Law of Bangladesh
|
Read other articles:

Aras Tammauni Bupati Mamuju Tengah ke-1PetahanaMulai menjabat 26 Februari 2021Masa jabatan17 Februari 2016 – 17 Februari 2021PresidenJoko WidodoGubernurAnwar Adnan Saleh Ismail Zainuddin (Plh.) Carlo Brix Tewu (Pj.) Ali Baal Masdar Akmal Malik (Pj.) Zudan Arif Fakrulloh (Pj.)WakilMuhammad Amin Jasa PendahuluIsmail ZainuddinPenggantiPetahana Informasi pribadiLahir31 Desember 1956 (umur 67)Topoyo, SulawesiPartai politikDemokrat (-2019) Golkar (2020-sekarang)Suami/istriNa...

Property law The examples and perspective in this article deal primarily with United States and do not represent a worldwide view of the subject. You may improve this article, discuss the issue on the talk page, or create a new article, as appropriate. (October 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Property law Part of the common law series Types Personal property Community property Real property Unowned property Acquisition Gift Adverse possession Deed Conquest Discovery...

Mountain range of the Transverse Ranges in California, United States San Bernardino MountainsThe San Bernardinos seen from near Sugarloaf MountainHighest pointPeakSan Gorgonio MountainElevation11,503 ft (3,506 m)[1]Coordinates34°05′57″N 116°49′29″W / 34.09917°N 116.82472°W / 34.09917; -116.82472DimensionsLength60 mi (97 km)Width41 mi (66 km)Area2,063 sq mi (5,340 km2)[2]Geography CountryUnite...

Fifth edition of the Laver Cup, a men's tennis tournament Tennis tournament2022 Laver CupDate23–25 September 2022Edition5thSurfaceHard (indoor)LocationLondon, EnglandVenueThe O2 ArenaChampionsTeam World 13 – 8 ← 2021 · Laver Cup · 2023 → The 2022 Laver Cup was the fifth edition of the Laver Cup, a men's tennis tournament between teams from Europe and the rest of the world. It was held on an indoor hard court at The O2 Arena in London, England ...

Garches - Marnes-la-Coquette Le bâtiment voyageurs de la gare. Localisation Pays France Commune Garches Adresse Place de la Gare92380 Garches Coordonnées géographiques 48° 50′ 18″ nord, 2° 11′ 14″ est Gestion et exploitation Propriétaire SNCF Exploitant SNCF Code UIC 87382259 Site Internet La gare de Garches - Marnes-la-Coquette, sur le site officiel de SNCF Gares & Connexions Service Caractéristiques Ligne(s) Saint-Cloud à Saint-Nom-...

Hendrick Automotive GroupIndustriRitel otomotifDidirikanCharlotte, North Carolina, AS (1976 (1976))[1]PendiriRick HendrickKantorpusatCharlotte, North Carolina, Amerika SerikatWilayah operasiASJasaPenjualan mobil dan asuransi mobilDivisiHendrick MotorsportsSitus webhttp://www.hendrickauto.com/ Hendrick Automotive Group merupakan sebuah perusahaan swasta Amerika Serikat yang didirikan dan dikembangkan oleh Rick Hendrick sejak tahun 1976. Pada awalnya perusahaan ini hanya bergerak d...

Contea di GlasscockconteaContea di Glasscock – VedutaTribunale della contea di Glasscock, situato a Garden City LocalizzazioneStato Stati Uniti Stato federato Texas AmministrazioneCapoluogoGarden City Data di istituzione1889 TerritorioCoordinatedel capoluogo31°52′12″N 101°31′48″W / 31.87°N 101.53°W31.87; -101.53 (Contea di Glasscock)Coordinate: 31°52′12″N 101°31′48″W / 31.87°N 101.53°W31.87; -101.53 (Contea di Glasscock)...
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会科索沃代表團科索沃国旗IOC編碼KOSNOC科索沃奧林匹克委員會網站www.noc-kosovo.org(英文)(阿爾巴尼亞文)(塞爾維亞文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員11參賽項目6个大项旗手开幕式:阿基爾·賈科瓦(英语:Akil Gjakova)和瑪琳達·開爾門蒂(柔道)[1]闭幕式�...

