilia Superorder: †Sauropterygia Order: †Placodontia Superfamily: †Cyamodontoidea Genus: †SinocyamodusLi 2000 Type species †Sinocyamodus xinpuensisLi 2000 Sinocyamodus is an extinct genus of plac...

Slamet Suryanto Wali Kota Surakarta ke-15Masa jabatan10 April 2000 – 10 April 2005PresidenAbdurrahman Wahid Megawati Soekarnoputri Susilo Bambang YudhoyonoGubernurMardiyantoWakilJ. Suprapto PendahuluIr. Tedjo Suminto (Pelaksana tugas)PenggantiAnwar Cholil (Pj.) Joko WidodoAnggota Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat Republik IndonesiaMasa jabatan1 Oktober 1999 – 10 April 2000KetuaAkbar Tanjung PenggantiMoehammad OetojoGrup parlemenFraksi Partai Demokrasi Indonesia PerjuanganDaera...
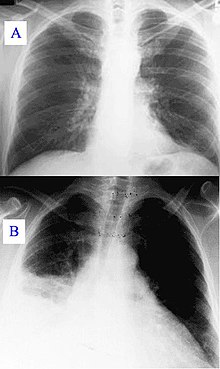
Pneumonia as seen on chest x-ray. A: Normal chest x-ray. B: Abnormal chest x-ray with shadowing from pneumonia in the right lung (left side of image). Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) or nosocomial pneumonia refers to any pneumonia contracted by a patient in a hospital at least 48–72 hours after being admitted. It is thus distinguished from community-acquired pneumonia. It is usually caused by a bacterial infection, rather than a virus.[1][2] Hospital acquired pneumonia is ...

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Bendo. Bendo adalah senjata dan peralatan yang berasal Jawa Indonesia. Di daerah lain ada yang menyamakan bendo dengan golok padahal kedua alat tersebut beda. Perbedaan bendo dan golok adalah bendo lebih pendek daripada golok serta bendo lebih lebar penampangnya daripada golok. Bendo sebenarnya merupakan alat dapur yang biasanya digunakan untuk memotong daging yang bertulang ataupun menggiris benda lain yang membutuhkan tenaga besar. Deskripsi Bendo Arit yang berfun...

Сирия Подробная карта Сирии Континент Евразия (Азия) Регион Ближний Восток Координаты 35°00′ с. ш. 38°00′ в. д.HGЯO Площадь 87-ое место185 180 км² в том числе 1295 км² аннексировано Израилем[1]99,4 % суша0,6 % вода Береговая линия 193 км; Граница 2253 км: с Ира�...

Private Christian school in Addison, Texas, United States The neutrality of this article is disputed. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please do not remove this message until conditions to do so are met. (May 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Trinity Christian AcademyAddress17001 Addison Rd.Addison, Texas 75001United StatesCoordinates32°58′56″N 96°50′16″W / 32.9821°N 96.8377°W / 32.9821; -96.8377InformationSchool t...

Les Jeux de la Lusophonie (en portugais : Jogos da Lusofonia) sont une compétition multisports organisée par l'Association des comités olympiques de langue officielle portugaise (en portugais : Associação dos Comités Olímpicos de Língua Oficial Portuguesa; ACOLOP) créée le 8 juin 2004. Les membres fondateurs de l'ACOLOP sont : l'Angola, le Brésil, le Cap-Vert, la Guinée-Bissau, Macao (Chine), le Mozambique, le Portugal, Sao Tomé-et-Principe et le Timor oriental. Me...

Der Titel dieses Artikels ist mehrdeutig. Weitere Bedeutungen sind unter Iranische Fußballnationalmannschaft (Begriffsklärung) aufgeführt. Iranتیم ملی فوتبال ایران Spitzname(n) Team Melli (Tīm Mellī تیم ملی) Verband Football Federation Islamic Republic of Iran Konföderation AFC Cheftrainer Iran Amir Ghalenoei (seit 2023) Kapitän Ehsan Hajsafi Rekordspieler Javad Nekounam (149) Rekordtorschütze Ali Daei (108) Heimstadion Azadi-Stadion FIFA-Code IRN FIFA-Ran...

