Human T-lymphotropic virus 2
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

7β-Hydroxy-DHEA Names IUPAC name 3β,7β-Dihydroxyandrost-5-en-17-one Systematic IUPAC name (3aS,3bR,4R,7S,9aR,9bS,11aS)-4,7-Dihydroxy-9a,11a-dimethyl-2,3,3a,3b,4,6,7,8,9,9a,9b,10,11,11a-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-1-one Other names 7β-OH-DHEA; Androst-5-en-3β,7β-diol-17-one Identifiers CAS Number 2487-48-1 3D model (JSmol) Interactive image ChEBI CHEBI:183368 ChEMBL ChEMBL1082098 ChemSpider 7993704 PubChem CID 9817954 UNII 923RBW7OJQ CompTox Dashboard (EPA) DTXSID50431284...

Символ масти ― цветок с шестью жёлтыми лепестками и оранжевым пестиком Розы (нем. Rosen) ― одна из четырёх мастей в швейцарской колоде. Эта масть появилась в XV веке.[1] Содержание 1 Аналоги в других колодах 2 Галерея 3 См. также 4 Примечания Аналоги в других колодах Во фра...
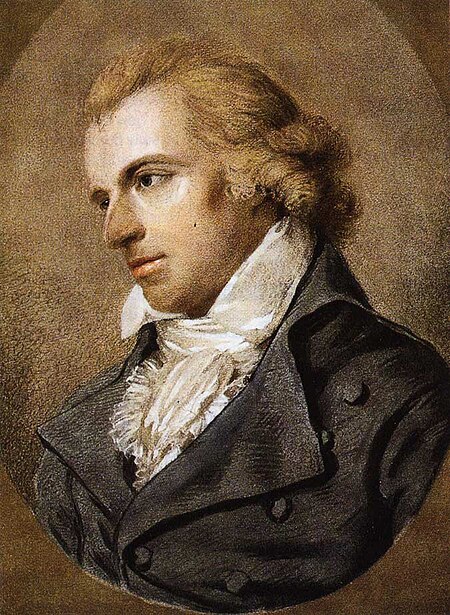

« Beethoven » redirige ici. Pour les autres significations, voir Beethoven (homonymie). Ludwig van Beethoven Ludwig van Beethoventravaillant à la Missa solemnis(portrait de Joseph Karl Stieler de 1820). Données clés Naissance 15 ou 16 décembre 1770 Bonn Électorat de Cologne Saint-Empire Décès 26 mars 1827 (à 56 ans) Vienne Empire d'Autriche Activité principale Compositeur Style Classique et romantique Années d'activité 1778-1826 Maîtres Luchesi, Neefe, ...

.id البلد إندونيسيا الموقع الموقع الرسمي تعديل مصدري - تعديل id. هو نطاق إنترنت من صِنف مستوى النطاقات العُليا في ترميز الدول والمناطق، للمواقع التي تنتمي إلى اندونيسيا.[1][2] مراجع ^ النطاق الأعلى في ترميز الدولة (بالإنجليزية). ORSN [الإنجليزية]. Archived from the original o...

Compact car Elantra redirects here. For the Chronicles of Elantra novels, see Michelle Sagara. Motor vehicle Hyundai ElantraOverviewManufacturerHyundaiAlso calledHyundai AvanteHyundai Lantra (1990–2000)Hyundai i30 Sedan (2020–present)Production1990–presentBody and chassisClassCompact car (C)LayoutFront-engine, front-wheel-driveChronologyPredecessorHyundai Stellar (South Korea) The Hyundai Elantra, also known as the Hyundai Avante (Korean: 현대 아반떼), is a compact car produce...