Hotel Tokyo DisneySea MiraCostaInformasi umumLokasiTokyo Disney ResortManajemenThe Oriental Land CompanyInformasi lainJumlah kamar502Situs webhttp://www.disneyhotels.jp/dhm/index_e.html Tokyo Disney Resort Tokyo Disneyland Tokyo DisneySea Ikspiari Bon Voyage! Hotel Disney Hotel Disney Ambassador Hotel Tokyo DisneySea MiraCosta Hotel Tokyo Disneyland The Oriental Land Company Hotel Tokyo DisneySea MiraCosta adalah hotel kedua yang dibangun di Tokyo Disney Resort di Urayasu, Chiba, Jepang. Hote...
Road in Malaysia Negeri Sembilan Route 9Major junctionsNorth endPedasMajor intersections FT 1 Federal Route 1 North–South Expressway Southern Route AH2 North–South Expressway Southern Route FT 5 Federal Route 5South endLinggi LocationCountryMalaysiaPrimarydestinationsRembau, Rantau, Seremban, Port Dickson Highway system Highways in Malaysia Expressways Federal State Jalan Pedas–Linggi (Negeri Sembilan state route N9) is a major road in Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia.[1] It ...
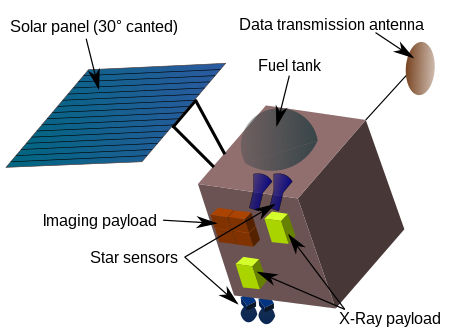
Chandrayaan-1OperatorOrganisasi Penelitian Ruang Angkasa IndiaTanggal perluncuran22 Oktober 2008 dari Sriharikota, IndiaWahana peluncurPSLV-XL / PSLV-C11) (versi modifikasi dari PSLV)Durasi misi2 tahunID COSPARCHANDRYN1Situs webChandrayaan-1Berat523 kgOrbital elementsEksentrisitashampir sirkulerInklinasikutubApoapsisawal 7500 km, final 100Periapsisawal 500 km, final 100 km Untuk rencana misi 2009, lihat Chandrayaan II. Chandrayaan-1 ( Sanskerta: चंद्रयान-1 )[1] ada...

1997 Indian filmDahanDVD coverDirected byRituparno GhoshWritten bySuchitra Bhattacharya (story) Rituparno Ghosh (screenplay)StarringShakuntala BaruaAbhishek ChatterjeeIndrani HalderSubhendu ChatterjeeAditi ChatterjeeRituparna SenguptaSuchitra MitraEdited byArghyakamal MitraRelease date 1997 (1997) Running time145 minutesCountryIndiaLanguageBengali Dahan (Crossfire) (1997) is an Indian Bengali social drama film directed by Rituparno Ghosh.[1][2] The film is based on Suchi...

「カタランの定数」とは異なります。 初等組合せ論におけるカタラン数(カタランすう、英: Catalan number)は、ベルギーの数学者ウジェーヌ・カタランに因んで名付けられた自然数のクラスである。n番目のカタラン数 Cn は C n = 1 n + 1 ( 2 n n ) = ( 2 n ) ! ( n + 1 ) ! n ! ( n ≥ 0 ) {\displaystyle C_{n}={\frac {1}{n+1}}{2n \choose n}={\frac {(2n)!}{(n+1)!\,n!}}\quad (n\geq 0)} で表される[1]�...

