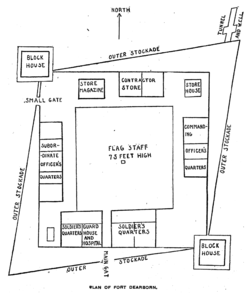
Fort Dearborn
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

SM Culture UniverseDiciptakan olehSM EntertainmentPemilikSM EntertainmentTahun2020-sekarang SM Culture Universe (SMCU) adalah alam semesta fiktif yang diproduksi oleh SM Entertainment. Perkembangan Pada tahun 2004, SM Entertainment telah bekerja untuk memproduksi alam semesta budaya mereka sendiri.[1] Selama tahap perencanaan, Lee Soo-man berpikir untuk menciptakan pandangan dunia dengan penceritaan yang inovatif dan kuat.[2] Ia menganggap bahwa berkreasi, menyampaikan cerita,...

Harnaaz SandhuHarnaaz Sandhu, Miss Universe 2021LahirHarnaaz Kaur Sandhu03 Maret 2000 (umur 24)Gurdaspur, Punjab, IndiaPekerjaanModelratu kecantikanaktrisTinggi175 cm (5 ft 9 in)Pemenang kontes kecantikanGelar Femina Miss India Punjab 2019 Miss Diva Universe 2021 Miss Universe 2021 Warna rambutHitamWarna mataCoklatKompetisiutama Femina Miss India 2019(12 Besar) Miss Diva 2021(Pemenang – Miss Diva Universe 2021) Miss Universe 2021(Pemenang) Harnaaz Kaur Sandhu (lahir 3 M...

Arkansas gubernatorial election 1938 Arkansas gubernatorial election ← 1936 8 November 1938 1940 → Nominee Carl E. Bailey Charles F. Cole Party Democratic Republican Popular vote 118,696 12,077 Percentage 86.32% 8.78% Governor before election Carl E. Bailey Democratic Elected Governor Carl E. Bailey Democratic Elections in Arkansas Federal government Presidential elections 1836 1840 1844 1848 1852 1856 1860 1868 1872 1876 1880 1884 1888 1892 1896 1900 1904 19...

American professional field lacrosse league Premier Lacrosse LeagueCurrent season, competition or edition: 2023 Premier Lacrosse League seasonSportField lacrosseFounded2018FounderMike Rabil, and Paul RabilFirst season2019No. of teams8Countries United States CanadaHeadquartersEl Segundo, CaliforniaMost recentchampion(s)Archers LC(1st title)Most titlesWhipsnakes LC(2 titles)TV partner(s)ESPNABCESPN2ESPN+Official websitepremierlacrosseleague.com Premier Lacrosse League (PLL) is an Amer...

Radio station in Rome, Georgia WLAQRome, GeorgiaBroadcast areaRome metropolitan area, GeorgiaFrequency1410 kHzBrandingAM 1410ProgrammingFormatNews Talk InformationAffiliationsCBS News RadioOwnershipOwnerCripple Creek Broadcasting CompanyTechnical informationFacility ID14502ClassBPower1,000 watts day1,000 watts nightTransmitter coordinates34°15′43.00″N 85°12′22.00″W / 34.2619444°N 85.2061111°W / 34.2619444; -85.2061111Translator(s)96.9 W245DG (Rome)Link...

Shi Pei PuLahir(1938-12-21)21 Desember 1938Shandong, TiongkokMeninggal30 Juni 2009(2009-06-30) (umur 70)Paris, PrancisKebangsaanTiongkokAlmamaterUniversitas KunmingPekerjaanPenyanyi opera, mata-mataPasanganBernard BoursicotAnakShi Dudu Shi Pei Pu Hanzi tradisional: 時佩璞 Hanzi sederhana: 时佩璞 Alih aksara Mandarin - Hanyu Pinyin: Shí Pèipú - Wade-Giles: Shih P'eip'u - Gwoyeu Romatzyh: Shyr Peypwu Shi Pei Pu (Hanzi: 时佩璞; Pinyin: Shí Pèipú; 21 Desember 1938 –...

Maître de la Légende de sainte LucieMaître de la Légende de sainte Lucie, Marie, reine des Cieux, Washington, National Gallery of Art.BiographieDécès BrugesActivité PeintrePériode d'activité vers 1475 - vers 1506Autres informationsMouvement Primitif flamandŒuvres principales Légende de sainte Lucie (daté 1480), Bruges, Église Saint-Jacques. Adoration des Mages, Cincinnati, Art Museum. Triptyque de la Lamentation, Minneapolis, Minneapolis Institute of Arts. Triptyque de la Lamenta...

2010 film directed by Julie Taymor The TempestTheatrical release posterDirected byJulie TaymorScreenplay byJulie TaymorBased onThe Tempestby William ShakespeareProduced byJulie TaymorRobert ChartoffLynn HendeeJulia Taylor-StanleyJason K. LauStarringHelen MirrenRussell BrandReeve CarneyTom ContiChris CooperAlan CummingDjimon HounsouFelicity JonesAlfred MolinaDavid StrathairnBen WhishawCinematographyStuart DryburghEdited byFrançoise BonnotMusic byElliot GoldenthalProductioncompaniesTouchstone ...