Bursa Efek OsakaOsaka Securities Exchange Co., Ltd.株式会社大阪証券取引所Gedung Bursa Efek Osaka di Chuo-ku, OsakaJenisKabushiki KaishaIndustriKeuanganDidirikan1 April 1949 (1949 -04-01)[1]KantorpusatOsaka, JepangTokohkunciHiromi Yamaji (Presiden/CEO)ProdukBursa sahamKaryawan207IndukJapan Exchange GroupSitus webhttps://www.jpx.co.jp/english/corporate/about-jpx/profile/02.html, https://www.jpx.co.jp/chinese/corporate/jpx-profile/02.html www.jpx.co.jp/corporate/about-jpx...
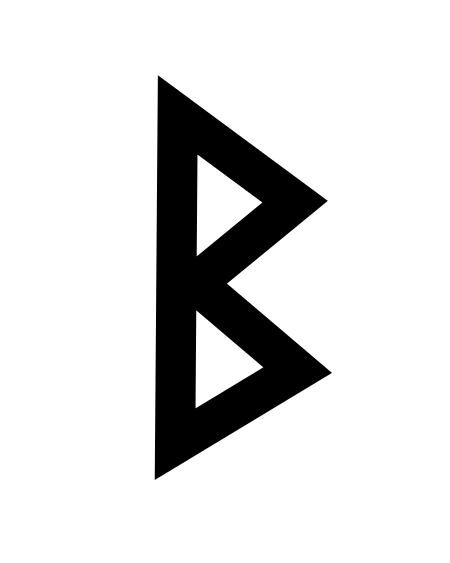
此條目介紹的是拉丁字母中的第2个字母。关于其他用法,请见「B (消歧义)」。 提示:此条目页的主题不是希腊字母Β、西里尔字母В、Б、Ъ、Ь或德语字母ẞ、ß。 BB b(见下)用法書寫系統拉丁字母英文字母ISO基本拉丁字母(英语:ISO basic Latin alphabet)类型全音素文字相关所属語言拉丁语读音方法 [b][p][ɓ](适应变体)Unicode编码U+0042, U+0062字母顺位2数值 2歷史發...

Proposed puppet state of Nazi Germany For other uses, see Independent Macedonia (disambiguation). The red and black flag used by the Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization and more broadly by supporters of an autonomous or independent Macedonia The Independent State of Macedonia[a] was a proposed puppet state of Nazi Germany during the Second World War in the territory of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia that had been occupied by the Kingdom of Bulgaria following the invasion of Yugo...

For the place in Adelaide, see Kingston Park, South Australia. For the rugby ground, see Kingston Park (stadium). Human settlement in EnglandKingston Park,Tesco Kingston Park (2007)Kingston Park,Location within Tyne and WearOS grid referenceNZ214686• London242 miles (389 km)Metropolitan boroughNewcastle upon TyneMetropolitan countyTyne and WearRegionNorth EastCountryEnglandSovereign stateUnited KingdomPost townNEWCASTLE UPON TYNEPostcode districtNE3Di...

DKW F91Descrizione generaleCostruttore DKW Tipo principaleberlina Altre versionicoupécabrioletgiardinettafurgoncino Produzionedal 1953 al 1957 Sostituisce laDKW F89 Sostituita daDKW F93 Esemplari prodotti72.608[senza fonte] Altre caratteristicheDimensioni e massaLunghezzada 4170 a 4225 mm Larghezzada 1520 a 1595 mm Altezzada 1450 a 1550 mm Passoda 2350 a 2450 mm Massada 860 a 925 kg AltroAssemblaggioDüsseldorf (Berlina)Osnabrück Stessa famigl...

Coconut chutneyAlternative nameskayi chattniCourseCondimentPlace of originIndiaRegion or stateOriginally limited to coastal plains of Old Madras Presidency (Coastal Karnataka, Coastal Andhra, Kerala, Pondicherry and Coastal Tamil Nadu) where coconut plantations was a tradition. Later spread out to high plateau of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Rayalaseema of erstwhile Andhra Pradesh, and later to TelanganaMain ingredientsCoconut, ginger, chillies, curry leaves, mustard seeds Cookbook: Coconut chutne...

此條目可能包含不适用或被曲解的引用资料,部分内容的准确性无法被证實。 (2023年1月5日)请协助校核其中的错误以改善这篇条目。详情请参见条目的讨论页。 各国相关 主題列表 索引 国内生产总值 石油储量 国防预算 武装部队(军事) 官方语言 人口統計 人口密度 生育率 出生率 死亡率 自杀率 谋杀率 失业率 储蓄率 识字率 出口额 进口额 煤产量 发电量 监禁率 死刑 国债 ...

