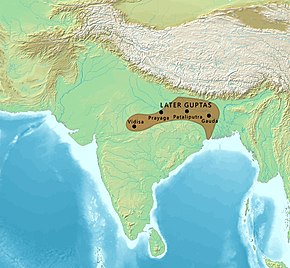
Later Gupta dynasty
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Chronologies Données clés 1723 1724 1725 1726 1727 1728 1729Décennies :1690 1700 1710 1720 1730 1740 1750Siècles :XVIe XVIIe XVIIIe XIXe XXeMillénaires :-Ier Ier IIe IIIe Chronologies thématiques Art Architecture, Arts plastiques (Dessin, Gravure, Peinture et Sculpture), Littérature, Musique classique et Théâtre Ingénierie (), Architecture et () Politique Droit Religion (,) Science Santé et ...

Ilustrasi Gustave Doré dari fabel tersebut, yang terbit pada 1880 Elang dan Merpati adalah sebuah fabel Jean de la Fontaine[1] yang diadaptasi dari sebuah karya Latin asli buatan Laurentius Abstemius,[2] berjudul De acciptribus inter se inimicis quos columbae pacaverant (Para elang yang bertikai didamaikan oleh para merpati). Abstemius mengisahkan bagaimana para merpati memutuskan untuk mengakhiri pertikaian antar para elang, yang malah hanya membuat mereka menjadi burung pem...

Island in the Tuscan Archipelago in the Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy For the island in the Tremiti Islands, off the Adriatic coast in the Apulia, see Tremiti Islands. 42°34′56″N 10°04′42″E / 42.58222°N 10.07833°E / 42.58222; 10.07833 Pianosa IslandNative name: Isola di PianosaThe harbour of PianosaPianosa IslandGeographyLocationTyrrhenian SeaArchipelagoTuscan ArchipelagoArea10.25 km2 (3.96 sq mi)Length5.8 km (3.6 mi)Width4.8 km (2.98&...

Republik Islam Pakistanاسلامی جمہوریۂ پاکستان Islāmī Jumhūriyah-yi Pākistān (Urdu) Islamic Republic of Pakistan (Inggris) Bendera Lambang Semboyan: ایمان، اتحاد، نظم (Urdu) Īmān, Ittiḥād, Naẓm (Indonesia: Iman, Persatuan, Disiplin)Lagu kebangsaan: قومی ترانہ پاکستان (Urdu) Qaumī Tarānah Pākistān (Indonesia: Himne Nasional Pakistan) Perlihatkan BumiPerlihatkan peta Bendera Ibu kotaIslamabad33°41′N 73°4′E...
Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Malawi (disambigua). Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento Malawi non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Malawi (dettagli) (dettagli) (EN) Unity and Freedom(IT) Unità e Libertà Malawi - Localizzazione Dati amministrativiNome completoRepubblica di Malawi Nome ufficiale(NY) Dziko la Mal...

Ancient Egyptian solar goddess Raet / Raet-TawyPtolemaic statue of Raet discovered at Medamud, on display at the Louvre Museum.Name in hieroglyphs Major cult centerMedamud, el Tod, ThebesConsortMontu Part of a series onAncient Egyptian religion Beliefs Afterlife Cosmology Duat Ma'at Mythology Index Numerology Philosophy Soul Practices Funerals Offerings: Offering formula Temples Priestess of Hathor Pyramids Deities (list)Ogdoad Amun Amunet Hauhet Heh Kauket Kek Naunet Nu Ennead Atum Geb Isis ...

1992 single by the Cranberries DreamsArtwork for 1994 European rerelease (UK CD1 single pictured)Single by the Cranberriesfrom the album Everybody Else Is Doing It, So Why Can't We? B-side What You Were Liar Released28 September 1992 (1992-09-28)[1]Genre Alternative rock dream pop[2][3] Length 4:32 (album version) 4:15 (UK radio edit) 4:02 (US radio edit) LabelIslandSongwriter(s)Dolores O'Riordan, Noel HoganProducer(s)Stephen StreetThe Cranberries single...

Esercito popolare di liberazione della Jugoslavia Esercito di Liberazione nazionale e distaccamenti partigiani di Jugoslavia Partigiani jugoslaviBandiera dei partigiani dal 1942 Descrizione generaleAttiva1941 - 1945 Nazione Jugoslavia Federale Democratica Servizio Partito Comunista di Jugoslavia TipoPartigiani Obiettivo Liberazione dei Balcani dalle potenze dell'Asse e dai loro paesi satelliti Instaurazione di una repubblica socialista Dimensione800.000 uomini MottoMorte al fascismo, libertà...

Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori svizzeri è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Battista Rezzonico Nazionalità Svizzera Calcio Ruolo Difensore Carriera Squadre di club1 1926-1928 Lugano? (?) Nazionale 1927-1928 Svizzera2 (0) 1 I due numeri indicano le presenze e le reti segnate, per le sole partite di campionato.Il simbolo → indica un trasferimento in prestito. Modif...

