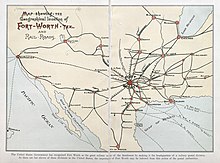
History of Fort Worth, Texas
|
Read other articles:
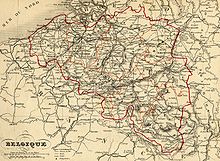
German-speaking region in eastern Belgium Eupen-Malmedy border changes between 1920 and 1945 Eupen-Malmedy is a small, predominantly German-speaking region in eastern Belgium. It consists of three administrative cantons around the towns of Eupen, Malmedy, and Sankt Vith which encompass some 730 square kilometres (280 sq mi). Elsewhere in Belgium, the region is commonly referred to as the East Cantons (French: Cantons de l'Est, Dutch: Oostkantons). Eupen-Malmedy became part of Belgiu...

Gereja KristusLogo Gereja KristusPenggolonganProtestanPemimpinKetua Umum Pdt. Adieli Waruwu, M.Div.WilayahIndonesiaDidirikan1928 JakartaUmat14.146 jiwaSitus web resmiwww.gerejakristus.org Gereja Kristus adalah salah satu organisasi gereja Kristen Protestan di Indonesia yang beraliran presbiterian. Gereja Kristus memiliki gereja yang tersebar di 4 provinsi di Indonesia.[1][2] Tentang Gereja Berawal dari Misi Penginjilan yang dijalankan oleh Methodist Episcopal Church Amerika ke...

Program Studi Teknik Sipil Universitas Kristen Petra Program Studi Teknik Sipil Universitas Kristen Petra didirikan pada tahun 1962 dan berada pada naungan Fakultas Teknik Sipil dan Perencanaan Universitas Kristen Petra. Sejarah Jurusan Teknik Sipil, Fakultas Teknik Sipil dan Perencanaan, Universitas Kristen Petra didirikan pada tanggal 15 September 1962. Pada awalnya Jurusan Teknik Sipil menempati gedung di Jalan Embong Kemiri No. 11 dan Jalan Indrapura, Surabaya. Kondisi ruang untuk perkuli...

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Syarh – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Syarh, Syarah, atau Syarhu adalah istilah dalam literatur Islam, digunakan secara umum sebagai bagian dari judul buku. Secara harafiah artinya pe...

Operation DraufgängerPart of World War II in YugoslaviaExhausted partisans after defeating Germans and breaking into Serbia, 4 August 1944Date18 July – 1 August 1944Locationparts of German-occupied Montenegro and Albania (northeastern Montenegro and southwestern Serbia)Result Yugoslav Partisan victoryBelligerents Germany Bulgaria Albania Chetniks Yugoslav PartisansCommanders and leaders Artur Phleps Peko DapčevićUnits involved 21st SS Skanderbeg and support units Parts of the II A...

Recipient of the Victoria Cross Bertram Best-DunkleyBorn3 August 1890York, EnglandDied5 August 1917 (aged 27)Pilckem Ridge, Passchendaele salient, BelgiumBuriedMendinghem Military Cemetery, ProvenAllegiance United KingdomService/branch British ArmyYears of service-1917 †RankLieutenant-ColonelUnitThe Lancashire FusiliersBattles/warsFirst World War Western Front Battle of Passchendaele Battle of Pilckem Ridge (DOW) AwardsVictoria Cross Lieutenant-Colonel Bertram Best-...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: HBO Comedy Half-Hour – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) American TV series or program HBO Comedy Half-HourGenreComedyCountry of originUnited StatesOriginal languageEnglishNo. of seasons4No. o...

Learning technique performed with flashcards This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Spaced repetition – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) In the Leitner system, correctly answered cards are advanced to the next, less frequent box,...

Частина серії проФілософіяLeft to right: Plato, Kant, Nietzsche, Buddha, Confucius, AverroesПлатонКантНіцшеБуддаКонфуційАверроес Філософи Епістемологи Естетики Етики Логіки Метафізики Соціально-політичні філософи Традиції Аналітична Арістотелівська Африканська Близькосхідна іранська Буддій�...
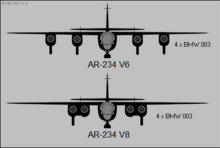
1943 German jet bomber by Arado Ar 234 Blitz Arado Ar 234 B-2 at the National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Virginia, US Role Reconnaissance / bomberType of aircraft Manufacturer Arado Flugzeugwerke Designer Walter Blume First flight 15 June 1943 Introduction September 1944 Retired May 1945 Primary user Luftwaffe Produced 1944-1945 Number built 214 The Arado Ar 234 Blitz (English: lightning) is a jet-powered bomber designed and produced by the German aircraft manu...

