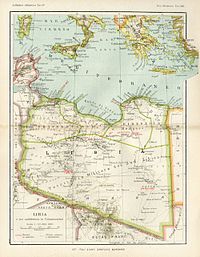
Italian settlers in Libya
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Yuliya SolntsevaLahirYuliya Ippolitovna Peresvetova(1901-08-07)7 Agustus 1901Moskwa, Kekaisaran RusiaMeninggal28 Oktober 1989(1989-10-28) (umur 88)Moskwa, USSRPekerjaanSutradaraPemeranTahun aktif1924–1979Suami/istriAleksandr Dovzhenko Yuliya Ippolitovna Solntseva (Rusia: Ю́лия Ипполи́товна Со́лнцеваcode: ru is deprecated ; nama lahir Yuliya Ippolitovna Peresvetova, 7 Agustus 1901 – 28 Oktober 1989) adalah seorang pemeran dan sutradara asa...

The Madman, His Parables and Poems AuthorKahlil GibranIllustratorKahlil GibranCountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglishPublisherAlfred A. KnopfPublication date1918TextThe Madman, His Parables and Poems at Wikisource The Madman, His Parables and Poems is a book written by Kahlil Gibran, which was published in the United States by Alfred A. Knopf in 1918, with illustrations reproduced from original drawings by the author. It was Gibran's first book in English to be published, also marking the beginni...

Historic commercial building in Virginia, United States This article contains content that is written like an advertisement. Please help improve it by removing promotional content and inappropriate external links, and by adding encyclopedic content written from a neutral point of view. (May 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) United States historic placeHanover TavernU.S. Historic districtContributing property A view looking across Route 301 from the courthouse green to...

Constituency of Bangladesh's Jatiya Sangsad Chittagong-8Constituencyfor the Jatiya SangsadDistrictChittagong DistrictDivisionChittagong DivisionElectorate475,996 (2018)[1]Current constituencyCreated1973Parliamentary PartyIndependent Member of ParliamentAbdus SalamCity Council areaChattogram City CorporationPrev. ConstituencyChittagong-7 (Constituency 284)Next ConstituencyChittagong-9 (Constituency 286) Chittagong-8 is a constituency represented in the Jatiya Sangsad (National Parliame...

Association football club in Giurgiu Football clubAstra GiurgiuFull nameAsociația Fotbal Club Astra GiurgiuNickname(s)AstraliiGiurgiuvenii (The Giurgiu People)Dracii negri (The Black Devils)Short nameAstraFounded18 September 1921as Clubul Sportiv Astra-Română[1]Dissolved19 October 2022GroundMarin AnastasoviciCapacity8,200[2] Asociația Fotbal Club Astra Giurgiu (Romanian pronunciation: [ˈastra ˈdʒjurdʒju]), commonly known as Astra Giurgiu or simply Astra, was a ...

Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori italiani è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Carlo Banfi Nazionalità Italia Calcio Ruolo Centrocampista Carriera Squadre di club1 1922-1924 SPAL26 (4) 1 I due numeri indicano le presenze e le reti segnate, per le sole partite di campionato.Il simbolo → indica un trasferimento in prestito. Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Ca...

42 ← 43 → 44素因数分解 43 (素数)二進法 101011三進法 1121四進法 223五進法 133六進法 111七進法 61八進法 53十二進法 37十六進法 2B二十進法 23二十四進法 1J三十六進法 17ローマ数字 XLIII漢数字 四十三大字 四拾参算木 43(四十三、しじゅうさん、よんじゅうさん、よそみ、よそじあまりみつ)は自然数、また整数において、42の次で44の前の数である。 性質 43は14番目の�...

Voice 4Poster promosiHangul보이스4: 심판의 시간 GenreCerita seruProseduralPembuatOCNStudio DragonChoi Jin-heeDitulis olehMa Jin-wonSutradaraShin Yong-hwiPengarah kreatifKang In-gooKim Mi-raPemeranLee Ha-naSong Seung-heonPenata musikGaemiNegara asalKorea SelatanBahasa asliKoreaJmlh. musim4Jmlh. episode14ProduksiProduser eksekutifLee Chan-ho Choi Kwang-yong Ma Jung-hoonProduserKim Ryun-heeSinematografiKang Seung-ki Choo Kwang-jaePenyuntingOh Sang-hwanPengaturan kameraKamera tungg...

1999 UCI Road World CupEleventh edition of the UCI Road World CupDetailsDates20 March – 16 OctoberLocationEuropeRaces10ChampionsIndividual champion Andrei Tchmil (BEL) (Lotto–Mobistar)Teams' championRabobank← 1998 2000 → The 1999 UCI Road World Cup was the eleventh edition of the UCI Road World Cup. It was won by Belgian classics specialist Andrei Tchmil.[1] Races Date Race Country Winner Team World Cup Leader Leader's Team Report 20 March Milan–S...

