Fort Augusta
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Angsa (disambiguasi). Artikel ini bukan mengenai Soang. Artikel ini sudah memiliki daftar referensi, bacaan terkait, atau pranala luar, tetapi sumbernya belum jelas karena belum menyertakan kutipan pada kalimat. Mohon tingkatkan kualitas artikel ini dengan memasukkan rujukan yang lebih mendetail bila perlu. (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) AngsaRentang fosil: Miosen akhir – sekarang[1][2] PreЄ Є O S D C P T J K ...

Andrew Jackson Presiden Amerika Serikat 7Masa jabatan4 Maret 1829 – 4 Maret 1837Wakil PresidenJohn C. Calhoun (1829-1832), Tidak ada (1832-1833), Martin Van Buren (1833-1837) PendahuluJohn Quincy AdamsPenggantiMartin Van BurenMiliter Gubernur FloridaMasa jabatan10 Maret 1821 – 31 Desember 1821Ditunjuk olehJames Monroe PendahuluPosisi didirikanPenggantiWilliam Pope DuvalSenator Amerika Serikat dari TennesseeMasa jabatan4 Maret 1823 – 14 Oktober 1825 Pendahu...

Kedaung A bed of blue mussels, Mytilus edulis, in the intertidal zone in Cornwall, England SubclassesPteriomorphia (marine mussels) Palaeoheterodonta (freshwater mussels) Heterodonta (zebra mussels)lbs Kedaung ( /ˈmʌsəl/) adalah nama umum yang digunakan untuk anggota beberapa famili moluska kerang, dari habitat air asin dan air tawar . Kelompok-kelompok ini memiliki kesamaan cangkang yang bentuknya memanjang dan asimetris dibandingkan dengan kerang lain yang dapat dimakan, yang seringkali ...

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut...

Alex Pearce Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Alexander James PearceTanggal lahir 9 November 1988 (umur 35)Tempat lahir Wallingford, Inggris[1]Tinggi 620 ft 0 in (188,98 m)Posisi bermain BekInformasi klubKlub saat ini ReadingNomor 5Karier junior2001–2006 ReadingKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2006– Reading 110 (11)2007 → Northampton Town (pinjaman) 15 (1)2007–2008 → Bournemouth (pinjaman) 11 (0)2008 → Norwich City (pinjaman) 11 (0)2008 → Southampton ...

American politician (born 1954) Cynthia LummisOfficial portrait, 2020United States Senatorfrom WyomingIncumbentAssumed office January 3, 2021Serving with John BarrassoPreceded byMike EnziMember of the U.S. House of Representativesfrom Wyoming's at-large districtIn officeJanuary 3, 2009 – January 3, 2017Preceded byBarbara CubinSucceeded byLiz Cheney27th Treasurer of WyomingIn officeJanuary 4, 1999 – January 9, 2007GovernorJim Geringer Dave Freudent...

Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori brasiliani è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Dudu Cearense Nazionalità Brasile Altezza 186 cm Calcio Ruolo Centrocampista Termine carriera 2018 Carriera Giovanili 1998-1999 Ceará Squadre di club1 2001-2003 Vitória49 (6)2004 Kashiwa Reysol11 (2)2004-2005→ Rennes15 (1)2005-2008 CSKA Mosca74 (8)2008-2011 Olympiak...
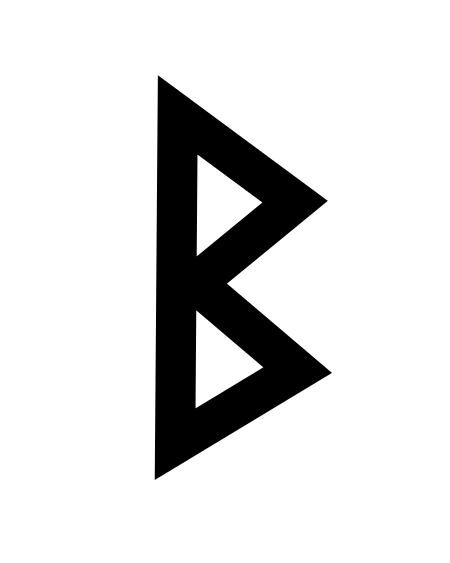
此條目介紹的是拉丁字母中的第2个字母。关于其他用法,请见「B (消歧义)」。 提示:此条目页的主题不是希腊字母Β、西里尔字母В、Б、Ъ、Ь或德语字母ẞ、ß。 BB b(见下)用法書寫系統拉丁字母英文字母ISO基本拉丁字母(英语:ISO basic Latin alphabet)类型全音素文字相关所属語言拉丁语读音方法 [b][p][ɓ](适应变体)Unicode编码U+0042, U+0062字母顺位2数值 2歷史發...

Astronomical coordinate analogous to latitude For other uses, see Declination (disambiguation). In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol δ) is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. The declination angle is measured north (positive) or south (negative) of the celestial equator, along the hour circle passing through the point in question.[1] Right ascension and declination as seen on ...

