Iqta'
|
Read other articles:

Dario Vidošić Vidošić pada tahun 2009Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Dario Vidošić[1]Tanggal lahir 8 April 1987 (umur 36)Tempat lahir Osijek, SFR YugoslaviaTinggi 184 cm (6 ft 0 in)[2]Posisi bermain GelandangInformasi klubKlub saat ini FC SionNomor 23Karier junior2000–2005 Queensland Lions2006 AISKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2006–2007 Brisbane Roar 17 (5)2007–2011 1. FC Nürnberg 30 (3)2010 → MSV Duisburg (pinjaman) 12 (1)2011 → Armini...

Dalam nama Korean ini, nama keluarganya adalah Wang. Wang Ji-HyeLahir29 Desember 1985 (umur 38)Masan, Provinsi Gyeongsang Selatan, Korea SelatanNama lainMin Ji-HyePendidikanUniversitas Konkuk – Film ArtsPekerjaanAktrisTahun aktif2003-sekarangAgenPeople Story Company[1](2018 - present) Nama KoreaHangul왕지혜 Alih AksaraWang Ji-hyeMcCune–ReischauerWang Chi-hyeNama panggungHangul민지혜 Alih AksaraMin Ji-hyeMcCune–ReischauerMin Chi-hye Wang Ji-Hye (lahir 29 Dese...

Mazmur 122Naskah Gulungan Mazmur 11Q5 di antara Naskah Laut Mati memuat salinan sejumlah besar mazmur Alkitab yang diperkirakan dibuat pada abad ke-2 SM.KitabKitab MazmurKategoriKetuvimBagian Alkitab KristenPerjanjian LamaUrutan dalamKitab Kristen19← Mazmur 121 Mazmur 123 → Mazmur 122 (disingkat Maz 122, Mzm 122 atau Mz 122; penomoran Septuaginta: Mazmur 121) merupakan salah satu Mazmur dalam Kitab Mazmur yang termasuk mazmur ziarah Daud.[1] Mazmur yang dinyanyikan umat Tu...

South African military decoration for bravery This article is about the Honoris Crux Gold. For other uses, see Honoris Crux. AwardHonoris Crux GoldTypeMilitary decoration for braveryAwarded forOutstanding bravery in extreme dangerCountry South AfricaPresented bythe State PresidentEligibilityAll RanksPost-nominalsHCGCampaign(s)1966-1989 Border WarStatusDiscontinued in 1992Established1975First awarded1975Last awarded1991Total5 and 1 BarRibbon bar SADF pre-1994 & SANDF post-2002 orders ...
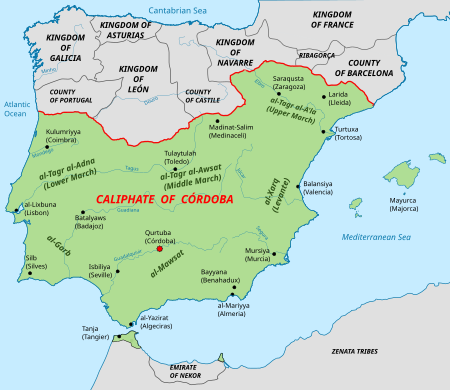
Battle of the Reconquista in 939 AD For the siege of Simancas barracks during the Spanish Civil War in 1936, see Siege of Gijón. Battle of SimancasPart of the ReconquistaMap of the Caliphate of Cordoba circa 1000.Date19 July 939LocationSimancas, SpainResult Leonese victory.Belligerents Kingdom of León Caliphate of CórdobaCommanders and leaders James the Great (According to the Legend)Ramiro II of LeónFernán González of CastileGarcía Sánchez I of Pamplona Abd-ar-Rahman III vteBattles i...

Major Roman rescue operation during the First Punic War Roman withdrawal from Africa, 255 BCPart of the First Punic WarDate255 BCLocationCape Bon Peninsula; the waters off it; and off the coast of south-east Sicily37°N 11°E / 37°N 11°E / 37; 11Result InconclusiveBelligerents Carthage RomeCommanders and leaders Unknown Fulvius Paetinus NobiliorAemilius PaullusStrength 200 warshipsUnknown number of soldiers 390 warshipsUnknown but large number of soldiersCasualties a...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Ménilmontant. Ménilmontant La rue de Ménilmontant. Administration Pays France Région Île-de-France Ville Paris Arrondissement municipal 20e Géographie Coordonnées 48° 51′ 58″ nord, 2° 23′ 01″ est Localisation Géolocalisation sur la carte : Paris Ménilmontant modifier La barrière de Ménilmontant. L'ancienne gare de Ménilmontant de la Petite Ceinture, située à l'intersection avec la rue de la Mar...

British political journalist Edmund FawcettNationalityBritishOccupationWriterNotable workLiberalism: The Life of an Idea Conservatism: The Fight for a TraditionParents James Fawcett Frances Lowe RelativesElias Avery Lowe (grandfather)Helen Tracy Lowe-Porter (grandmother)Charlotte Johnson Wahl (sister)Boris Johnson (nephew)Jo Johnson (nephew)Rachel Johnson (niece) Edmund Fawcett is a British political journalist and author. Family This section of a biography of a living person needs additional...
See also: Index of ethics articles Part of a series onPhilosophy Philosophy portal Contents Outline Lists Glossary History Categories Disambiguation Philosophies By period Ancient Ancient Egyptian Ancient Greek Medieval Renaissance Modern Contemporary Analytic Continental By region African Egypt Ethiopia South Africa Eastern philosophy Chinese Indian Indonesia Japan Korea Vietnam Indigenous American Aztec philosophy Middle Eastern philosophy Iranian Western American British French German...