Statement of belief adopted at the First Ecumenical Council in 325 Icon depicting Constantine the Great, accompanied by the bishops of the First Council of Nicaea (325), holding the Niceno-Constantinopolitan Creed of 381. First line of main text in Greek: Πιστεύω εἰς ἕνα Θ[εό]ν, πατέρα παντοκράτορα, ποιητὴν οὐρανοῦ κ[αὶ] γῆς,. Translation: I believe in one God, the Father the Almighty, Maker of heaven and earth. The Nicene Creed (/...

Tabla de rangos. La Tabla de rangos (en ruso: Табель о рангах; Tábel o rángaj) era un listado oficial de cargos y puestos pertenecientes al ámbito militar, al gobierno y a la corte de la Rusia imperial. Fue introducida en 1722 por Pedro el Grande en su pugna contra el poder de los boyardos, la nobleza hereditaria de la época. La Tabla fue abolida por el gobierno bolchevique el 11 de noviembre de 1917. La tabla de rangos determinaba la posición y el estado de una persona toma...

Detachable collar worn by Christian clergy Church of Sweden Lutheran priest Sven-Erik Brodd [sv] wearing a clerical shirt with a tab collar.An Anglican military chaplain wearing a dog collar (full collar) during World War I A clerical collar, clergy collar, or, informally, dog collar,[1][2][3] is an item of Christian clerical clothing.[4] Overview The clerical collar is almost always white and was originally made of cotton or linen but is now frequ...

منتخب أندورا لكرة السلة أندورا التصنيف 77 ▲ 4 (16 سبتمبر 2019)[1] انضم للاتحاد الدولي 1988 منطفة فيبا الاتحاد الأوروبي لكرة السلة البلد أندورا الألعاب الأولمبية المشاركة لا يوجد الميداليات لا يوجد كأس العالم لكرة السلة المشاركة لا يوجد الميداليات لا يوجد بطولة أمم أوروبا لكر...

Colombian drug lord (1943–2012) In this Spanish name, the first or paternal surname is Blanco and the second or maternal family name is Restrepo. Griselda BlancoMugshot of Blanco in 1997BornGriselda Blanco Restrepo(1943-02-15)February 15, 1943Cartagena, Bolivar, Colombia[1]DiedSeptember 3, 2012(2012-09-03) (aged 69)Medellín, Antioquia, ColombiaCause of deathGunshot woundsOther namesLa Dama de la Mafia ('The Lady of the Mafia')The GodmotherThe Black WidowSpous...

Район 6(вьет. Quận 6) 10°44′46″ с. ш. 106°38′10″ в. д.HGЯO Страна Вьетнам Входит в Хошимин История и география Площадь 7,14 км2 Часовой пояс UTC+7 Официальный сайт Медиафайлы на Викискладе Район 6 (вьет. Quận 6) — городской район Хошимина, Вьетнам. По состоянию на 2010 год, ...

Tarte TatinJenisTartTempat asalPrancisDaerahCentre-Val de LoireDibuat olehTatin sistersBahan utamaApel atau buah lainnyaSunting kotak info • L • BBantuan penggunaan templat ini Buku resep: Tarte Tatin Media: Tarte Tatin Caroline dan Stéphanie Tatin Tarte Tatin (pengucapan bahasa Prancis: [taʁt tatɛ̃]), dinamakan berdasarkan nama Tatin bersaudari yang memperkenalkan dan menyajikannya di hotel mereka sebagai hidangan khas.[1] Kue ini sebenarnya kue kerin...

Este artículo o sección necesita referencias que aparezcan en una publicación acreditada. Busca fuentes: «Tácito» – noticias · libros · académico · imágenesEste aviso fue puesto el 30 de junio de 2020. Para otros usos de este término, véase Tácito (desambiguación). Tácito Estatua moderna que representa a Tácito en el exterior del edificio del parlamento austriaco.Información personalNombre de nacimiento Cornelio TácitoNombre en latín Publius Cornelius...

Challenge League 2005-2006Challenge League 2005-2006 Competizione Challenge League Sport Calcio Edizione 85ª Organizzatore ASF-SFV Luogo Svizzera Formula Girone all'italiana Cronologia della competizione 2004-2005 2006-2007 Manuale La stagione 2005-2006 della Challenge League vide la promozione in Super League del Lucerna. Indice 1 Classifica finale 2 Play-off promozione-retrocessione 3 Classifica marcatori 4 Note 5 Collegamenti esterni Classifica finale Pos. Squadra Pt G V N P GF GS DR 1. ...

Italian scholar and diplomat It has been suggested that portions of Botero be split from it and merged into this article. (Discuss) (June 2024) Giovanni BoteroBorn1544Bene Vagienna, Savoyard stateDied23 June 1617 (aged 72–73)Turin, Savoyard stateResting placeChiesa dei Santi MartiriEducation Roman College University of Padua Notable workThe Reason of StateEraBaroque philosophyRegionWestern philosophyNotable ideasReason of stateNational interest Giovanni Botero (c. 1544 – 1617) was an ...