Lorain Journal Co. v. United States
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

1993 single by Freak Power Turn On, Tune In, Cop OutSingle by Freak Powerfrom the album Drive-Thru Booty B-sideGetting Over the HumpReleased4 October 1993 (1993-10-04)[1]GenreAcid jazzLength4:20LabelIsland, 4th & BroadwaySongwriter(s)Norman CookProducer(s)Norman Cook, Ashley SlaterFreak Power singles chronology Turn On, Tune In, Cop Out (1993) Rush (1994) Turn On, Tune In, Cop Out is a song by Norman Cook's acid jazz group Freak Power, released in October 1993 by Is...

Florence ReedTheatre Magazine, 1921Lahir(1883-01-10)10 Januari 1883Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, A.S.Meninggal21 November 1967(1967-11-21) (umur 84)East Islip, New York, U.S.PekerjaanActressTahun aktif1904-1960Suami/istriMalcolm Williams (1908–1937; hingga wafat)Orang tuaRoland ReedJohanna Sommer ReedIsadore Rush (ibu tiri) Florence Reed (10 Januari 1883 – 21 November 1967) adalah seorang aktris panggung dan film Amerika. Dia dikenang untuk beberapa produksi panggun...

2012 2022 Élections législatives de 2017 en Corse-du-Sud 2 sièges de députés à l'Assemblée nationale 11 et 18 juin 2017 Type d’élection Élections législatives Campagne 22 mai au 10 juin12 juin au 16 juin Débat(s) 2e circonscription : 1er juin sur France 3 Corse[1]1re circonscription : 15 juin organisé par France Bleu RCFM et Corse-Matin[2] Corps électoral et résultats Population 149 234 Inscrits 108 772 Votants au 1er tour 51 609 47,...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Domyoji Line – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Domyoji LineKintetsu 6400 series train crossing the Yamato River on the Domyoji Line, February 2007OverviewLine numberNLocaleOsaka Prefec...

Kegubernuran Wasit Ibu kota Al-Kut Kota terbesar Kepala pemerintah Luas (km²) Populasi (jiwa) Kepadatan (/km²) Bahasa Arab Komposisi etnis Kegubernuran Wasit (Arab: واسط) merupakan sebuah kegubernuran di Irak. Kegubernuran ini terletak di bagian timur di negara itu. Ibu kotanya ialah Al-Kut. Kota besar lainnya ialah Al-Hayy. Hingga 1976 biasanya dipanggil Provinsi Kut. lbsKegubernuran di Irak Al-Anbar Arbīl Bābil Baghdād Al-Basrah Dahūk Dhī Qār Diyālā Al-Karbalā' Maysān An-Na...

Untuk film karya Louis Malle, lihat Murmur of the Heart. Murmur of the HeartsPosterNama lain念念SutradaraSylvia ChangDitulis olehYukihiko KageyamaSylvia ChangPemeranIsabella LeongJoseph ChangLawrence KoAngelica LeePenata musikChen YangSinematograferLeung Ming-kaiPenyuntingChen Po-wenPerusahaanproduksiDream Creek ProductionDistributorApplause Taiwan (Taiwan)Tanggal rilis 10 April 2015 (2015-04-10) (Taiwan) Durasi119 menitNegaraHong KongTaiwanBahasaMandarinPendapatankotor...

1917 Last Russian offensive of WW1 Kerensky offensivePart of the Eastern Front of World War IThe Kerensky offensive and its aftermath.Date1–19 July 1917LocationGalicia, Central EuropeResult Central Powers victoryBelligerents Russia Germany Austria-Hungary Ottoman EmpireCommanders and leaders Aleksei Brusilov Aleksei Gutor Lavr Kornilov Leopold of Bavaria Eduard von Böhm-Ermolli Felix Graf von BothmerUnits involved Southwestern Front 11th Army 7th Army 8th Army // Army Group...

