Herbert Feigl
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Liga Angkatan Laut atau Asosiasi Armada (Jerman: Deutscher Flottenvereincode: de is deprecated ) di Kekaisaran Jerman adalah kelompok kepentingan yang dibentuk pada tanggal 30 April 1898 atas prakarsa Laksamana Alfred von Tirpitz melalui Kantor Angkatan Laut Kekaisaran Jerman (Reichsmarineamt) yang dipimpinnya (1897–1916) untuk mendukung perluasan Angkatan Laut Kekaisaran Jerman (Kaiserliche Marine) . Secara khusus itu dimaksudkan untuk mengembangkan tekanan populer di parlemen Jerman (Reic...

American art collective active during the Great Depression This article is about the New York–based Expressionist artists of the 1930s. For the earlier American Impressionist group of the same name, see the Ten American Painters. The TenFormation1935FoundersBen-ZionIlya BolotowskyAdolph GottliebLouis HarrisYankel KufeldMarcus RothkowitzLouis SchankerJoseph SolmanNahum TschacbasovDissolved1940TypeArtist's collectivePurposeExhibition of members' artwork outside mainstream venuesLocationNew Yo...

العلاقات الليبيرية المدغشقرية ليبيريا مدغشقر ليبيريا مدغشقر تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الليبيرية المدغشقرية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين ليبيريا ومدغشقر.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه الم...

1970 science fiction novel by Larry Niven Not to be confused with Discworld. Ringworld Paperback first editionAuthorLarry NivenIllustratorDean EllisCountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglishSeriesRingworld storyline from Known SpaceGenreScience fictionPublisherBallantine BooksPublication dateOctober 1970Media typePrint (hardcover, paperback), audiobookPages342 pagesAwardsLocus Award for Best Novel (1971)ISBN0-345-02046-4Followed byThe Ringworld Engineers, 1979 Ringworld is a 1970 sci...

Mixed-use in Kuala Lumpur, MalaysiaFairmont Kuala Lumpur Tower 1&2Construction site in April 2024General informationStatusOn holdTypeMixed-useLocationJalan Lumba Kuda, Kuala Lumpur, MalaysiaConstruction started2014[1]CompletedtbaHeightArchitectural370 m (1,214 ft)[2] 278 m (912 ft)[3]Technical detailsFloor count78[2] 71[3]Design and constructionDeveloperKLCC Holdings & QD Asia Pacific [2] Fairmont Kuala Lumpur Towers...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) The topic of this article may not meet Wikipedia's general notability guideline. Please help to demonstrate the notability of the topic by citing reliable secondary sources that are independent of the topic and provide significant coverage of it beyond a mere trivial mention. If notability cannot be shown, the article is likely to be merged,...

「俄亥俄」重定向至此。关于其他用法,请见「俄亥俄 (消歧义)」。 俄亥俄州 美國联邦州State of Ohio 州旗州徽綽號:七葉果之州地图中高亮部分为俄亥俄州坐标:38°27'N-41°58'N, 80°32'W-84°49'W国家 美國加入聯邦1803年3月1日,在1953年8月7日追溯頒定(第17个加入联邦)首府哥倫布(及最大城市)政府 • 州长(英语:List of Governors of {{{Name}}}]]) •&...

ヨハネス12世 第130代 ローマ教皇 教皇就任 955年12月16日教皇離任 964年5月14日先代 アガペトゥス2世次代 レオ8世個人情報出生 937年スポレート公国(中部イタリア)スポレート死去 964年5月14日 教皇領、ローマ原国籍 スポレート公国親 父アルベリーコ2世(スポレート公)、母アルダその他のヨハネステンプレートを表示 ヨハネス12世(Ioannes XII、937年 - 964年5月14日)は、ロ...

Cyclone 2A making landfall near Karachi at peak intensity as Category 3 equivalent hurricane in May 1999 Pakistan lies in the temperate zone. The climate is generally arid, characterized by the extreme southwestern part of the country where Gwadar and Karachi are the main port cities. Though cyclones are rare in the Arabian sea which a part of North Indian Ocean, cyclones that form in this sea mostly move towards Western India rather than Pakistan.[1] Cyclones in the Arabian sea form...

Town in New South Wales, AustraliaHowlongNew South WalesThe main street of HowlongHowlongCoordinates35°58′0″S 146°38′0″E / 35.96667°S 146.63333°E / -35.96667; 146.63333Population2,997 (2021 census Census)[1]Established1854Postcode(s)2643Location 582 km (362 mi) SW of Sydney 297 km (185 mi) NE of Melbourne 29 km (18 mi) W of Albury LGA(s)Federation CouncilCountyHumeState electorate(s)AlburyFederal division(s)Farrer...

1971 science fiction film from the Planet of the Apes franchise directed by Don Taylor This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Escape from the Planet of the Apes – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Escape from the Planet of the Ap...

