Harlem–125th Street station
|
Read other articles:

Amir MoradiAmir Moradi pada 2017Informasi pribadiLahir10 April 1990 (umur 33)Gandoman, IranTinggi187 m (613 ft 6 in)[1]Berat68 kg (150 pon) OlahragaOlahragaAtletikLomba800 m, 1500 m Amir Moradi (Persia: امیر مرادیcode: fa is deprecated ; lahir 10 April 1990, di Gandoman) adalah seorang atlet lari jarak menengah asal Iran yang mengkhususkan diri dalam lomba 800 meter.[2] Ia memenangkan medali perunggu pada Pesta Olahraga Dalam Ruangan dan ...

Buildings in the West End of Fremantle, Western Australia For Commissariat Building in Ottawa, see Bytown Museum. For the Commissariat Store in Brisbane, see Commissariat Store, Brisbane. For the former Commissariat Store in Sydney, see Sydney Cove West Archaeological Precinct. Commissariat BuildingsThe south façade of the Commissariat buildings as viewed from opposite Marine Terrace in 2013General informationTypeMuseumLocationFremantle, Western AustraliaCoordinates32°03′25″S 115°44′...
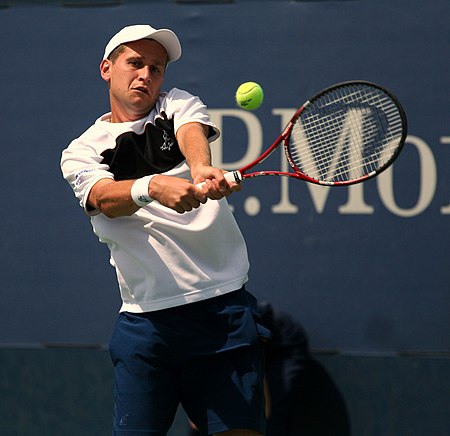

Slovak professional tennis player Karol BeckCountry (sports) SlovakiaResidenceZvolen, SlovakiaBorn (1982-04-03) 3 April 1982 (age 41)Zvolen, CzechoslovakiaHeight1.80 m (5 ft 11 in)Turned pro2001Retired2018 (last match in 2020)PlaysRight-handed (two-handed backhand)Prize money$2,110,846SinglesCareer record65–116Career titles0Highest rankingNo. 36 (22 August 2005)Grand Slam singles resultsAustralian Open3R (2005)French Open1R (2003, ...

العلاقات المالديفية القبرصية قبرص المالديف قبرص تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات المالديفية القبرصية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين المالديف وقبرص.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارنة [[تصنيف:ص�...

Kraft durch FreudeEmblema della Kraft durch Freude AbbreviazioneKdF Fondazione27 novembre 1933 FondatoreRobert Ley del Deutsche Arbeitsfront Scioglimento1945 ScopoAttività ricreative Sede centrale Berlino PresidenteRobert Ley Lingua ufficialeTedesco Bilancio538 milioni di Reichsmark (DAF) (1939) Impiegati4.400 (1937) Volontari106.000 (1937) MottoKraft durch Freude Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale La Kraft durch Freude (in italiano forza attraverso la gioia, abbreviato in KdF), era u...

Bosnia dan Herzegovina padaOlimpiadeKode IOCBIHKONKomite Olimpiade Bosnia dan HerzegovinaSitus webwww.okbih.ba (dalam bahasa Bosnia)Medali 0 0 0 Total 0 Penampilan Musim Panas19921996200020042008201220162020Penampilan Musim Dingin19941998200220062010201420182022Penampilan terkait lainnya Yugoslavia (1920–1992 W) Bosnia dan Herzegovina mengirim para atlet ke Olimpiade Musim Panas di bawah bendera mereka sendiri untuk pertama kalinya pada 1992. Para atlet Bosnia berkompeti...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento giornalisti non è ancora formattata secondo gli standard. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Mauro Mazza (2023) Mauro Mazza (Roma, 18 agosto 1955) è un giornalista e scrittore italiano. Indice 1 Carriera 1.1 Gli inizi da giornalista 1.2 Gli inizi in Rai e la vicedirezione del TG1 1.3 La direzione del TG2 1.4 La direzione della rete ammiraglia 1.5 La direzione di Rai Spor...

Style of formal logical argumentation In mathematical logic, sequent calculus is a style of formal logical argumentation in which every line of a proof is a conditional tautology (called a sequent by Gerhard Gentzen) instead of an unconditional tautology. Each conditional tautology is inferred from other conditional tautologies on earlier lines in a formal argument according to rules and procedures of inference, giving a better approximation to the natural style of deduction used by mathemati...

Santo Nikolaus dari Myra Santo Nikolaus dari Myra, yang dieja pula dengan nama Nikolas, adalah seorang uskup yang sangat populer yang berasal dari Myra.[1] Ia pernah dipenjarakan di bawah pemerintahan Kaisar Dioklesianus.[1] Nikolaus adalah santo pelindung Rusia, para pelaut dan anak-anak.[1] Pada hari pestanya pada tanggal 6 Desember, ia membawa berbagai macam hadiah untuk anak-anak.[1] Santo Nikolaus dikenal sebagai santo yang sangat baik hati dan oleh karena...

Koordinat: 6°20′03″S 106°49′17″E / 6.3343°S 106.8215°E / -6.3343; 106.8215 JagakarsaKecamatanNegara IndonesiaProvinsi DKI JakartaKota AdministrasiJakarta SelatanPemerintahan • CamatH. Santoso, SH, M.A.PPopulasi • Total311,484 diri (2.019)[1] jiwaKode Kemendagri31.74.09 Kode BPS3171010 Desa/kelurahan6 Kecamatan Jagakarsa terletak di Jakarta Selatan. Di kecamatan ini terletak beberapa universitas ternama antara lain Polite...