Mario Cotellessa Deputato della Repubblica ItalianaDurata mandato25 giugno 1946 –15 maggio 1963 LegislaturaAC, I, II, III GruppoparlamentareDemocratico Cristiano CircoscrizioneAC: XXII-II-III: XX Incarichi parlamentari Componente della XI Commissione (Lavoro e Previdenza Sociale) - I e II legislatura Componente della I Commissione (Affari Interni) - II legislatura Componente della Commissione speciale per l'esame dei disegni di legge nn. 2453 e 2454: Provvedimenti...

Maria MagdalenaSenimanAnthony Frederick Augustus SandysTahunsekitar 1858–1860TipeMinyak di atas panelUkuran33.5 cm × 28 cm (13 ¼ in × 11 in)LokasiDelaware Art Museum, Wilmington, Delaware Maria Magdalena adalah sebuah lukisan Pra-Rafaelit tahun 1858-1860 karya Frederick Sandys. Maria Magdalena adalah satu-satunya figur dari Alkitab yang pernah dilukis oleh Sandys.[1] Referensi ^ Shadowlight: The Pre-Raphaelite Goddess. Diakses tangg...

This template was considered for deletion on 2020 January 7. The result of the discussion was no consensus. United States: Texas Template‑class United States portalThis template is within the scope of WikiProject United States, a collaborative effort to improve the coverage of topics relating to the United States of America on Wikipedia. If you would like to participate, please visit the project page, where you can join the ongoing discussions. Template Usage Articles Requested! Become a Me...

This article is about the district. For its eponymous headquarters, see Golaghat. District of Assam in IndiaGolaghat districtDistrict of AssamFrom top, left-to-right: Rhinoceros in Kaziranga National Park, Negheriting Shiva Doul, Deopahar, Golaghat city view, Athkheliya Namghar.Location in AssamCoordinates: 26°00′N 93°00′E / 26.0°N 93.0°E / 26.0; 93.0CountryIndiaStateAssamDivisionUpper AssamHeadquartersGolaghatGovernment • Lok Sabha constituenciesKa...

Ця стаття потребує додаткових посилань на джерела для поліпшення її перевірності. Будь ласка, допоможіть удосконалити цю статтю, додавши посилання на надійні (авторитетні) джерела. Зверніться на сторінку обговорення за поясненнями та допоможіть виправити недоліки. Мат...

博里萨夫·约维奇攝於2009年 南斯拉夫社會主義聯邦共和國第12任總統任期1990年5月15日—1991年5月15日总理安特·马尔科维奇前任亚内兹·德尔诺夫舍克继任塞吉多·巴伊拉莫维奇(英语:Sejdo Bajramović) (代任)第12任不结盟运动秘书长任期1990年5月15日—1991年5月15日前任亚内兹·德尔诺夫舍克继任斯捷潘·梅西奇第3任塞尔维亚常驻南斯拉夫社会主义联邦共和国主席团代表任�...

ヨハネス12世 第130代 ローマ教皇 教皇就任 955年12月16日教皇離任 964年5月14日先代 アガペトゥス2世次代 レオ8世個人情報出生 937年スポレート公国(中部イタリア)スポレート死去 964年5月14日 教皇領、ローマ原国籍 スポレート公国親 父アルベリーコ2世(スポレート公)、母アルダその他のヨハネステンプレートを表示 ヨハネス12世(Ioannes XII、937年 - 964年5月14日)は、ロ...

State Wildlife Management Area in Lincoln County, West Virginia Hilbert Wildlife Management AreaIUCN category V (protected landscape/seascape)[1]The Ruffed Grouse (Bonasa umbellus) may be found in the Hilbert WMALocation of Hilbert Wildlife Management Area in West VirginiaLocationLincoln, West Virginia, United StatesCoordinates38°15′00″N 81°54′56″W / 38.25000°N 81.91556°W / 38.25000; -81.91556Area289 acres (117 ha)[2]Elevation850 f...

Provider of pre-hospital emergency care in New South Wales, Australia NSW AmbulanceSealFlagAgency overviewFormed2014; 10 years ago (2014)Preceding agenciesCivil Ambulance and Transport Brigade (1895–1904)Civil Ambulance and Transport Corps (1904–1921)NSW Ambulance Transport Service Board (1921–1977)Ambulance Service of New South Wales (1977–2014)JurisdictionNew South WalesHeadquartersRozelle, New South Wales, AustraliaEmployees6,100+Minister responsibleRyan Park, Min...

American telecommunications company An AT&T Long Lines tower in Phoenix, AZ. For the division of the AT&T Inc. that was created in 2017, see AT&T Communications. AT&T Communications, Inc.Company typeSubsidiaryIndustryTelecommunicationsPredecessorAmerican Telephone and Telegraph CompanyFounded1984; 40 years ago (1984)Defunct2010; 14 years ago (2010)SuccessorAT&T CommunicationsHeadquartersBedminster, New Jersey, United StatesProductsLong d...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada April 2012. Templat:Audrey CalciaLahir9 Oktober 1985 (umur 38)Jakarta, IndonesiaPekerjaanpenyanyiTahun aktif2011 - sekarang Audrey Calcia (lahir 9 Oktober 1985) merupakan seorang penyanyi berkebangsaan Indonesia. Dia menjadi terkenal saat menyanyikan lagu ...




