Matthias W. Baldwin
| |||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Asado de tira. Asado di Patagonia, Argentina. Asado adalah teknik memotong daging, yang dimasak pada penggorengan (parrilla) atau api terbuka. Asado cukup populer di wilayah Pampa, Amerika Selatan, dan merupakan makanan tradisional Argentina, Chili, Uruguay, dan Paraguay. Asado juga merupakan makanan di Filipina dan berbeda dengan versi Amerika Selatan. Pranala luar Sample recipe from the Australian Broadcasting Corporation[pranala nonaktif permanen] Asado Argentina Learn How to prepa...

Radio station in Reading, PennsylvaniaWRFY-FMReading, PennsylvaniaBroadcast areaBerks CountyFrequency102.5 MHz (HD Radio)BrandingY102ProgrammingLanguage(s)EnglishHD2: Spanish/EnglishFormatAdult contemporarySubchannelsHD2: Tropical music Rumba 92.3OwnershipOwneriHeartMedia, Inc.(iHM Licenses, LLC)Sister stationsWRAWHistoryFirst air dateSeptember 23, 1962Technical information[1]Licensing authorityFCCFacility ID69562ClassBERP10,000 watts (analog)400 watts (digital)[2]HAAT246 mete...

3 جونو المكتشف كارل لودفيج هاردينغ[1] تاريخ الاكتشاف 1 سبتمبر 1804 سمي باسم جونو[2] الأسماء البديلة A804 RA فئةالكوكب الصغير حزام الكويكبات الأوج 3.353164253300355 وحدة فلكية الحضيض 1.985361960880662 وحدة فلكية نصف المحور الرئيسي 2.669263108938305 وحدة فلكية الش...

1969 live album by Charley PrideCharley Pride in PersonLive album by Charley PrideReleasedJanuary 1969VenuePanther Hall, Fort Worth, TexasGenreCountryLabelRCA VictorProducerFelton Jarvis, Jack ClementCharley Pride chronology Songs of Pride...Charley That Is(1968) Charley Pride in Person(1969) The Sensational Charley Pride(1969) Charley Pride in Person is a live album by country music artist Charley Pride. It was recorded at Panther Hall in Fort Worth, Texas, and released on the RCA Vi...

GagamboySutradaraErik MattiProduserRonald Stephen MonteverdeRoselle Monteverde-TeoDitulis olehDwight GastonRoselle Monteverde-TeoPemeranVhong NavarroJay ManaloAubrey MilesSinematograferJ.A. TadenaPenyuntingVito CajiliDistributorMAQ ProductionsRegal EntertainmentTanggal rilis2004Durasi100 minutesBahasaFilipinoPendapatankotor₱17,6 million Gagamboy adalah film FIlipina produksi tahun 2004 bergenre drama fiksi ilmiah komedi laga yang disutradarai oleh Erik Matti dan dibintangi oleh Vhong Navarr...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this article. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Vepr-12 – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) This article is about the Russian shotgun. For the Russian hunting rifle, see Molot Vepr. For the Ukrainian assault ri...

† Египтопитек Реконструкция внешнего вида египтопитека Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:Четвероно...

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁�...
حلوان للأجهزة المعدنية مصنع 360 الحربيالشعارمعلومات عامةالبلد مصرالتأسيس 1964 (منذ 60 سنة)النوع شركة مساهمة حكوميةالمقر الرئيسي حلوان، القاهرةموقع الويب fact360.mompالمنظومة الاقتصاديةالشركة الأم الهيئة القومية للإنتاج الحربيالنشاطات صناعات مدنيةمناطق الخدمة مصرأهم الشخصي...

Defunct radio station in Davao City, Philippines For the television station, see DXAB-TV. DXAB (Radyo Patrol Davao)Radyo Patrol Davao interim logo after May 5 shutdownDavao CityBroadcast areaDavao Region and the surrounding areasFrequency1296 kHzBrandingDXAB Radyo Patrol 1296ProgrammingLanguage(s)Cebuano, FilipinoFormatSilentNetworkRadyo PatrolOwnershipOwnerABS-CBN CorporationSister stationsMOR 101.1 Davao ABS-CBN Channel 4 Davao S+A Channel 21 DavaoHistoryFirst air date1957 (as DXAW) March 1...