Ancient Egyptian script This article is about the Egyptian script. For the later phase of the Egyptian language, see Egyptian language § Demotic. DemoticDemotic script on a Rosetta Stone replicaScript type Logographic with consonantsTime periodc. 650 BC – 5th century ADDirectionRight-to-leftLanguagesEgyptian language (Demotic)Related scriptsParent systemsEgyptian hieroglyphsHieraticDemoticChild systemsMeroitic, Coptic (influenced)ISO 15924ISO 15924Egyd (070), Egyptian dem...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi WWF (disambigua). World Wide Fund for Nature AbbreviazioneWWF Fondazione29 aprile 1961 FondatoreJulian HuxleyBernardo dei Paesi BassiFilippo d'EdimburgoEdward Max NicholsonPeter Scott ScopoConservazione della natura Sede centrale Gland Presidente Pavan Sukhdev Sito web Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Il World Wide Fund for Nature, in precedenza denominato World Wildlife Fund e comunemente abbreviato con l'acronimo WWF, è...

Навчально-науковий інститут інноваційних освітніх технологій Західноукраїнського національного університету Герб навчально-наукового інституту інноваційних освітніх технологій ЗУНУ Скорочена назва ННІІОТ ЗУНУ Основні дані Засновано 2013 Заклад Західноукраїнський �...

Raymond McKeeMotion Picture Magazine, 1915LahirEldon Raymond McKee(1892-12-07)7 Desember 1892Keokuk, Iowa, Amerika SerikatMeninggal3 Oktober 1984(1984-10-03) (umur 91)Long Beach, California, Amerika SerikatNama lainRoy McKeePekerjaanPemeranTahun aktif1912–1935Suami/istriMarguerite Courtot (m. 1923) Eldon Raymond McKee (7 Desember 1892 – 3 Oktober 1984), juga disebut sebagai Roy McKee, adalah seorang pemeran panggung dan layar le...

Aspect of daylight saving time Facsimile of the original issue of the Czechoslovak public journal with the act 212/1946 Sb. and the government ordinance 213/1946 Sb. Winter time is the practice of shifting the clock behind the standard time during winter months, usually −1 hour. It is a form of daylight saving time in which standard time is in effect during summer months, rather than the usual case where standard time is in effect during winter months. However, while summer time is widely a...

County in Illinois, United States Not to be confused with Henry County, Illinois. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: McHenry County, Illinois – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this message) County in IllinoisMcHenry CountyCountyOld McHenry Cou...

United States historic placeManitou Springs Historic DistrictU.S. National Register of Historic PlacesU.S. Historic district Shoshone Spring, Manitou AvenueShow map of ColoradoShow map of the United StatesLocationManitou Springs, ColoradoCoordinates38°51′28″N 104°55′14″W / 38.85778°N 104.92056°W / 38.85778; -104.92056NRHP reference No.83003516Added to NRHP1983[1] Manitou Springs, Colorado Manitou Springs Historic DistrictFirst Congregatio...

1946 film Somewhere in BerlinFilm posterDirected byGerhard LamprechtWritten byGerhard LamprechtStarringCharles Brauer, Hans Trinkaus, Siegfried Utecht, Harry Hindemith, Hedda SarnowCinematographyWerner KrienMusic byErich EineggRelease date 1946 (1946) Running time85 minutesCountryGermanyLanguageGerman Somewhere in Berlin (German: Irgendwo in Berlin) is a film produced in the Soviet occupation zone of Allied-occupied Germany, the area that later became East Germany. It was released in 194...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (فبراير 2016) المجموعة 5 من تصفيات بطولة أمم أوروبا لكرة القدم للسيدات 2013 هي واحدة من المجموعات التأهيلية لبطولة أمم أو...

الجماليةمعلومات عامةالبداية عقد 1870[1] البلد المملكة المتحدة لبريطانيا العظمى وأيرلندا[1] تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات الجمالية -أيضًا تُعرف بالحركة الجمالية- هي حركة فكرية وفنية تهدف إلى التركيز على القيم الجمالية أكثر من الموضوعات الاجتماعية السياسية ل�...

1970 studio album by Charles KynardAfro-DisiacStudio album by Charles KynardReleased1970RecordedApril 6, 1970StudioVan Gelder Studio, Englewood Cliffs, New JerseyGenreJazzLength38:54LabelPrestigePR 7796ProducerBob PorterCharles Kynard chronology Reelin' with the Feelin'(1970) Afro-Disiac(1970) Wa-Tu-Wa-Zui (Beautiful People)(1970) Afro-Disiac is an album by organist Charles Kynard which was recorded in 1970 and released on the Prestige label.[1] Reception Professional ratingsR...
!["Swordsman type" gold coin of Mahasenagupta from the 6th century CE. On the obverse, the King is shown holding a sword in his left hand. On the reverse, a Goddess is shown seated in a lotus pose.[1] of Later Gupta dynasty](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c5/Swordsman_type_coinage_of_Mahasenagupta_of_the_Later_Gupta_dynasty.png/300px-Swordsman_type_coinage_of_Mahasenagupta_of_the_Later_Gupta_dynasty.png)