Franco Pacini
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Un Cessna 140 in volo Le regole del volo a vista, in inglese visual flight rules, abbreviate in VFR, sono l'insieme delle norme e procedure cui un pilota deve attenersi per condurre in sicurezza un volo, utilizzando principalmente la propria vista, ossia senza la necessità di affidarsi a radioassistenze per la navigazione, la quale quindi può essere condotta basandosi sull'osservazione del terreno (cosiddetta navigazione osservata) o sulla previsione di avanzamento in intervalli di tempo pr...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Mesin ATM Bitcoin di California, Amerika Serikat, Mesin ini memungkinkan transaksi dua arah untuk menjual dan membeli Bitcoin menggunakan uang tunai. ATM Bitcoin adalah kios yang memungkinkan pengguna untuk membeli Bitcoin atau mata uang kripto l...

Terapi khelasiIntervensiDua molekul deferasiroks, khelator yang dimasukkan lewat mulut. Bahan ini dapat mengikat besi dan digunakan untuk mengatasi kelebihan besi transfusional pada pengidap talasemia.[sunting di Wikidata] Terapi khelasi adalah prosedur medis yang menggunakan bahan-bahan khelasi untuk menghilangkan logam berat dari tubuh.[1] Terapi khelasi telah lama digunakan dalam bidang toksikologi klinis,[2] walaupun penggunaannya harus diawasi dengan sangat teliti kar...

Rural district in Tehran province, Iran Rural District in Tehran, IranSulqan Rural District Persian: دهستان سولقانRural DistrictSulqan Rural DistrictCoordinates: 35°52′35″N 51°14′06″E / 35.87639°N 51.23500°E / 35.87639; 51.23500[1]CountryIranProvinceTehranCountyTehranDistrictKanElevation1,600−1,750 m (−4,140 ft)Population (2016)[2] • Total5,013Time zoneUTC+3:30 (IRST) Sulqan Rural District...

Des navires de l'OTAN dans l'Adriatique en mars 1995 lors de l'opération Sharp Guard. L'operation Sharp Guard est une opération conjointe entre l'OTAN et l'Union de l'Europe occidentale pour s'assurer de l'application des sanctions économiques et de l'embargo sur les armes décidés par de nombreuses résolutions du Conseil de sécurité des Nations unies contre l'ancienne République fédérale de Yougoslavie. Elle commença le 15 juin 1993, fut suspendue le 19 juin 1996 et prit officiel...

London Overground station South Tottenham South Tottenham stationSouth TottenhamLocation of South Tottenham in Greater LondonLocationSouth TottenhamLocal authorityLondon Borough of HaringeyManaged byLondon OvergroundOwnerNetwork RailStation codeSTODfT categoryENumber of platforms2AccessibleYes[1]Fare zone3OSISeven Sisters [2]National Rail annual entry and exit2018–19 1.169 million[3]2019–20 0.948 million[3]2020–21 0.683 million[3]2021–22 1.054 m...

Agostino Pantò Agostino Pantò (Alcamo, 11 settembre 1675 – Palermo, 11 giugno 1735) è stato un teologo, oratore e giurista italiano. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Opere 3 Note 4 Bibliografia 5 Voci correlate 6 Collegamenti esterni Biografia Agostino Pantò nacque ad Alcamo l'11 settembre 1675 e qui fece i primi suoi studi. Era un discendente dei Conti di Pierras in Catalogna;[1] fin da giovane evidenziò alte capacità intellettive. All'età di sedici anni, indossato l'abito talare, si tr...

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目的引用需要清理,使其符合格式。参考文献应符合正确的引用、脚注及外部链接格式。 此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充,此條目在對應語言版為高品質條目。 (2023年8月17日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低�...

Location of Tyler County in Texas This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Tyler County, Texas. This is intended to be a complete list of properties listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Tyler County, Texas. There are three properties listed on the National Register in the county. One property is also a Recorded Texas Historic Landmark. This National Park Service list is complete through NPS recent listin...

Cemal PashaLahir(1872-05-06)6 Mei 1872Midilli, Kesultanan UtsmaniyahMeninggal21 Juli 1922(1922-07-21) (umur 50)Tbilisi, Republik Sosialis Soviet GeorgiaPengabdian Kesultanan UtsmaniyahLama dinas1893–1918PangkatJenderalKesatuanMenteri Angkatan LautKomandanAngkatan Darat KeempatPerang/pertempuranPeperangan Balkan, kampanye militer Sinai dan Palestina, kampanye militer Mesopotamia (1915-1917) Ahmed Djemal Pasha (Turki Otoman: احمد جمال پاشا, modern Turki: Ahm...

