History of Indian law
|
Read other articles:

Bagian dari seri Biologi mengenai Evolusi Pengenalan Mekanisme dan Proses Adaptasi Hanyutan genetika Aliran gen Mutasi Seleksi alam Spesiasi Riset dan sejarah Bukti Sejarah evolusi kehidupan Sejarah Sintesis modern Efek sosial Teori dan fakta Keberatan / Kontroversi Bidang Kladistika Genetika ekologi Perkembangan evolusioner Evolusi manusia Evolusi molekuler Filogenetika Genetika populasi Portal Biologi ·lbs Catagenesis adalah istilah kuno dari biologi evolusioner yang merujuk ke arah evolu...

Pertandingan Calcio Fiorentino pada tahun 2008. Calcio Fiorentino atau calcio storico (dalam bahasa Italia) yang berarti sepakbola kuno atau sepak bola zaman dulu, adalah perayaan yang menggabungkan sepak bola, rugby, dan perkelahian. Acara ini rutin diadakan di Italia. Permainan ini berkembang pertama kali pada abad ke-16 di Italia. Meskipun dulu dipraktikkan secara luas, tetapi diperkirakan awalnya bermula di Piazza Santa Croce, Firenze. Sehingga berkembanglah nama giuoco del calcio fiorent...
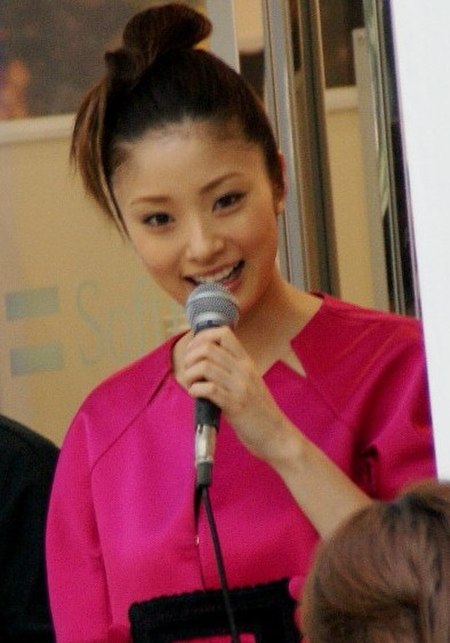

Japanese singer and actress In this Japanese name, the surname is Ueto. Aya Ueto上戸 彩Ueto attending the iPhone 3GS launch event at the SoftBank flagship store, June 2009Born (1985-09-14) September 14, 1985 (age 38)Nerima, Tokyo, JapanOccupations Actress singer television personality Years active1999–presentSpouse Hiroyuki Igarashi (m. 2012)Children3Musical careerGenres Pop pop rock Instrument(s)VocalsLabels Flight Master Pony Canyon Musical arti...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Wellesley, Massachusetts – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Town in Massachusetts, United StatesWellesley, MassachusettsTownWellesley Town Hall SealLocation of Wellesley in Norfolk ...

مقاطعة خواف الإحداثيات 34°30′N 60°00′E / 34.5°N 60°E / 34.5; 60 [1] تقسيم إداري البلد إيران[2] التقسيم الأعلى خراسان رضوي[3] العاصمة خواف عدد السكان عدد السكان 138972 (2016)[3] عدد الأسر 36399 (2016)[3] رمز جيونيمز 1482426 تعديل مص�...

Moustapha IV Le sultan Moustapha IV. Titre 29e sultan ottoman93e calife de l’islam 29 mai 1807 – 28 juillet 1808(1 an, 1 mois et 29 jours) Prédécesseur Sélim III Successeur Mahmoud II Biographie Dynastie Dynastie ottomane Date de naissance 8 septembre 1779 Lieu de naissance Constantinople Date de décès 17 novembre 1808 (à 29 ans) Lieu de décès Constantinople Père Abdülhamid Ier Mère Ayşe Sine Fratrie Mahmoud II Conjoint 4 épouses Enfants 1 enfant Liste de...

Il tempo geologico, visualizzato in un diagramma chiamato orologio geologico, che mostra la durata relativa dei vari eoni della storia della Terra. La storia della Terra descrive l'insieme dei più importanti eventi e stadi nello sviluppo e nell'evoluzione che ha avuto luogo sul pianeta Terra dalla sua formazione. Comprende le teorie scientifiche ritenute più verosimili e quasi tutti i rami delle scienze naturali che contribuiscono alla comprensione degli avvenimenti nel passato del nostro p...

Chicago and Southern Air Lines IATA ICAO Callsign CS CSA C & S Founded1933Ceased operations1953 (merged into Delta Air Lines)Fleet sizeN/ADestinationsN/AHeadquartersMemphis, TennesseeKey peopleCarleton Putnam, Founder Chicago and Southern Air Lines (C&S) was a United States airline that started life as Pacific Seaboard Air Lines in California and was organized on June 15, 1933. Following the move from California, the airline's headquarters were initially located in St. Louis, Missouri...
Sporting event delegationNiger at the2011 World Aquatics ChampionshipsFlag of NigerFINA codeNIGNational federationFederation Nigerienne des Sport Nautiquesin Shanghai, ChinaCompetitors3 in 1 sportMedals Gold 0 Silver 0 Bronze 0 Total 0 World Aquatics Championships appearances197319751978198219861991199419982001200320052007200920112013201520172019202220232024 Niger competed at the 2011 World Aquatics Championships in Shanghai, China between July 16 and 31, 2011. Swimming Main article: Swimming...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Desember 2022. Mazarópi Informasi pribadiTanggal lahir 27 Januari 1953 (umur 71)Tempat lahir BrasilPosisi bermain Penjaga gawangKepelatihanTahun Tim 1999 Nagoya Grampus Eight2000 Nagoya Grampus Eight Mazarópi (lahir 27 Januari 1953) adalah pemain sepak bola a...