British documentary filmmaker (1907–1950) Humphrey JenningsJennings in Poets' Corner, Westminster Abbey, suggesting a shot to Chick Fowle of the Crown Film UnitBornFrank Humphrey Sinkler Jennings19 August 1907Walberswick, Suffolk, EnglandDied24 September 1950 (aged 43)Poros, GreeceAlma materPembroke College, CambridgeOccupationDocumentary filmmakerKnown forWorld War II film propaganda Frank Humphrey Sinkler Jennings (19 August 1907 – 24 September 1950) was an English documentary...

Sports season 2008 Champ Car seasonChamp Car World SeriesSeasonRaces14Start dateApril 20End dateNovember 9Awards← 20072009 (ICS) → The 2008 Champ Car World Series season would have been the 5th season of the Champ Car World Series and 30th season of the series dating back to the 1979 formation of Championship Auto Racing Teams (CART). It was scheduled to begin on April 20, 2008, and end on November 9. The season was canceled on February 21, 2008, because of the buyout of...

Romanian traditional sport For the village in Estonia, see Oina, Estonia. OinăHighest governing bodyRomanian Oină FederationFirst played1364 (first documented)1899 (modern rules)CharacteristicsContactYes, players are hit with the ball, but no body contactTeam members11 per sideTypeOutdoorEquipmentOină ballVenueOină pitchPresenceOlympicno Oină (Romanian pronunciation: [ˈoj.nə]) is a Romanian traditional bat-and-ball game, similar in many ways to baseball.[1] History...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando lo stadio a Praga detto T-Mobile Arena dell 2002 al 2008, vedi Tipsport Arena (Praga). Questa voce sugli argomenti arene di pallacanestro degli Stati Uniti d'America e stadi di calcio degli Stati Uniti d'America è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Questa voce sull'argomento architetture di Las Vegas è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. T-Mobile ArenaTh...

Голубянки Самец голубянки икар Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ПервичноротыеБез ранга:ЛиняющиеБез ранга:PanarthropodaТип:ЧленистоногиеПодтип:ТрахейнодышащиеНадкласс:ШестиногиеКласс...

岸信介佐藤信介 日本第56、57任內閣總理大臣任期1957年2月25日—1960年7月19日君主昭和天皇副首相石井光次郎益谷秀次前任石橋湛山继任池田勇人 日本內閣總理大臣(臨時代理)任期1957年1月31日—1957年2月25日总理石橋湛山前任石橋湛山继任岸信介 日本防衛廳長官(臨時代理)任期1957年1月31日—1957年2月2日总理岸信介(代,兼)前任石橋湛山(代)继任小瀧彬(�...

2007 American filmMoving McAllisterTheatrical release posterDirected byAndrew BlackWritten byBen GourleyProduced byJason FallerKynan GriffinBen GourleyStarringBen GourleyMila KunisJon HederRutger HauerCinematographyDoug ChamberlainEdited byMasahiro HirakuboChantelle SquiresMusic byDidier RachouDistributed byMagnolia Pictures (DVD) First Independent PicturesRelease date September 14, 2007 (2007-09-14) (limited)Running time91 minutesCountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglishBox office$4...
Halstenbek. Halstenbek adalah kota yang terletak di distrik Pinneberg, Schleswig-Holstein, Jerman. Kota Halstenbek memiliki luas sebesar 12.6 km². Halstenbek pada tahun 2006, memiliki penduduk sebanyak 16.200 jiwa. lbsKota dan kotamadya di Pinneberg (distrik) Appen Barmstedt Bevern Bilsen Bokel Bokholt-Hanredder Bönningstedt Borstel-Hohenraden Brande-Hörnerkirchen Bullenkuhlen Ellerbek Ellerhoop Elmshorn Groß Nordende Groß Offenseth-Aspern Halstenbek Haselau Haseldorf Hasloh Heede H...

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要編修,以確保文法、用詞、语气、格式、標點等使用恰当。 (2013年8月6日)請按照校對指引,幫助编辑這個條目。(幫助、討論) 此條目剧情、虛構用語或人物介紹过长过细,需清理无关故事主轴的细节、用語和角色介紹。 (2020年10月6日)劇情、用語和人物介紹都只是用於了解故事主軸,輔助�...

Частина серії проФілософіяLeft to right: Plato, Kant, Nietzsche, Buddha, Confucius, AverroesПлатонКантНіцшеБуддаКонфуційАверроес Філософи Епістемологи Естетики Етики Логіки Метафізики Соціально-політичні філософи Традиції Аналітична Арістотелівська Африканська Близькосхідна іранська Буддій�...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Desember 2023. Jane GarrettLahirJane Dipika GarrettOktober 2000 (umur 23–24)Amerika SerikatPekerjaanModelPerawatGelarMiss Universe Nepal 2023Pemenang kontes kecantikanKompetisiutamaMiss Universe Nepal 2023(Pemenang)Miss Universe 2023(Winner) Jane Dipika G...

عمل تجاريمعلومات عامةصنف فرعي من منظمةكيان اقتصادي المالك رائد أعمال يدرسه إدارة أعمال له هدف ربح محاسبيالربح لديه جزء أو أجزاء مقاولةنشاط اقتصادي تصنيف للتصنيفات التي تحمل هذا الاسم تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات جُزء من سلسلة مقالات حولالرأسمالية مفاهيم عمل تج�...