Women's 100 metres at the 2018 Commonwealth GamesVenueCarrara StadiumDates8 April (heats and semifinals)9 April (final)Competitors42 from 28 nationsWinning time11.14Medalists Michelle-Lee Ahye Trinidad and Tobago Christania Williams Jamaica Gayon Evans Jamaica← 20142022 → Athletics at the2018 Commonwealth GamesTrack events100 mmenwomen200 mmenwomen400 mmenwomen800 mmenwomen1500 mmenwomen5000 mm...

For the town in Dumfries and Galloway, see Castle Douglas. Historic siteDouglas CastleDouglas Castle (demolished in 1938)Coordinates55°33′58″N 3°50′10″W / 55.56610°N 3.83624°W / 55.56610; -3.83624 Listed Building – Category C(S)Designated12 January 1971Reference no.LB1449 Location within South Lanarkshire Douglas Castle in 1883 Douglas Castle was a stronghold of the Douglas (later Douglas-Home) family from medieval times to the 20th century. The firs...

American pediatrician and activist (1929–2001) Helen Rodríguez TríasThe first Latina president of The American Public Health AssociationBornJuly 7, 1929New York City, U.S.DiedDecember 27, 2001(2001-12-27) (aged 72)Santa Cruz, California, U.S.Occupation(s)Pediatrician, educator, activistSpouseDavid Neumark Brainin (m. 1949-d.1954) Eliezer Curet (m. 1954-d. ?) Edward Gonzales (m. ?- 2001)Children4 Part of a series on thePuerto RicanNationalist PartyFlag of the Puerto Rican N...

Russian politician (born 1978) Andrey AlekseyenkoАндрей АлексеенкоMayor of KrasnodarIn office21 October 2021 – 18 August 2022Succeeded byYevgeny Naumov[1]Chair of the Kharkov Military-Civilian AdministrationIn office19 August 2022 – 9 September 2022Preceded byPost establishedSucceeded byPost abolishedChair of the Kherson Military-Civilian AdministrationIncumbentAssumed office 25 November 2022 Personal detailsBorn (1978-04-23) April 23, 1978 (a...

H.PaisalSKM,MARS Wali Kota Dumai ke-6PetahanaMulai menjabat 26 Februari 2021PresidenJoko WidodoGubernurSyamsuar Edy Nasution S. F. Hariyanto (Pj.)WakilAmris (Februari 2021-April 2021)PendahuluZulkifli Adnan Singkah Herdi Salioso (Plh.) Jonli (Pj.)PenggantiPetahana Informasi pribadiLahir12 Januari 1975 (umur 49)Bagansiapiapi,Rokan Hilir, RiauKebangsaanIndonesiaPartai politikNasDemSuami/istriHj. Leni Ramaini,SKMAnak4Alma materUniversitas Sumatera UtaraPekerjaanPolitisiBirokratSunti...

American javelin thrower Marcus Paul Mark Murro (born June 4, 1949)[1] is an American former javelin thrower. Murro held the United States record in men's javelin throw from 1969 to 1982 and competed in the 1968 Summer Olympics. Career Murro broke the national high school record in men's javelin throw in 1967 while attending Essex Catholic High School in Newark, New Jersey, throwing 252 ft 8 in (77.01 m).[2] In June 1968 he placed third at the national cham...
Video game genre Action-adventure redirects here. For other uses, see Action-adventure (disambiguation). This article possibly contains original research. Please improve it by verifying the claims made and adding inline citations. Statements consisting only of original research should be removed. (February 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Part of a series onAction games Subgenres Action-adventure Metroidvania Battle royale Fighting Beat 'em up Hack and slash Platform fighter ...
Antti Hackzell Perdana Menteri FinlandiaMasa jabatan8 Augustus 1944 – 21 September 1944PendahuluEdwin LinkomiesPenggantiUrho Castrén Informasi pribadiLahir20 September 1881MikkeliMeninggal14 Januari 1946(1946-01-14) (umur 64)Partai politikPartai Koalisi NasionalSunting kotak info • L • B Antti Verner Hackzell (20 September 1881 – 14 Januari 1946) adalah seorang politikus Finlandia dari Partai Koalisi Nasional dan Perdana Menteri Finlandia pada 19...