Shipping Forecast adalah program BBC Radio yang menyiarkan laporan dan prakiraan cuaca di perairan sekitar Kepulauan Britania. Program ini diproduksi oleh Met Office dan disiarkan oleh BBC Radio 4 atas nama Maritime and Coastguard Agency. Siaran yang dikirimkan melalui sistem Navtex menggunakan format dan wilayah laut yang sama. Perairan sekitar Kepulauan Britania terbagi menjadi 31 wilayah laut, lebih dikenal dengan sebutan weather area (wilayah cuaca).[1] Setiap hari ada empat siara...

Proclamation granting citizen of Ethiopia Ethiopian Nationality ProclamationEthiopian Federal Parliamentary AssemblyEnacted byGovernment of EthiopiaStatus: Current legislation Ethiopian nationality law is regulated by the Constitution of Ethiopia, as amended; the Ethiopian Nationality Proclamation, and its revisions; and various international agreements to which the country is a signatory.[1] These laws determine who is, or is eligible to be, a national of Ethiopia.[2] T...

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang bentuk pemerintahan. Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Teknokrasi (disambiguasi). Bagian dari seri PolitikBentuk dasar dari pemerintahan Struktur kekuatan Konfederasi Federasi Hegemoni Kerajaan Negara kesatuan Sumber kekuatan Demokrasi Langsung Perwakilan Semi lainnya Kerajaan Mutlak Konstitusi Oligarki Aristokrasi Junta militer Kleptokrasi Plutokrasi Stratokrasi Timokrasi Otokrasi Otoritarianisme Despotisme Diktatur (Kediktatoran) Totalitarianisme Republik Pa...

L'orientamento sessuale è l'attrazione emozionale, romantica e/o sessuale di una persona verso individui di sesso opposto, dello stesso sesso o di entrambi i sessi.[1][2] I principali orientamenti sessuali sono l’eterosessualità, l’omosessualità e la bisessualità,[3][4][5] mentre l'asessualità è talvolta identificata come la quarta categoria.[6][7] L'orientamento sessuale non sembra essere una scelta.[8][9]&...

1958 film The Csardas KingDirected byHarald PhilippWritten byHelmuth M. BackhausJanne FurchHarald PhilippCurt RiessLeo SteinHans WilhelmProduced byArtur BraunerStarringGerhard RiedmannRudolf SchockElma KarlowaCinematographyFritz Arno WagnerEdited byJohanna MeiselMusic byEmmerich KalmanProductioncompanyCCC FilmDistributed byConstantin FilmRelease date 15 August 1958 (1958-08-15) Running time96 minutesCountryWest GermanyLanguageGerman The Csardas King (German: Der Czardas-König)...
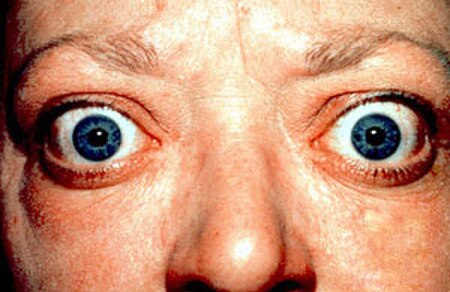
Penyakit Basedow atau Graves Penyakit Basedow atau penyakit graves adalah kondisi medis yang ditandai dengan kadar hormon tiroid yang berlebihan akibat produksi berlebihan oleh kelenjar tiroid.[1][2] Kelenjar tiroid adalah bagian dari sistem endokrin yang terletak di bawah pita suara yang berperan dalam menghasilkan hormon seperti tiroid.[1] Pasien menunjukkan kelenjar tiroid yang membesar merata atau menyeluruh.[2] Kelenjar tetap teraba lunak, tidak keras sepe...

37th DivisionFormation sign of the 37th Division.[1]ActiveMarch 1915 – March 1919Country United KingdomBranch British ArmyTypeInfantrySizeDivisionEngagementsFirst World War Battles of the Somme Battle of the Ancre Battle of Arras (1917) First Battle of the Scarpe Monchy le Preux Second Battle of the Scarpe Battle of Arleux Battles of Ypres Battle of Pilckem Ridge Battle of Menin Road Battle of Polygon Wood Battle of Broodseinde Battle of Poelcapelle First Battle of Passch...

Battle of the Cuban Revolution Operation VeranoPart of the Cuban RevolutionDate28 June 1958 – 8 August 1958(1 month, 1 week and 4 days)LocationSierra Maestra hills, CubaResult Rebel victory The rebels launch a counter-offensiveBelligerents Republic of Cuba 26th of July MovementCommanders and leaders General Eulogio Cantillo General Alberto del Rio Chaviano Fidel Castro Che Guevara René Ramos Latour †Strength 12,000 men 300 menCasualties and losses 207 killed...

Voce principale: 1. Fußball-Club Nürnberg Verein für Leibesübungen. 1. Fußball-Club Nürnberg Verein für LeibesübungenStagione 1995-1996Sport calcio Squadra Norimberga Allenatore Hermann Gerland (1ª-27ª) Willi Entenmann (28ª-34ª) 2. Bundesliga17º posto Coppa di GermaniaQuarti di finale Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Ćurko (34)Totale: Ćurko (38) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Moore (8)Totale: Moore (10) StadioFrankenstadion Maggior numero di spettatori29 000 vs. Wolfsburg ...