This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (September 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) The Port Olímpic (English: Olympic Harbour) is a marina located in Barcelona, Catalonia. Located east of the Port of Barcelona, it hosted the sailing events for the 1992 Summer Olympics. It will be the main venue for ...

Dutch swimmer (born 1943) For the Dutch gymnast, see Ria van Velsen (gymnast). Ria van Velsen Medal record Women's swimming Representing the Netherlands European Championships 1962 Leipzig 100 m backstroke 1962 Leipzig 4×100 m medley Maria Martina Ria van Velsen (born 22 March 1943 in The Hague) is a retired Dutch backstroke swimmer who participated in the 1960 and 1964 Summer Olympics. In 1960, she was sevenths individually in the 100m backstroke event. She was also part of the Dutch ...

Outdoor team game from Cornwall, England For the Gaelic sport from Ireland, see Hurling. Former Pub sign at St Columb Major Hurling (Cornish: Hurlian) is an outdoor team game played only in Cornwall, England, played with a small silver ball. While the sport shares its name with the Irish game of hurling, the two sports are completely different. Once played widely in Cornwall, the game has similarities to other traditional football or inter parish 'mob' games played in various parts of Britain...

Swedish singer (born 1984) Elize RydRyd performing in 2024Background informationBirth nameHanna Elise Isabell Maj Höstblomma RydBorn (1984-10-15) 15 October 1984 (age 39)Värnamo, SwedenGenresPower metalmetalcoremelodic black metalmelodic death metalsymphonic metalpop metalOccupation(s)SingerYears active2003–presentMember ofAmarantheRaskasta JouluaWebsiteelizeryd.comMusical artist Hanna Elise Isabell Maj Höstblomma Ryd (born 15 October 1984), known professionally as Elize Ryd (Swedis...

A proton conductor in a static electric field. Ionic conductivity (denoted by λ) is a measure of a substance's tendency towards ionic conduction. Ionic conduction is the movement of ions. The phenomenon is observed in solids and solutions. Ionic conduction is one mechanism of current.[1] In crystalline solids In most solids, ions rigidly occupy fixed positions, strongly embraced by neighboring atoms or ions. In some solids, selected ions are highly mobile allowing ionic conduction. T...

American Army men's basketball team Army Black Knights 2023–24 Army Black Knights men's basketball team UniversityUnited States Military AcademyHead coachKevin Kuwik (1st season)ConferencePatriotLocationWest Point, New YorkArenaChristl Arena (Capacity: 5,043)NicknameBlack KnightsColorsBlack, gold, and gray[1] Uniforms Home Away Pre-tournament Premo-Porretta champions1923, 1944Pre-tournament Helms champions1944 The Army Black Knights men's ...

سوبرتان 2002 تفاصيل الموسم سوبرتان البلد السويد التاريخ بداية:11 أبريل 2002 نهاية:26 أكتوبر 2002 البطل نادي أوسترس مباريات ملعوبة 240 عدد المشاركين 16 الموقع الرسمي الموقع الرسمي سوبرتان 2001 سوبرتان 2003 تعديل مصدري - تعديل سوبرتان 2002 (بالسويدية: Sup...
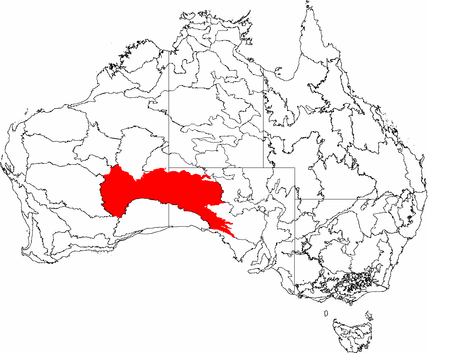
صحراء فكتوريا الكبرى الإحداثيات 29°09′08″S 129°15′35″E / 29.152222222222°S 129.25972222222°E / -29.152222222222; 129.25972222222 سبب التسمية فيكتوريا ملكة المملكة المتحدة تقسيم إداري البلد أستراليا[1] التقسيم الأعلى أستراليا الغربيةجنوب أستراليا خصائص جغرافية ا...

American baseball player (1954–1989) Baseball player Donnie MoorePitcherBorn: February 13, 1954Lubbock, Texas, U.S.Died: July 18, 1989(1989-07-18) (aged 35)Anaheim, California, U.S.Batted: LeftThrew: RightMLB debutSeptember 14, 1975, for the Chicago CubsLast MLB appearanceAugust 7, 1988, for the California AngelsMLB statisticsWin–loss record43–40Earned run average3.67Strikeouts416Saves89 Teams Chicago Cubs (1975, 1977–1979) St. Louis Cardinals (1980)...

1908 academic conference held to standardize the Albanian alphabet The core commission of the Congress: 1. Gjergj Fishta 2. Mid'hat Frashëri 3. Luigj Gurakuqi 4. Gjergj Qiriazi 5. Dom Ndre Mjeda 6. Grigor Cilka 7. Dhimitër Buda 8. Shahin Kolonja 9. Sotir Peci 10. Bajo Topulli 11. Nyz'het Vrioni Photo by Kel Marubi The Congress of Manastir (Albanian: Kongresi i Manastirit) was an academic conference held in the city of Manastir (now Bitola) from November 14 to 22, 1908, with the goal of stan...


