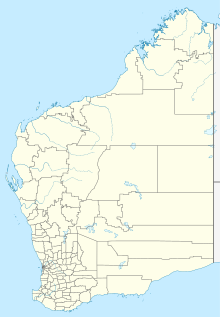
Gwalia Gold Mine
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

العلاقات البيلاروسية اللاوسية روسيا البيضاء لاوس روسيا البيضاء لاوس تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات البيلاروسية اللاوسية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين روسيا البيضاء ولاوس.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدول...

Fashion is known to be a form of expression throughout many cultures, just like the Mexican American culture. Over the decades Mexican American women's fashion evolved to celebrate beauty and fashion standards of the day. However, such evolution wasn't often well seen by society, instead it was often deemed non-normative or un-American. This style evolution started in the 1920's with American influence creating the Pelonas, the1940s when the Pachuca culture came to be, and later evolved into ...

Documentation[voir] [modifier] [historique] [purger] Ce modèle respecte les conventions des Infobox V2. Les infobox version 2 améliorent l’aspect, la simplicité et la flexibilité des infobox de Wikipédia. L’intérêt est d’harmoniser l’apparence par des feuilles de style en cascade, des pictogrammes thématiques, une simplification du code ainsi que la possibilité de généricité qui consiste à fusionner plusieurs modèles en un seul ...

Catholic church in Scarsdale, New York Church in Scarsdale, New YorkChurch of the Immaculate Heart of MaryFront of the church on White Plains Post Road40°58′54″N 73°47′57″W / 40.98167°N 73.79917°W / 40.98167; -73.79917LocationScarsdale, New YorkDenominationCatholic ChurchWebsiteihm-parish.orgHistoryStatusParish churchFounded1912DedicationImmaculate Heart of MaryArchitectureStyleEnglish GothicGroundbreakingAugust 1913AdministrationArchdioceseArchdiocese of N...

Japanese pizza chain You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Japanese. (February 2012) Click [show] for important translation instructions. View a machine-translated version of the Japanese article. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated t...

Artikel atau sebagian dari artikel ini mungkin diterjemahkan dari Aamir Khan filmography di en.wikipedia.org. Isinya masih belum akurat, karena bagian yang diterjemahkan masih perlu diperhalus dan disempurnakan. Jika Anda menguasai bahasa aslinya, harap pertimbangkan untuk menelusuri referensinya dan menyempurnakan terjemahan ini. Anda juga dapat ikut bergotong royong pada ProyekWiki Perbaikan Terjemahan. (Pesan ini dapat dihapus jika terjemahan dirasa sudah cukup tepat. Lihat pula: panduan p...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada April 2024. Pemerintahan kolaboratif adalah strategi pengelolaan pemerintahan yang melibatkan pemangku kepentingan di luar pemerintah secara langsung, bertujuan untuk melaksanakan kebijakan publik dan program-program publik, serta berorientasi pada konsensus dan mus...

Coppa di Francia 1964-1965Coupe de France 1964-1965 Competizione Coppa di Francia Sport Calcio Edizione 48ª Organizzatore Federazione calcistica della Francia Luogo Francia Risultati Vincitore Rennes(1º titolo) Secondo Sedan-Torcy Semi-finalisti Saint-Étienne Stade Français Cronologia della competizione 1963-1964 1965-1966 Manuale La Coppa di Francia 1964-1965 è stata la 48ª edizione della coppa nazionale di calcio francese. Indice 1 Risultati 1.1 Trentadue...

Навчально-науковий інститут інноваційних освітніх технологій Західноукраїнського національного університету Герб навчально-наукового інституту інноваційних освітніх технологій ЗУНУ Скорочена назва ННІІОТ ЗУНУ Основні дані Засновано 2013 Заклад Західноукраїнський �...

Imperial Japan's use of the Shinto religion Part of a series onShinto Beliefs Kami List of deities Polytheism Animism/Animatism Mythology Sacred objects Sects and schools Major kami Amaterasu Ame-no-Uzume Inari Izanagi Izanami Susanoo Tsukuyomi Important literature Kojiki (c. 711 CE) Nihon Shoki (720 CE) Fudoki (713–723 CE) Shoku Nihongi (797 CE) Kogo Shūi (807 CE) Kujiki (807–936 CE) Engishiki (927 CE) Shinto shrines List of Shinto shrines Ichinomiya Twenty-Two Shrines Modern syst...