National anthem of North Korea For the national anthem of South Korea, see Aegukga. For the national anthem of the Korean Empire, see National anthem of the Korean Empire. AegukkaEnglish: Patriotic Song애국가Sheet music atop North Korean state emblemNational anthem of North KoreaAlso known as(English: Song of a Devotion to a Country)LyricsPak Se-yong, 1946,[1] 2024 (modified)MusicKim Won-gyun, 1945[1]Adopted1947Audio sampleInstrumental recording by the Korean Peop...

Memorial Patativa do Assaré, Ceará, Brasile. Patativa do Assaré pseudonimo di Antônio Gonçalves da Silva (Assaré, 5 marzo 1909 – Assaré, 8 luglio 2002) è stato un poeta, scrittore e cantastorie brasiliano, specializzato nella Letteratura di cordel[1]. (PT) «Caboclo Roceiro, das plaga do NorteQue vive sem sorte, sem terra e sem lar,tua desdita é tristonho que canto,Se escuto o meu pranto me ponho a chorar.....Tu és meu amigo, tu és meu irmão.» (IT) «Caboclo Roceiro del...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Februari 2023. Tropos [1][2] adalah metodologi pengembangan perangkat lunak berorientasi agen yang dibuat oleh sekelompok penulis dari berbagai universitas di Kanada dan Italia. Metodologi Tropos dimaksudkan untuk mendukung semua kegiatan analisis da...

1975 studio album by Loleatta HollowayCry to MeStudio album by Loleatta HollowayReleased1975RecordedThe Sound Pit(Atlanta, Georgia)GenreR&BLabelAwareProducerFloyd SmithLoleatta Holloway chronology Loleatta(1973) Cry to Me(1975) Loleatta(1977) Professional ratingsReview scoresSourceRatingAllmusic[1] Cry to Me is the second studio album recorded by American singer Loleatta Holloway, released in 1975 on the Aware label. Chart performance The album peaked at No. 47 on the US R...

习近平 习近平自2012年出任中共中央总书记成为最高领导人期间,因其废除国家主席任期限制、开启总书记第三任期、集权统治、公共政策与理念、知识水平和自述经历等争议,被中国大陸及其他地区的民众以其争议事件、个人特征及姓名谐音创作负面称呼,用以恶搞、讽刺或批评习近平。对习近平的相关负面称呼在互联网上已经形成了一种活跃、独特的辱包亚文化。 权力�...

American poet (1883–1963) Carlos Williams redirects here. For the Liberian footballer, see Carlos Williams (footballer). William Carlos WilliamsPortrait by Man Ray, 1924Born(1883-09-17)September 17, 1883Rutherford, New Jersey, U.S.DiedMarch 4, 1963(1963-03-04) (aged 79)Rutherford, New Jersey, U.S.OccupationWriterphysicianEducationUniversity of Pennsylvania (MD)Literary movementModernismImagismNotable worksSpring and AllThis Is Just To SayThe Red WheelbarrowThe Great FigurePictures from...

Untuk orang lain dengan nama yang sama, lihat Supardi. Supardi Inspektur Jenderal Departemen Pendidikan dan KebudayaanMasa jabatan9 Mei 1973 – 28 April 1980MenteriSyarief ThayebDaoed JoesoefPendahuluR.F. SoedardiPenggantiF.X. SoedijanaDirektur Jenderal Pemuda dan Olahraga[a]Masa jabatan18 April 1968 – 9 Mei 1973MenteriSanusi HardjadinataMashuri SalehSumantri BrodjonegoroPendahuluHusein Mutahar(Direktur Jenderal Pemuda)Sukamto Sajidiman(Direktur Jenderal Olahraga)...

1992 television film directed by Paul Seed Dead Ahead: The Exxon Valdez DisasterGenreDramaWritten byMichael BakerDirected byPaul SeedStarringChristopher LloydJohn HeardRip TornBob GuntonMichael MurphyMark MetcalfMusic byDavid FergusonCountry of originUnited StatesOriginal languageEnglishProductionExecutive producersRichard BrokeColin CallenderLeslie WoodheadProducersJohn SmithsonDavid M. ThompsonProduction locationsAlaskaVancouverCinematographyIan PunterEditorDave KingRunning time90 minutesPr...

Vanzaghellocomune LocalizzazioneStato Italia Regione Lombardia Città metropolitana Milano AmministrazioneSindacoArconte Gatti (lista civica) dal 27-5-2019 TerritorioCoordinate45°35′N 8°47′E45°35′N, 8°47′E (Vanzaghello) Altitudine194 m s.l.m. Superficie5,56 km² Abitanti5 246[1] (31-12-2021) Densità943,53 ab./km² Comuni confinantiCastano Primo, Lonate Pozzolo (VA), Magnago, Samarate (VA) Altre informazioniCod. postale20020 P...

Component of avian reproduction A diagram of a bird egg Eggs of various birds, labelled (Trinity College Zoological Museum, Dublin) Bird eggs are laid by the females and range in quantity from one (as in condors) to up to seventeen (the grey partridge). Clutch size may vary latitudinally within a species. Some birds lay eggs even when the eggs have not been fertilized; it is not uncommon for pet owners to find their lone bird nesting on a clutch of infertile eggs, which are sometimes called w...