Questa voce sull'argomento ciclisti belgi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Kenny Dehaes Kenny Dehaes nel 2015 Nazionalità Belgio Altezza 188 cm Peso 73 kg Ciclismo Specialità Strada Termine carriera 2019 CarrieraSquadre di club 2005Amuzza.com-Davo2006-2007 Chocolade Jacques2008 Topsport Vlaand.2009 Katusha2009 Silence-Lotto2010-2011 Omega Pharma2012-2015 Lotto2016-2017 Wanty-Gobert2018 WB ...
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会波兰代表團波兰国旗IOC編碼POLNOC波蘭奧林匹克委員會網站olimpijski.pl(英文)(波兰文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員206參賽項目24个大项旗手开幕式:帕维尔·科热尼奥夫斯基(游泳)和马娅·沃什乔夫斯卡(自行车)[1]闭幕式:卡罗利娜·纳亚(皮划艇)&#...
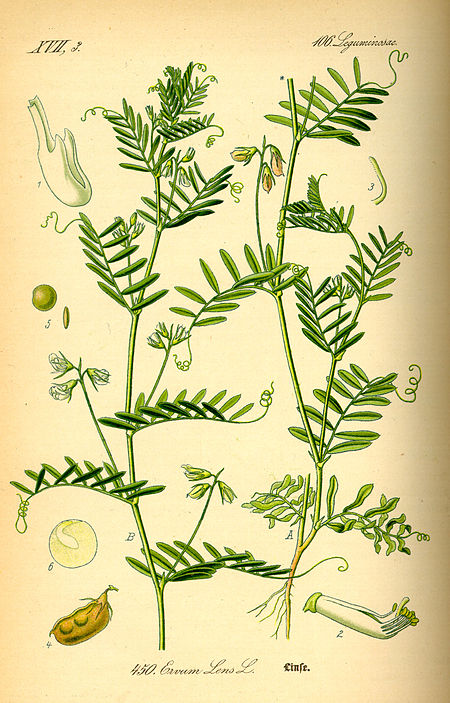
Species of flowering plant with edible seeds in the family Fabaceae This article is about the species Vicia lens. For the meaning of lentil in Indian English, see legume. Lentil Puy (left), green (center), and red (right) lentils Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae Clade: Tracheophytes Clade: Angiosperms Clade: Eudicots Clade: Rosids Order: Fabales Family: Fabaceae Subfamily: Faboideae Genus: Vicia Species: V. lens Binomial name Vicia lens(L.) Coss. & Germ. (1845) Subspecies&#...

Національний науково-природничий музей НАН України 50°26′43″ пн. ш. 30°30′53″ сх. д. / 50.44544722002777348° пн. ш. 30.51489444002777773° сх. д. / 50.44544722002777348; 30.51489444002777773Координати: 50°26′43″ пн. ш. 30°30′53″ сх. д. / 50.44544722002777348° пн. ш. 30.51489444002777773°...

この音とまれ! ジャンル 少年漫画、音楽、学園 漫画 作者 アミュー 出版社 集英社 その他の出版社 青文出版社 掲載誌 ジャンプスクエア レーベル ジャンプ・コミックス 発表号 2012年9月号 - 発表期間 2012年8月4日[1] - 巻数 既刊30巻(2024年2月現在) アニメ 原作 アミュー 監督 水野竜馬 シリーズ構成 久尾歩 脚本 久尾歩 キャラクターデザイン 山中純子 音楽 羽岡�...

Pemilihan umum Parlemen Eropa di Yunani 20142009201925 Mei 2014← Anggota sebelumnyaAnggota terpilih →Seluruh 21 kursi perwakilan Yunani di Parlemen EropaKehadiran pemilih59,97%[1]Kandidat Partai pertama Partai kedua Partai ketiga [[Berkas:|170px]] Ketua Alexis Tsipras Antonis Samaras Nikolaos Michaloliakos Partai Syriza ND XA Aliansi GUE-NGL EPP NI Ketua sejak 9 Februari 2008 30 November 2009 1 November 1993 Pemilu sebelumnya 1 kursi, 4,7...

