Everett Rogers
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Salah satu tempat yang berada di Jalan Raya Kalibata, Taman Makam Pahlawan Nasional Utama Kalibata Jalan Raya Kalibata adalah nama salah satu jalan utama di Jakarta yang menghubungkan Jalan Raya Pasar Minggu di barat dengan kawasan Jalan Dewi Sartika di timur. Jalan ini membentang sepanjang 2,3 KM dari Simpang Taman Makam Pahlawan Kalibata sampai Simpang Kalibata Dewi Sartika. Jalan ini berada di Jakarta Selatan dan Jakarta Timur. Jalan ini melintasi 5 Kelurahan, yaitu kelurahan: Duren Tiga, ...

Indian racing driver This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) The topic of this article may not meet Wikipedia's notability guideline for sports and athletics. Please help to demonstrate the notability of the topic by citing reliable secondary sources that are independent of the topic and provide significant coverage of it beyond a mere trivial mention. If notability cannot be show...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Pamphlet – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Unbound book An 18th-century painting of a girl with a basket of pamphlets Due to their low cost and ease of production, pamphlets have o...

يعبر تحويل جيب التمام المتقطع (بالإنجليزية: Discrete cosine transform) اختصاراً DCT، عن سلسلة محددة من نقاط البيانات من حيث مجموع توابع جيب التمام المتذبذب على ترددات مختلفة. إن دي سي تي، الذي اقترحه ناصر أحمد لأول مرة في عام 1972، هو تقنية تحويل تستخدم على نطاق واسع في معالجة الإشارة وض�...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Portelli. Florence Portelli Florence Portelli en 2017. Fonctions Vice-présidente du conseil régional d'Île-de-Francechargée de la Culture, du Patrimoine et de la Création En fonction depuis le 29 mai 2019(4 ans, 10 mois et 20 jours) Élection 29 mai 2019 Réélection 2 juillet 2021 Président Valérie Pécresse Prédécesseur Agnès Evren Conseillère régionale d'Île-de-France En fonction depuis le 18 décembre 2015(8 ans et 4 ...

The effect of downwash from a hovering Sikorsky Seahawk is clearly visible on the surface of water below. In aeronautics, downwash is the change in direction of air deflected by the aerodynamic action of an airfoil, wing, or helicopter rotor blade in motion, as part of the process of producing lift.[1] In helicopter aerodynamics discussions, it may be referred to as induced flow.[2] Lift on an airfoil is an example of the application of Newton's third law of motion – the for...
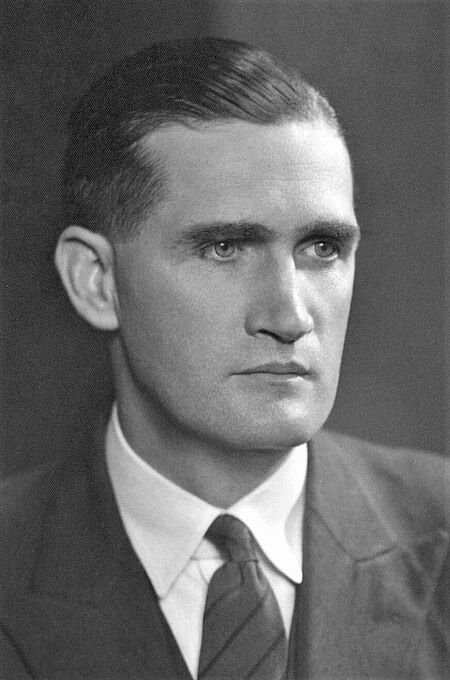

Prime Minister of Australia from 1967 to 1968 For other people with the same name, see John McEwen (disambiguation). The Right HonourableSir John McEwenGCMG CHMcEwen in 196018th Prime Minister of AustraliaIn office19 December 1967 – 10 January 1968MonarchElizabeth IIGovernor‑GeneralLord CaseyPreceded byHarold HoltSucceeded byJohn GortonDeputy Prime Minister of AustraliaIn office10 January 1968 – 5 February 1971Prime MinisterJohn GortonPreceded byoffice establi...

费迪南德·马科斯Ferdinand Marcos 菲律賓第10任總統任期1965年12月30日—1986年2月25日副总统費爾南多·洛佩斯(1965-1972)阿圖羅·托倫蒂諾前任奧斯達多·馬卡帕加爾继任柯拉蓉·阿基诺 菲律賓第4任總理任期1978年6月12日—1981年6月30日前任佩德羅·帕特諾(1899年)继任塞薩爾·維拉塔 个人资料出生1917年9月11日 美屬菲律賓北伊羅戈省薩拉特(英语:Sarrat)逝世1989年9月28日(...

الدوري المصري الممتاز لكرة القدم الشعار الرسمي للدوري الموسم 2023–24 البلد مصر النسخة 65 عدد الفرق 18 فريق الفترة 18 سبتمبر 2023 – الفرق الصاعدة بلدية المحلة -زد - الجونة عدد المباريات 189 عدد الأهداف 449 (2.38 هدف في المباراة) الهداف حسام أشرف(11 أهداف حتى الآن) أفضل حارس مرمى أحمد...

