List of unprotected cruisers of Germany
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Classic greyhound racing competition (1928-2019) Horse race Scottish Greyhound DerbyOriginal Classic race (discontinued)Dusty Trail (far left)LocationShawfield StadiumInaugurated1928Last run2019SponsorRacing Post TVRace informationDistance480 metresSurfaceSand The Scottish Greyhound Derby was an original classic greyhound competition held at Shawfield Stadium, held from 1928 to 2019.[1] Held at Carntyne Stadium from 1928 to 1968, after the closure of Carntyne the race appeared at Shaw...

2 Samuel 14Kitab Samuel (Kitab 1 & 2 Samuel) lengkap pada Kodeks Leningrad, dibuat tahun 1008.KitabKitab 1 SamuelKategoriNevi'imBagian Alkitab KristenPerjanjian LamaUrutan dalamKitab Kristen10← pasal 13 pasal 15 → 2 Samuel 14 (atau II Samuel 14, disingkat 2Sam 14) adalah pasal keempat belas Kitab 2 Samuel dalam Alkitab Ibrani dan Perjanjian Lama di Alkitab Kristen. Dalam Alkitab Ibrani termasuk Nabi-nabi Awal atau Nevi'im Rishonim [נביאים ראשונים] dalam bagian Nev...

Wakil Bupati PohuwatoPetahanaHj. Suharsi Igirisa, S.IP., M.Si.sejak 26 Februari 2021Masa jabatan5 tahunDibentuk2005Pejabat pertamaIr. H. Yusuf Giasi Berikut ini adalah daftar Wakil Bupati Pohuwato dari masa ke masa. No Wakil Bupati Mulai Jabatan Akhir Jabatan Prd. Ket. Bupati 1 Ir. H.Yusuf Giasi 2005 2010 1 H.Zainuddin HasanM.B.A. 2 Drs. H.Amin Haras 22 September 2010 22 September 2015 2 H.Syarif MbuingaS.Pd.I., S.E., M.M. Jabatan kosong 22 September 2015 28 September 2015 ...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Myerson. Roger Myerson Roger Myerson Données clés Naissance 29 mars 1951 (73 ans)Boston ( États-Unis) Nationalité américaine Données clés Domaines Économie Institutions Université de Chicago Diplôme Université Harvard Renommé pour Théorie des mécanismes d'incitation Distinctions Prix de la Banque de Suède en sciences économiques en mémoire d'Alfred Nobel(2007) modifier Roger Myerson (né le 29 mars 1951 à Boston) est un économiste am�...

Capital of the Special Region of Yogyakarta, Indonesia This article is about the city. For the province, see Special Region of Yogyakarta. For other uses, see Yogyakarta (disambiguation). Special region capital in Java, IndonesiaYogyakarta JogjaSpecial region capitalCity of YogyakartaKota YogyakartaRegional transcription(s) • JavaneseꦔꦪꦺꦴꦒꦾꦏꦂꦠNgayogyakartaTugu YogyakartaKraton Ngayogyakarta HadiningratTaman Sari Water CastleSouthern Alun-alun of YogyakartaGe...

Song first recorded by James Beale Street Clark in 1945 Get Ready to Meet Your ManSingle by James Beale Street ClarkB-sideLove Me or Let Me BeReleased1945 (1945)RecordedOctober 24, 1945GenreBluesLabelColumbiaSongwriter(s)James Clark Look on Yonder Wall (or Look over Yonders Wall; originally titled Get Ready to Meet Your Man) is a blues song first recorded in 1945 by James Beale Street Clark. Clark, also known as Memphis Jimmy, was a blues pianist from Memphis, Tennessee. During the 1940s...

Historic cave Organ CaveThe main historical (and commercial) entrance to Organ CaveOrgan CaveLocation of Organ Cave in West VirginiaFloor elevation2,188 ft (667 m)Length38.452 miles (61.882 km)GeographyLocationUnited States, West Virginia, GreenbrierCoordinates37°43′05″N 80°26′13″W / 37.71806°N 80.43694°W / 37.71806; -80.43694 The eponymous organ formation in Organ Cave Salt petre vats in Organ Cave Organ Cave is a large and historic c...

Ballybofey Bealach FéichKotaBallybofeyLokasi di IrlandiaKoordinat: 54°48′00″N 7°47′24″W / 54.8°N 7.790°W / 54.8; -7.790Koordinat: 54°48′00″N 7°47′24″W / 54.8°N 7.790°W / 54.8; -7.790NegaraIrlandiaProvinsiUlsterCountyCounty DonegalKetinggian30 m (100 ft)Populasi (2016)[1]4.852Zona waktuUTC+0 (WET) • Musim panas (DST)UTC+1 (IST (WEST))Situs webballybofeystranorlar.com Ballybofey ialah seb...