Religious phrase in SikhismNot to be confused with Eckankar, the American new religious movement. Ik Onkār,[1] a Sikh symbol (encoded as a single character in Unicode at U+0A74, ੴ)Part of a series on theGuru Granth Sahibਗੁਰੂ ਗ੍ਰੰਥ ਸਾਹਿਬ Popular compositions Ik Onkar Mul Mantar Japji Sahib Anand Sahib Sukhmani Sahib Asa di Var Other compositions Salok Mardana Bhattan De Savaiye Ragamala Sidh Gosti Dakhni Oankar Ramkali Sadu Salok Sahaskriti Mahalla Pehla ...

For the album by Mad at the World, see Flowers in the Rain (album). 1967 single by the MoveFlowers in the RainDutch picture sleeveSingle by the Movefrom the album Move B-side(Here We Go Round) the Lemon TreeReleased25 August 1967Recorded6 July 1967StudioAdvision Sound Studios, LondonGenre Psychedelic pop art pop[1] Length2:29 (original version)2:41 (2007 remastered version)LabelRegal Zonophone (UK)A&M (US)Songwriter(s)Roy WoodProducer(s)Denny CordellThe Move singles chronology I C...

Human history between prehistory and the Medieval period This article is about history from the beginning of writing. For earlier periods, see Prehistory. For other uses, see Ancient history (disambiguation). Ancient and Ancient World redirect here. For the TV series, see The Ancient World (TV series). For other uses, see Ancient (disambiguation). Well-known ancient artworks, each representing a certain civilisation. From left to right: the Standard of Ur (Sumerian), the Mask of Tutankhamun (...

Record label founded in 1899 This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Zonophone – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Universal Talking Machine CompanyCompany typeCorporationIndustryRecording industryFounded1899FounderFrank SeamanDefu...

2007 single by John LegendP.D.A. (We Just Don't Care)Single by John Legendfrom the album Once Again ReleasedFebruary 27, 2007Length4:38Label GOOD Sony Music Songwriter(s) John Stephens Eric Hudson Kawan Prather Jessyca Wilson Producer(s) Eric Hudson Jack Splash John Legend singles chronology Heaven (2006) P.D.A. (We Just Don't Care) (2007) Stereo (2007) P.D.A. (We Just Don't Care) is a song by American singer John Legend, taken from his second studio album, Once Again (2006). It was written b...

Frédéric d'IsenbergTitre de noblesseComteBiographieNaissance 1193Décès 14 novembre 1226ColognePère Arnold d'Altena (en)Mère Mathilde de Stirum (d)Fratrie Thierry III (en)Engelbert I. von Isenberg (en)Bruno d'Isenberg (en)Conjoint Sofia van Limburg (d) (à partir de 1220)Enfants Thierry d'Altena-IsenbergElisabeth von Altena und Isenburg (d)Sophie von Altena-Isenburg (d)Frederik II van Isenberg (d)Agnes von Altena-Isenburg (d)Autres informationsVictimes 1Blasonmodifier - mo...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。 出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: サウンドデザイン – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL (2019年9月) サウンドデザインとは、さまざまなニー�...

رومانو شميد معلومات شخصية الميلاد 27 يناير 2000 (العمر 24 سنة)غراتس الطول 1.68 م (5 قدم 6 بوصة)[1][1] مركز اللعب وسط الجنسية النمسا معلومات النادي النادي الحالي فيردر بريمن الرقم 20 مسيرة الشباب سنوات فريق –2005 Union SV Vasoldsberg 2005–2009 شتورم غراتس المسيرة الاحتراف�...
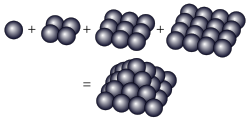
1 + 4 + 9 + 16 = 30 は四角錐数 四角錐数(しかくすいすう、square pyramidal number)は球を右図のように1段目に1個、2段目に4個、3段目に9個、…というように正四角錐の形に積んだとき、そこに含まれる球の総数にあたる自然数である。つまり1から順に平方数をいくつか加えた数のことである。 四角錐数を小さい順に列記すると 1, 5, 14, 30, 55, 91, 140, 204, 285, 385, 506, 650, 819, 1015, 124...

This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (March 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) 2007 studio album by Carmen RasmusenNothin' Like the SummerStudio album by Carmen RasmusenReleasedAugust 14, 2007 (iTunes)August 28, 2007GenreCountryLabelLofton CreekProducerJason Deere Executive producer Gregory S. Ericksen[1]Carmen Rasmuse...