1908 U.S. law that protects and compensates railroaders injured on the job Part of a series onRail transport History Company types Infrastructure Management Rail yard Railway station list Railway track Maintenance Track gauge Variable gauge Gauge conversion Dual gauge Service and rolling stock Operating Locomotives Steam locomotives Trains Railroad cars Railway couplings Couplers by country Coupler conversion Dual coupling Wheelset Bogie (truck) Passenger train Commuter rail Regional rail Int...

Mosque in Sachsenhausen, Frankfurt, Germany Noor MosqueNuur-MoscheeReligionAffiliationAhmadiyyaLocationLocationSachsenhausen, Frankfurt, GermanyShown within Frankfurt am MainGeographic coordinates50°05′08″N 8°41′47″E / 50.08556°N 8.69639°E / 50.08556; 8.69639ArchitectureTypemosqueCompleted1959SpecificationsCapacity125 worshippersMinaret(s)2Minaret height5-8 metersWebsitehttp://nuur-moschee.de/ The Noor Mosque (German: Nuur-Moschee; Urdu: مسجدِ نور) ...

Politics of Samoa Constitution Executive O le Ao o le Malo (head of state) Tuimalealiʻifano Vaʻaletoʻa Sualauvi II Council of Deputies Prime Minister Fiamē Naomi Mataʻafa Deputy Prime Minister Tuala Iosefo Ponifasio Cabinet Ministries Legislative Legislative Assembly Speaker: Papali’i Li’o Taeu Masipau Members Judiciary Court of Appeal of Samoa Supreme Court Chief Justice: Satiu Simativa Perese Elections Recent elections General: 201120162021Next Political parties Administrative div...

National convention centre situated in the Dublin Docklands Not to be confused with Dublin Convention. Convention Centre DublinIonad Comhdhála, Baile Átha CliathGeneral informationArchitectural styleModernAddressSpencer Dock, North Wall Quay, Dublin 1, D01 T1W6Town or cityDublinCountry IrelandCoordinates53°20′53.412″N 6°14′21.561″W / 53.34817000°N 6.23932250°W / 53.34817000; -6.23932250Construction started1998Completed5 May 2010; 14 year...

For other uses, see Point Pleasant. City in West Virginia, United StatesPoint Pleasant, West VirginiaCityPoint Pleasant (foreground) at the confluence of the Kanawha and Ohio Rivers. Gallipolis, Ohio is in the background right while Henderson, West Virginia is on the left. FlagLocation of Point Pleasant in Mason County, West Virginia.Coordinates: 38°51′27″N 82°7′43″W / 38.85750°N 82.12861°W / 38.85750; -82.12861CountryUnited StatesStateWest VirginiaCountyMa...

Kolyaposter filmSutradaraJan SvěrákProduserEric AbrahamJan SvěrákDitulis olehZdeněk SvěrákPemeranZdeněk SvěrákAndrey Khalimon (Andrej Chalimon)Libuše ŠafránkováPenata musikOndřej SoukupBedřich SmetanaSinematograferVladimír SmutnýPenyuntingAlois FišárekDistributorSpace FilmsTanggal rilisMei 1996 (tayang perdana di Cannes)15 Mei 1996 (Republik Ceko)24 Januari 1997(A.S.)3 April 1997 (Australia)9 Mei 1997 (Britania Raya)Durasi105 menitNegaraRepublik CekoBahasaCeko, Slowa...

Coppa centroamericanaSport Calcio TipoSquadre nazionali FederazioneUNCAF ContinenteCentro America OrganizzatoreUnione calcistica del Centro America TitoloCampione del Centro America CadenzaBiennale Partecipanti7 FormulaDue gironi all'italiana, semifinali, finale. Sito Internethttp://uncaf.net/ StoriaFondazione1991 Soppressione2017 Detentore Honduras Record vittorie Costa Rica (8) Ultima edizionePanama 2017 Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale La Coppa centroamericana (in spagnolo Copa Ce...