Type of knot Snuggle hitchCategoryHitchOriginFirst publication 1987RelatedClove hitch, Ground-line hitch The snuggle hitch is a modification of the clove hitch, and is stronger and more secure. Owen K. Nuttall of the International Guild of Knot Tyers came up with this unique hitch, and it was first documented in the Guild's Knotting Matters magazine issue of January, 1987.[1] Generally, hitches are used to attach a line to another rope or spar, pole, etc., and are usually temporary. T...

Cyane(403 Cyane) Scoperta18 maggio 1895 ScopritoreAuguste Honoré Charlois ClassificazioneFascia principale Classe spettraleS Designazionialternative1895 BX Parametri orbitali(all'epoca K074A) Semiasse maggiore2,8102680 UA Inclinazionesull'eclittica9,15497° Eccentricità0,0964774 Longitudine delnodo ascendente244,84231° Argom. del perielio251,87974° Anomalia media2,67925° Par. Tisserand (TJ)3,295 (calcolato) Dati fisiciDiametro medio49,49 km Periodo di rotazione12,288 ore Albedo0,165...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Lūsis. Jānis Lūsis Jānis Lūsis en 2011. Informations Disciplines Lancer du javelot Période d'activité 1957-1976 Nationalité Union soviétique puis Letton Naissance 19 mai 1939 Jelgava (RSS de Lettonie, URSS) Décès 28 avril 2020 (à 80 ans) Riga (Lettonie) Taille 1,81 m Masse 91 kg Club A.S.C. Riga Entraîneur Valentin Mazzalatis Records Ancien détenteur du record du monde Distinctions Élu au Temple de la renommée de l'IAAF en 2014 Palmarès...
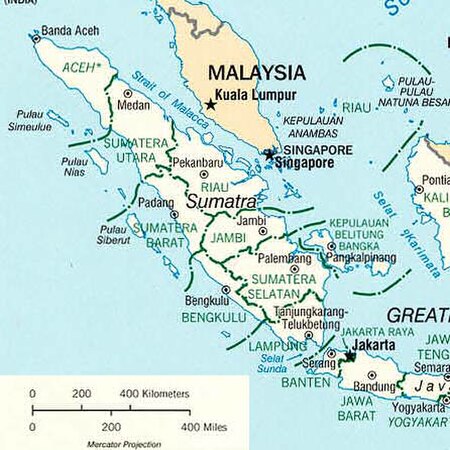
「Sumatra」重定向至此。關於一种电脑软件,請見「Sumatra PDF」。 蘇門答臘蘇門答臘地形圖地理位置東南亞坐标0°N 102°E / 0°N 102°E / 0; 102群岛大巽他群岛面積473,481 平方公里(182,812 平方英里)面积排名世界面積第6大島嶼最高海拔3,805 公尺最高點葛林芝管轄 印度尼西亞省分亞齊特別行政區、明古鲁省、占碑省、楠榜省、廖內省、西蘇門答臘省、�...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: International Bank of Commerce – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) International Bancshares CorporationCompany typePublicTraded asNasdaq: IBOCS&P 400 ComponentIndustryFinance and Insur...
Australian rules football match 1997 SANFL Grand Final Port Adelaide Norwood 7.11 (53) 19.12 (126) 1 2 3 4 PTA 1.2 (8) 3.3 (21) 4.7 (31) 7.11 (53) NOR 3.4 (22) 6.5 (41) 13.8 (86) 19.12 (126) DateSunday, 5 October (2:10 pm)StadiumFootball ParkAttendance44,161UmpiresBettridge, Chambers, WoodcockBroadcast in AustraliaNetworkABC TVCommentatorsKen SheldonMark Naley (special comments)Rob Popplestone (boundary rider) ← 1996 1998 → The 1997 SANFL Grand Final was an Austral...
王振西可以指: 王振西 (1934年),中国军事人物,中国人民解放军少将,曾任军事科学院外国军事研究部部长 王振西 (?),中国军事人物,中国人民解放军少将,曾任陕西省军区政治委员 这是一个消歧义页,羅列了有相同或相近的标题,但內容不同的条目。如果您是通过某條目的内部链接而转到本页,希望您能協助修正该處的内部链接,將它指向正确的条目。

Staats- und Regierungsformen der Welt von Legislative bestimmtes Direktorium Republik mit exekutivem Staatschef Präsidentielle Republik Semipräsidentielle Republik Parlamentarische Republik Parlamentarische Monarchie Konstitutionelle Monarchie Absolute Monarchie Einparteiensystem (ggf. mit Blockparteien) Verfassungsrechtliche Bestimmungen ausgesetzt Kein verfassungsrechtlich festgelegtes Regime ...

This biography of a living person needs additional citations for verification. Please help by adding reliable sources. Contentious material about living persons that is unsourced or poorly sourced must be removed immediately from the article and its talk page, especially if potentially libelous.Find sources: Liane Foly – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) French singer Liane FolyBackgrou...

Extinct hominin from Early Pliocene Ethiopia Ardipithecus ramidusTemporal range: Zanclean 4.5–4.32 Ma PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N ↓ A. ramidus at the Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Primates Suborder: Haplorhini Infraorder: Simiiformes Family: Hominidae Subfamily: Homininae Tribe: Hominini Genus: †Ardipithecus Species: †A. ramidus Binomial name †Ardip...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。 出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: 神学校 – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL (2024年9月) 日本のバイブルクラス(1909年) 神学校(しんがっ�...