Memphis GrizzliesStagione 2008-2009Sport pallacanestro Squadra Memphis Grizzlies AllenatoreMarc Iavaroni (fino al 22 gennaio)Johnny Davis (dal 22 al 25 gennaio)Lionel Hollins (dal 25 gennaio) Vice-allenatoriJohnny Davis, Dave Joerger, Ron DuBois (fino al 27 gennaio), Kevin O'Neill (fino al 27 gennaio), Andy Greer (fino al 27 gennaio), Barry Hecker (dal 27 gennaio), Henry Bibby (dal 6 febbraio), Damon Stoudamire (dal 6 febbraio) NBA24-58 (.293)Division: 5º posto (Southwest)Conference: 12...

乌特勒支大学Universiteit Utrecht(荷兰文)Utrecht University(英文)Universitas Rheno-Traiectina(拉丁文)校训Sol Iustitiae Illustra Nos(拉丁文)(正义之阳,光照我心)创办时间1636年,387年前(1636)学校类型公立大学校长Hans Stoof职工人數8,614学生人數32,821校址荷兰乌特勒支隶属欧洲研究型大学联盟世界大學聯盟科英布拉集團歐洲大學協會國際大學協會乌德勒支网络網站http:...

Tập tin:Paris-Philharmonie1.jpgPhilharmonie de Paris Philharmonie de Paris là một thiết chế văn hóa ở Paris, Pháp, chủ yếu dành cho âm nhạc giao hưởng. Nằm trong công viên La Villette ở quận 19, Philharmonie de Paris bao gồm Philharmonie 1, công trình của kiến trúc sư Jean Nouvel khánh thành năm 2015, và Philharmonie 2, tức Cité de la musique, công trình của kiến trúc sư Christian de Portzamparc hoàn thành năm 1995. Philharmonie 1, ...

Variety of Arabic spoken by Upper Egyptians Saʽīdi ArabicUpper Egyptian ArabicصعيدىNative toEgyptRegionAl Minya Governorate and south to Sudan border; Red Sea area; Cairo area[1]EthnicitySa'idisSpeakers25 million (2021)[1]Language familyAfro-Asiatic SemiticWest SemiticCentral SemiticArabicSaʽīdi ArabicWriting systemArabic alphabetLanguage codesISO 639-3aecGlottologsaid1239Linguasphere12-AAC-eb[2][image reference needed]This article contains I...

AcodistrettoMunicipalidad distrital de Aco LocalizzazioneStato Perù Regione Junín ProvinciaConcepción (Perù) AmministrazioneCapoluogoAco Data di istituzione3 de diciembre de 1917 TerritorioCoordinatedel capoluogo11°57′19.22″S 75°23′49.49″W11°57′19.22″S, 75°23′49.49″W (Aco) Altitudine3 480 m s.l.m. Superficie37,8 km² Abitanti2 149 (2005) Densità56,85 ab./km² Altre informazioniLinguespagnolo, quechua Fuso orarioUTC-5 CartografiaAco ...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Gouges et Gouze. Olympe de GougesPortrait de Olympe de Gouges par Alexandre Kucharski (XVIIIe siècle).BiographieNaissance 7 mai 1748MontaubanDécès 3 novembre 1793 (à 45 ans)Paris (Première République française)Nom de naissance Marie GouzePseudonyme Olympe de GougesNationalité françaiseActivités Dramaturge, écrivaine, philosophe, journaliste, femme politiqueConjoint Louis Aubry (d) (à partir de 1765)Enfant Pierre Aubry de Gouges (d)Autre...

تحتاج هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر إضافية لتحسين وثوقيتها. فضلاً ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة بإضافة استشهادات من مصادر موثوق بها. من الممكن التشكيك بالمعلومات غير المنسوبة إلى مصدر وإزالتها. مراصد فضائية وحيز طول الموجة (بالنانومتر) التي تقوم بقياسها. الشكل 2: درجة امتصا�...