Snowboarding event at the 2022 Winter Olympics Women's halfpipeat the XXIV Olympic Winter GamesSnowboardingVenueGenting Snow Park,ZhangjiakouDate9 February (qualification) 10 February (final)Competitors22 from 12 nationsWinning score94.00Medalists Chloe Kim United States Queralt Castellet Spain Sena Tomita Japan← 20182026 → Snowboarding at the2022 Winter OlympicsQualification Big airmenwomenHalfpipemenwomenParallel giant slalommenwomenSlopesty...
Zaque MichuázaqueMichuá, ruler of HunzaReign1470–1490PredecessorHunzahúaSuccessorQuemuenchatochaBornunknownMuisca ConfederationDied1490Chocontá,Muisca ConfederationDynastyHunza Michuá or Michica[1] (died Chocontá, 1490) was the second zaque of Hunza, currently known as Tunja, as of 1470. His contemporary enemy zipa of the southern Muisca was Saguamanchica. Biography Little is known about the history of Michuá, who accessed the throne of the northern Muisca in 1470. He broke t...

British television and radio presenter Ore OdubaOduba in 2018Born (1985-11-17) 17 November 1985 (age 38)London, EnglandOccupationPresenterNotable credit(s)NewsroundBBC SportClaimed and ShamedMatch of the Day KickaboutThe One ShowThe National Lottery DrawsStrictly Come DancingAnd They're Off!HardballNoughts + CrossesSpouse Portia Oduba (m. 2015)Children2Websitehttp://oreodubaofficial.com Ore Oduba (born 17 November 1985)[1][2][3] is a...

In intertidal reef-flat environments, massive Porites form characteristic microatoll formations, with living coral around the perimeter and dead skeleton on the exposed upper surface.[1] A microatoll is a circular colony of coral, dead on the top but living around the perimeter. Growth is mainly lateral, as upward growth is limited by exposure to air. Microatolls may be up to 6 meters (20 ft) in diameter.[2] They are named for their resemblance to island atolls formed dur...

Railway station in Pruszków, Poland PruszkówGeneral informationLocationPruszków, MasovianPolandCoordinates52°10′05″N 20°47′55″E / 52.16806°N 20.79861°E / 52.16806; 20.79861Owned byPolskie Koleje Państwowe S.A.Platforms1Tracks2HistoryOpened1845Services Preceding station KM Following station Parzniewtowards Skierniewice R1 Piastówtowards Warszawa Wschodnia or Warszawa Główna Preceding station SKM Following station Terminus S1 Piastówtowards Otwock or ...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Западный округ. Западный внутригородской округ город Краснодар Дата основания 1936 год Дата упразднения 1994 Прежние имена Кагановичский, Ленинский районы Микрорайоны Дубинка, Черёмушки, Покровка Площадь 22[1] км² Насе...

Mathematician (c. 940-1000) Reproduction of Millī MS 867 fol. 7r, showing his discovery of the law of refraction (from Rashed, 1990). The lower part of the figure shows a representation of a plano-convex lens (at the right) and its principal axis (the intersecting horizontal line). The curvature of the convex part of the lens brings all rays parallel to the horizontal axis (and approaching the lens from the right) to a focal point on the axis at the left. Interpretation of Ibn Sahl's constru...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (مارس 2021) التاميل ضد الإبادة الجماعيةالتاريخالتأسيس 2008 الإطارالنوع منظمة البلد الولايات المتحدة تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات التاميل ضد الإبادة الجماعي�...
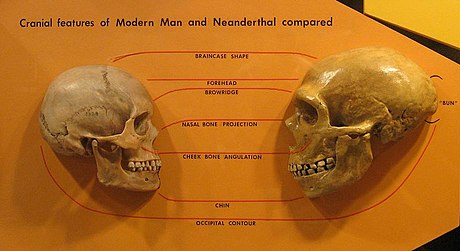
Homo rhodesiensis Broken Hill Cranium: berumur sekitar 130.000 tahun lalu (menggunakan determinasi asam amino racemization) atau 800.000 sampai 600.000 tahun lalu (pada waktu yang sama dengan Homo erectus), bergantung kepada metode pengukuran yang digunakan. Sejumlah keberagaman dari Homo dikelompokkan menjadi kategori yang lebih luas yaitu Manusia Purba, berlawanan dengan manusia modern (Homo sapiens), pada periode dimulai dari 500.000 tahun lalu. Kategori-kategori tersebut biasanya mengikut...

British writer This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Edward Upward – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Edward UpwardUpward c. 1938Born(1903-09-09)9 September 1903Romford, Essex, EnglandDied13 February 2009(2009-02-13) (aged 1...

بريان إدواردز معلومات شخصية الميلاد 27 أكتوبر 1930 تاريخ الوفاة 21 يونيو 2016 (85 سنة) مركز اللعب وسط الجنسية المملكة المتحدة المسيرة الاحترافية1 سنوات فريق م. (هـ.) 1947–1965 بولتون واندررز 483 (8) الفرق التي دربها 1971–1975 برادفورد سيتي 1 عدد مرات الظهور مع الأندية وعدد الأهداف ...

Lesbian feminist literary magazine ConditionsThe Black Women's Issue, November 1979FrequencyBiannual (1976 - 1980)Annual (1980 - 1990)FounderElly BulkinJan ClausenIrena KlepfiszRima ShoreFirst issue1976Final issue1990CountryUnited StatesBased inBrooklyn, New YorkLanguageEnglishISSN2381-5620OCLC646884046 Conditions (full title: Conditions: a feminist magazine of writing by women with a particular emphasis on writing by lesbians) was a lesbian feminist literary magazine that came out biannually...