Ward Lee, Tucker Henderson, and Romeo—born Cilucängy, Pucka Gaeta, and Tahro in the Congo River basin—were trafficked to the United States in 1859 on the Wanderer (1908 photograph by Charles J. Montgomery for the journal American Anthropologist) Following the discovery of 18 enslaved people from Jamaica who were deposited along the Mississippi River at a spot between Fort St. Philip and English Turn, U.S. Attorney for the Eastern District of Louisiana John W. Smith published this notice...

15th century Bosnian nobleman Vladislav HercegovićGrand Duke of BosniaFull nameVladislav Hercegović KosačaBorn1426Died1489RabNoble familyKosača noble family FatherStjepan Vukčić KosačaMotherJelena Balšić Vladislav Hercegović (Serbian Cyrillic: Владислав Херцеговић; 1426 or 1427 – 1489) was oldest son of Stjepan Vukčić. The Kosača noble family held lands in the region known as Humska zemlja, later named Herzegovina. Unlike his father, who quarreled with the Bo...

French National Gendarmerie unit National Gendarmerie Intervention GroupGroupe d'intervention de la Gendarmerie nationaleOfficial insignia (2021)Active1973–presentCountry FranceAgencyNational GendarmerieTypePolice tactical unitRoleCounter-terrorismHostage rescueProtection of VIPs and important sitesOperations jurisdictionInternationalHeadquartersSatory, Yvelines, France48°47′6.59″N 2°06′25.80″E / 48.7851639°N 2.1071667°E / 48.7851639; 2.1071667MottoS...

2001 single by the Strokes This article is about the song by the Strokes. For other uses, see Last Night (disambiguation). Last NiteSingle by The Strokesfrom the album Is This It B-sideWhen It StartedReleasedOctober 23, 2001 (2001-10-23)RecordedMarch and April 2001StudioTransporterraum, New York CityGenreIndie rock[1]garage rock revival[2]Length3:13LabelRCARough TradeBMGSongwriter(s)Julian CasablancasProducer(s)Gordon RaphaelThe Strokes singles chronology Hard t...

Railway station in Hereford, Herefordshire, England For a history of railways in Hereford, see Railways in Hereford. HerefordGeneral informationLocationHereford, HerefordshireEnglandCoordinates52°03′41″N 2°42′30″W / 52.06139°N 2.70833°W / 52.06139; -2.70833Grid referenceSO515405Managed byTransport for WalesPlatforms4Other informationStation codeHFDClassificationDfT category C1HistoryOriginal companyShrewsbury and Hereford RailwayPre-groupingShrewsbury and H...

Village in Southern Transdanubia, HungaryViszVillage Coat of armsLocation of Somogy county in HungaryViszLocation of ViszCoordinates: 46°43′41″N 17°47′02″E / 46.72819°N 17.78394°E / 46.72819; 17.78394Country HungaryRegionSouthern TransdanubiaCountySomogyDistrictFonyódRC DioceseKaposvárArea • Total6.02 km2 (2.32 sq mi)Population (2017) • Total207[1]DemonymvisziTime zoneUTC+1 (CET) • Summe...

座標: 北緯55度44分15.38秒 東経37度35分24.92秒 / 北緯55.7376056度 東経37.5902556度 / 55.7376056; 37.5902556 スプートニク 業種 通信社前身 ロシアの声 設立 2014年11月10日本社 ロシア モスクワ製品 国際放送ラジオ、ニュースサイト親会社 ロシアの今日ウェブサイト sputniknews.com スプートニク(SPUTNIK、露: Спутник)は、ロシアの通信社。2014年11月10日に設立さ�...

ゲルハルト・ハナッピ・シュターディオン 施設情報所在地 ウィーン開場 1977年閉場 2014年グラウンド 天然芝ピッチサイズ 105 x 68 m設計者 ゲルハルト・ハナッピ使用チーム、大会 SKラピード・ウィーン収容人員 18,422人 ゲルハルト・ハナッピ・シュターディオン(Gerhard-Hanappi-Stadion)は、2015年までオーストリアの首都ウィーンに存在したサッカー専用スタジアム。 概要 元...

散布山Богдан Хмельницкий 散布山(中央、1,587m)と北散布山(左奥、1,561m)標高 1,587 m所在地 領土問題あり 日本(北海道紗那郡紗那村) ロシア(サハリン州クリル管区)位置 北緯45度20分26秒 東経147度55分14秒 / 北緯45.34056度 東経147.92056度 / 45.34056; 147.92056座標: 北緯45度20分26秒 東経147度55分14秒 / 北緯45.34056度 東経147.92056度 / 45.3...

Väinö Tanner Perdana Menteri FinlandiaMasa jabatan13 Desember 1926 – 17 Desember 1927PresidenLauri Kristian RelanderPendahuluKyösti KallioPenggantiJuho Sunila Informasi pribadiLahir12 Maret 1881HelsinkiMeninggal19 April 1966(1966-04-19) (umur 85)HelsinkiPartai politikPartai Demokratik Sosial Sunting kotak info • L • B Väinö Tanner (12 Maret 1881 – 19 April 1966; nama belakang sampai 1895 Thomasson) adalah seorang figur utama dalam Partai Demokratik Sosial ...

Hildesheimer Rabbinical Seminaryבית המדרש לרבנים בברליןBerlin Rabbinical Seminary, 25 years anniversary of work, 1898.EstablishedOctober 10, 1873 (1873-22-10)FounderIsrael HildesheimerAffiliationOrthodox JudaismLocationBerlin, Germany52°31′36.9″N 13°23′36.8″E / 52.526917°N 13.393556°E / 52.526917; 13.393556Websiterabbinerseminar.de The Hildesheimer Rabbinical Seminary (officially in ‹See Tfd›German: Rabbinersemi...