土库曼斯坦总统土库曼斯坦国徽土库曼斯坦总统旗現任谢尔达尔·别尔德穆哈梅多夫自2022年3月19日官邸阿什哈巴德总统府(Oguzkhan Presidential Palace)機關所在地阿什哈巴德任命者直接选举任期7年,可连选连任首任萨帕尔穆拉特·尼亚佐夫设立1991年10月27日 土库曼斯坦土库曼斯坦政府与政治 国家政府 土库曼斯坦宪法 国旗 国徽 国歌 立法機關(英语:National Council of Turkmenistan) ...
Le informazioni riportate non sono consigli medici e potrebbero non essere accurate. I contenuti hanno solo fine illustrativo e non sostituiscono il parere medico: leggi le avvertenze. DispareuniaSpecialitàginecologia Classificazione e risorse esterne (EN)ICD-9-CM625.0 ICD-10N94.1 MeSHD004414 Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale La dispareunia (dal greco, dys, cattivo, e pareunos, che giace accanto) è un dolore che la donna avverte nell'area della vagina o della pelvi durante un rappo...

This article uses bare URLs, which are uninformative and vulnerable to link rot. Please consider converting them to full citations to ensure the article remains verifiable and maintains a consistent citation style. Several templates and tools are available to assist in formatting, such as reFill (documentation) and Citation bot (documentation). (August 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Shalom Catholic CommunityComunidade Católica ShalomHeadquarters - Diaconia ShalomAbbreviati...

Military conflict that deploys nuclear weaponry Not to be confused with NukeWar or nukewar (warez). Nuclear War and Nuclear strike redirect here. For other uses, see Nuclear War (disambiguation). Atomic war redirects here. Not to be confused with Atomic Wars. The mushroom cloud over Hiroshima following the detonation of the Little Boy nuclear bomb on 6 August 1945. The atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki remain the first and only wartime uses of nuclear weapons in history. Part of a ser...

日本內閣第三次吉田第一次改造内閣だいさんじよしだだいいちじかいぞうないかく內閣總理大臣吉田茂(第49任)成立日期1950年6月28日總辭日期1951年7月4日執政黨/派系自由黨內閣閣僚名簿(首相官邸) 第三屆吉田首屆改組内閣(日语:第三次吉田第一次改造内閣/だいさんじよしだだいいちじかいぞうないかく Daisanji Yoshida Daiichi Kaizō Naikaku */?)是日本眾議�...

Genus of stick insects Diapheromera Diapheromera arizonensis Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Class: Insecta Order: Phasmatodea Family: Diapheromeridae Subfamily: Diapheromerinae Genus: DiapheromeraGray, 1835 Diapheromera is a genus of stick insects in the family Diapheromeridae. There are about 14 described species in Diapheromera.[1][2][3] Diapheromera arizonensis Species These 14 species belong to the genus Diapheromer...

Tax deduction Part of a series onTaxation An aspect of fiscal policy Policies Government revenue Property tax equalization Tax revenue Non-tax revenue Tax law Tax bracket Flat tax Tax threshold Exemption Credit Deduction Tax shift Tax cut Tax holiday Tax amnesty Tax advantage Tax incentive Tax reform Tax harmonization Tax competition Tax withholding Double taxation Representation Unions Medical savings account Economics General Theory Price effect Excess burden Tax incidence Laffer curve Opti...

Discipline that studies communication across different cultures and social groups See also: Cross-cultural communication This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Intercultural communic...

Railway station in Horonobe, Hokkaido, Japan W70 Minami-Horonobe Station南幌延駅 regional railMinami-Horonobe Station platform in May 2005General informationLocationMinami-horonobe, Horonobe-chō, Teshio-gun, Hokkaidō 098-3200JapanCoordinates44°57′54.9″N 141°53′4.8″E / 44.965250°N 141.884667°E / 44.965250; 141.884667Operated by JR HokkaidoLine(s) Sōya Main LineDistance191.6 km (119.1 mi) from AsahikawaPlatforms1 ...

2024 FireKeepers Casino 400 Race details[1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9] Race 24 of 36 in the 2024 NASCAR Cup Series Date August 18–19, 2024Location Michigan International Speedway in Brooklyn, MichiganCourse Permanent racing facility2.0 mi (3.2 km)Distance 206 laps, 412 mi (663 km)Scheduled Distance 200 laps, 400 mi (640 km)Average speed 135.675 miles per hour (218.348 km/h)Pole positionDriver Denny Hamlin Joe Gibbs Ra...