1992–1998 removal and flight of Georgians from Abkhazia Ethnic cleansing of Georgians in AbkhaziaA visitor at a gallery recognizes her dead son in a photograph on the 12th anniversary of the ethnic cleansing in Abkhazia, 2005.LocationAbkhazia, GeorgiaDate1992–1998TargetGeorgian population, Oppositions to the new Government of AbkhaziaAttack typeEthnic cleansing, Massacres, Deportations, othersDeaths5,000–5,738 killed[1]Victims200,000[2] – 267,345[1] displaced, ...

American conservative political website FrontPage MagazineFormatOnlineOwner(s)David Horowitz Freedom CenterEditor-in-chiefDavid HorowitzManaging editorJamie GlazovPolitical alignmentRight-wing to far-rightLanguageEnglishHeadquartersSherman Oaks, California, U.S.OCLC number47095728 Websitefrontpagemag.com FrontPage Magazine, also known as FrontPageMag.com, is an American right-wing,[1][2][3][4] anti-Islam[5][6] political website edited by David H...

AlbeseNama lengkapAssociazione Sportiva Dilettantistica Albese CalcioBerdiri1917StadionStadio San Cassiano,Alba, Italy(Kapasitas: 2,050)KetuaPiero CorneroManajerGiancarlo RossoLigaEccellenza2011-12Serie D/A, 17th Kostum kandang Kostum tandang Associazione Sportiva Dilettantistica Albese Calcio adalah sebuah klub sepak bola Italia, yang berada di Alba, Piedmont. Albese saat ini bermain di Eccellenza Piedmont dan Aosta Valley. Templat:Eccellenza Piedmont dan Aosta Valley lbsSerie D Klub 2019–...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Baby, Baby Don't Cry – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message) 1968 single by Smokey Robinson & the MiraclesBaby, Baby Don't CrySingle by Smokey Robinson & the Miraclesfrom the album Time Ou...
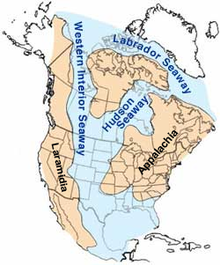
Laramidia sekitar 100 juta tahun yang lalu Laramidia adalah sebuah benua yang pernah ada pada zaman Kapur Akhir (99,6 hingga 66 juta tahun yang lalu) di Amerika Utara bagian barat ketika Western Interior Seaway memisahkan benua Laramidia dari Appalachia. Laut ini pada akhirnya menyusut dan benua Amerika Utara pun bersatu. Benua ini dinamai dari Laramie, Wyoming. Nama ini sendiri dicetuskan oleh J. David Archibald pada tahun 1996.[1] Geografi Laramidia terbentang dari Alaska hingga Mek...

2017 Australian TV series or program Hell's Kitchen AustraliaGenreRealityPresented byMarco Pierre WhiteCountry of originAustraliaOriginal languageEnglishNo. of series1No. of episodes15ProductionExecutive producerMatt AppsProduction locationsSydney, New South WalesProduction companyITV Studios AustraliaOriginal releaseNetworkSeven NetworkRelease6 August (2017-08-06) –5 September 2017 (2017-09-05) Hell's Kitchen Australia is an Australian cooking reality competition television...

Cuban architect This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Mario Romañach – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Mario RomañachBorn1917 (1917)Havana, CubaDied1984 (aged 66–67)PhiladelphiaAlma materUniversity of Hav...

アムリトサル ਅੰਮ੍ਰਿਤਸਰ, अमृतसर, Amritsar 夜のハリマンディル・サーヒブ 位置 アムリトサルアムリトサル (パンジャーブ州)パンジャーブ州の地図を表示アムリトサルアムリトサル (インド)インドの地図を表示 座標 : 北緯31度38分24秒 東経74度51分36秒 / 北緯31.64000度 東経74.86000度 / 31.64000; 74.86000 行政 国 インド 州 パンジャーブ州 ...

This article is about the conservation park in South Australia. For the islets, see Beatrice Islets. Protected area in South AustraliaBeatrice Islet Conservation ParkSouth AustraliaIUCN category Ia (strict nature reserve)[1] Beatrice Islet Conservation ParkNearest town or cityKingscote[2]Coordinates35°38′23″S 137°40′46″E / 35.63972°S 137.67944°E / -35.63972; 137.67944Established16 March 1967[3]Area1.03 km2 (0.4 sq mi)&...

French geographer (1837–1916) Onésime Reclus (1837–1916) Onésime Reclus (22 September 1837[1] – 30 June 1916) was a French geographer who specialized in the relations between France and its colonies. In 1880 he coined the term Francophonie as a means of classification of peoples of the world, being determined by the language they all spoke.[2] While this term did not appear in dictionaries until 1930, it has become more important since the late 20th century as part of ...