Peach Bowl El Mercedes-Benz Stadium es la sede del partido desde 2017.Datos generalesDeporte Fútbol americanoSede Estados UnidosConfederación NCAANombre oficial Peach BowlNombre comercial Chick-fil-A Peach BowlEquipos participantes 2Datos históricosFundación 1968Primer campeón LSU Tigers (1968)Datos estadísticosCampeón actual Georgia BulldogsSubcampeón actual Ohio State BuckeyesMás campeonatos LSU Tigers NC State Wolfpack (7 c/u)Más participaciones Clemson Tigers (8)Datos de c...

「俄亥俄」重定向至此。关于其他用法,请见「俄亥俄 (消歧义)」。 俄亥俄州 美國联邦州State of Ohio 州旗州徽綽號:七葉果之州地图中高亮部分为俄亥俄州坐标:38°27'N-41°58'N, 80°32'W-84°49'W国家 美國加入聯邦1803年3月1日,在1953年8月7日追溯頒定(第17个加入联邦)首府哥倫布(及最大城市)政府 • 州长(英语:List of Governors of {{{Name}}}]]) •&...

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Get Married (disambiguasi). Get Married the SeriesGenre Drama Roman Komedi PembuatStarvisionSutradaraM. HaikalPemeran Gritte Agatha Randy Martin Levty Auriga Brian Austin H. Jaja Mihardja Lydia Kandou Inggrid Widjanarko Joe P Project Derry Drajat Penggubah lagu temaSlank feat Nirina ZubirLagu pembukaPandangan Pertama oleh Slank feat Nirina ZubirLagu penutupPlis oleh Slank feat Nirina ZubirNegara asalIndonesiaBahasa asliBahasa IndonesiaJmlh. musim2Jmlh. episode55 (da...

Национальное аэрокосмическое агентство Азербайджана Штаб-квартира Баку, ул. С. Ахундова, AZ 1115 Локация Азербайджан Тип организации Космическое агентство Руководители Директор: Натиг Джавадов Первый заместитель генерального директора Тофик Сулейманов Основание Осн�...
Badminton at the 2015 SEA GamesVenueSingapore Indoor StadiumDates10–16 June 2015Competitors110 from 9 nations← 20132017 → Badminton at the 2015 SEA Games is held in Singapore Indoor Stadium, in Kallang, Singapore from 10 to 16 June 2015. Seven competitions were held in men and women's singles and in men, women and mixed's doubles and in men and women's team.[1] Participating nations A total of 110 athletes from nine nations is competing in ...

United States Army facility located adjacent to Aberdeen, Maryland, US Aberdeen Proving GroundAberdeen, Maryland This sign on U.S. Route 40 in Aberdeen, Maryland commemorates the establishment of Aberdeen Proving Ground in 1917.Aberdeen Proving GroundLocation of Aberdeen Proving GroundShow map of MarylandAberdeen Proving GroundAberdeen Proving Ground (the United States)Show map of the United StatesCoordinates39°28′24″N 76°08′27″W / 39.473451°N 76.140837°W /...

Australian publishing company This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Allen & Unwin – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Allen & UnwinFounded1914 (United Kingdom) 1976 (Australian arm)FounderStanley UnwinCountry of originUni...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Wish You Were Here Badfinger album – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) 1974 studio album by BadfingerWish You Were HereStudio album by BadfingerReleased15 November 1974Recorded9 ...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018) الدوري الإسباني الدرجة الثانية الموسم 2012–2013 البلد إسبانيا المنظم الاتحاد الملكي الإسباني لكرة القد�...

Empire in France from 1852 to 1870 Not to be confused with French colonial empire. French EmpireEmpire Français (French)1852–1870 Flag Imperial coat of arms Anthem: Partant pour la Syrie[1] (de facto)[2][3]Departing for SyriaThe Second French Empire in 1861Colonies and territories held by the Second French Empire in 1867, highlighted in blueCapitalParis48°51′23″N 02°21′08″E / 48.85639°N 2.35222°E / 48.85639; 2.35222Offic...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Gondomar (homonymie). Cet article est une ébauche concernant une localité portugaise. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Gondomar Héraldique Église de Rio Tinto - Gondomar - Portugal Administration Pays Portugal Région Nord Sous-région Grand Porto Ancienne province Douro littoral District Porto Maire Marco Martins PS Code postal 4420 Démographie Population 16...