For the novel, see The Luck of Ginger Coffey (novel). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: The Luck of Ginger Coffey film – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) 1964 Canadian filmThe Luck of Ginger CoffeyDVD coverDirected byIrv...
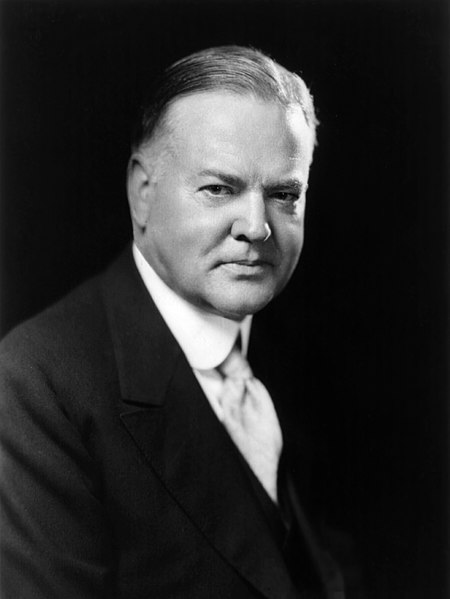

Foreign policy of Herbert Hoover covers the international activities and policies of Herbert Hoover for his entire career, with emphasis to his roles from 1914 to 1933. American Relief Administration (ARA) American relief mission to Russia headed by Herbert Hoover 1921 Hoover had many interests around the world: Belgian relief in 1914-1917. He worked with Berlin and London to allow shipments of food to Belgium. Food: When the US entered the war in 1917 Hoover left London and headed the new U....

Lighthouse in Staten Island, New York LighthouseFort Tompkins Light LocationFort Wadsworth on Staten IslandCoordinates40°36′21″N 74°03′14″W / 40.6057°N 74.0539°W / 40.6057; -74.0539TowerConstructed1828Height40 feet (12 m)MarkingsTower on white dwelling with Mansard roof; lantern, black.LightFirst lit1873LensFourth Order Fresnel lensCharacteristicFlashing alternately red and white, interval between flashes 10 seconds Fort Tompkins Light was a lighth...

منتخب جمهورية الدومينيكان لكرة السلة جمهورية الدومينيكان التصنيف 19 ▼ 1 (16 سبتمبر 2019)[1] انضم للاتحاد الدولي 1954 منطفة فيبا اتحاد الأمريكتين لكرة السلة المدرب نيستور غارسيا (كرة سلة) البلد جمهورية الدومينيكان الألعاب الأولمبية المشاركة لا يوجد الميداليات لا يوجد كأس ...

American football player (born 1980) American football player Michael VickVick in 2017No. 7, 1, 2Position:QuarterbackPersonal informationBorn: (1980-06-26) June 26, 1980 (age 44)Newport News, Virginia, U.S.Height:6 ft 0 in (1.83 m)Weight:210 lb (95 kg)Career informationHigh school:Warwick(Newport News, Virginia)College:Virginia Tech (1998–2000)NFL draft:2001 / Round: 1 / Pick: 1Career history As a player: Atlanta Falcons (2001–2008) Philad...

American government official (born 1944) Bernard D. RostkerUnited States Under Secretary of Defense for Personnel and ReadinessIn officeMay 23, 2000 – June 2001PresidentBill ClintonGeorge W. BushPreceded byCharles Cragin (acting)Succeeded byDavid S. C. ChuUnited States Under Secretary of the ArmyIn officeOctober 1998 – May 23, 2000PresidentBill ClintonPreceded byRobert M. WalkerSucceeded byGregory R. DahlbergUnited States Assistant Secretary of the Navy for Manpower and ...

For the observatory in Mount Pleasant, Michigan, see Brooks Astronomical Observatory. ObservatoryBrooks ObservatoryOrganizationUniversity of ToledoLocationOhio, USCoordinates41°39′45″N 83°36′41.6″W / 41.66250°N 83.611556°W / 41.66250; -83.611556Websitewww.rpbo.utoledo.eduTelescopesUnnamed6 inch RefractorLocation of Brooks Observatory[edit on Wikidata] Brooks Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by the University of Toledo. The o...

Paris-Nice 1985GénéralitésCourse Paris-NiceCompétition Super Prestige Pernod 1985 (d)Étapes 9 étapes + 1 prologueDate 3 au 10 mars 1985Distance 1 187 kmPays FranceLieu de départ NanterreLieu d'arrivée Col d'ÈzeCoureurs au départ 86Coureurs à l'arrivée 58Vitesse moyenne 31 h 10 min 19 s 38,079 km/hRésultatsVainqueur Sean Kelly (IRL) (Skil-Sem)Deuxième Stephen RocheTroisième Frédéric VichotMeilleur grimpeur Jean-Claude Bagot (Fagor)Meilleur jeune Charly Mottet (Renault-Elf)Pari...

This biography of a living person needs additional citations for verification. Please help by adding reliable sources. Contentious material about living persons that is unsourced or poorly sourced must be removed immediately from the article and its talk page, especially if potentially libelous.Find sources: Rachel Billington – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Lady Rachel BillingtonOBE...

Pour des articles plus généraux, voir Chronologie des États-Unis et 1991. Éphémérides Chronologie des États-Unis 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994Décennies aux États-Unis :1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 2020 Chronologie dans le monde 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994Décennies :1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 2020Siècles :XVIIIe XIXe XXe XXIe XXIIeMillénaires :-Ier Ier IIe IIIe Chronologies ...