Ernst Bloch
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Duet PlusKompilasi karya Dodo ZakariaDirilisJuli 1988Direkam-GenrePopRockDurasi-LabelEka RecordsProduserDodo ZakariaKronologi Dodo Zakaria Mallisa(1986)'Mallisa'1986 Duet Plus (1988) D.Do (1990)'D.Do'1990 Duet Plus adalah proyek album yang dikerjakan oleh Dodo Zakaria yang melibatkan musisi dan penyanyi ternama pada masanya yang dirilis pada tahun 1988. Disebut Duet Plus karena hampir semua lagu di album ini dinyanyikan secara duet. Penggarapan album ini juga melibatkan penyanyi muda Held...

Chemical compound OcedurenoneClinical dataOther namesKBP-5074Legal statusLegal status Investigational Identifiers IUPAC name 4-[(3S,3aR)-3-Cyclopentyl-7-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-carbonyl)-3,3a,4,5-tetrahydropyrazolo[3,4-f]quinolin-2-yl]-2-chlorobenzonitrile CAS Number1359969-24-6PubChem CID75593324UNIIL46509378RChemical and physical dataFormulaC28H30ClN5O2Molar mass504.03 g·mol−1 Ocedurenone, formerly known as KBP-5074,[1] is a nonsteroidal, selective mineralocorticoid receptor ...

История ШвейцарииШвейцария до объединения (1291) Доисторическая Швейцария Римская Швейцария Верхняя Бургундия Швейцарский союз (1291—1798) Федеративная хартия Экспансия Реформация в Швейцарии Три Лиги Лига десяти сообществ Лига дома Божьего Серая лига Во время Наполеоновс...

Men's Greco-Roman 100 kgat the Games of the XXII OlympiadVenueCentral Sports Club of the ArmyDates21–23 JulyCompetitors9 from 9 nationsMedalists Georgi Raikov Bulgaria Roman Bierła Poland Vasile Andrei Romania← 19761984 → Wrestling at the1980 Summer OlympicsFreestyleGreco-Roman48 kg48 kg52 kg52 kg57 kg57 kg62 kg62 kg68 kg68 kg74 kg74 kg82 kg82 kg90 kg90 kg100 kg100 kg+100 kg+100 kgvte The Men's Greco-Roman 100 kg at the 1980 Summer Ol...

Michael BasmanBasman di Cambridge (2006)Nama lengkapMichael John BasmanAsal negaraInggrisLahir(1946-03-16)16 Maret 1946London, InggrisMeninggal26 Oktober 2022(2022-10-26) (umur 76)GelarMaster InternasionalRating FIDE2313 (Oktober 2016)Rating tertinggi2410 (Juli 1971) Michael John Basman (16 Maret 1946 – 26 Oktober 2022) seorang master catur, pengarang, dan teoretikus pembukaan catur berkebangsaan Britania Raya. Pada 1980 ia menjadi Master Internasional...

ComercialCalcio O Bode da Terra dos Carnaubais Segni distintivi Uniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Colori sociali Blu, bianco Dati societari Città Campo Maior Nazione Brasile Confederazione CONMEBOL Federazione CBF Campionato Campionato Piauiense Fondazione 1945 Stadio Deusdeth Melo(4 000 posti) Palmarès Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Il Comercial Atlético Clube, noto anche semplicemente come Comercial, è una società calcistica brasiliana con sede nella città di Campo M...

追晉陸軍二級上將趙家驤將軍个人资料出生1910年 大清河南省衛輝府汲縣逝世1958年8月23日(1958歲—08—23)(47—48歲) † 中華民國福建省金門縣国籍 中華民國政党 中國國民黨获奖 青天白日勳章(追贈)军事背景效忠 中華民國服役 國民革命軍 中華民國陸軍服役时间1924年-1958年军衔 二級上將 (追晉)部队四十七師指挥東北剿匪總司令部參謀長陸軍�...

Данио-рерио Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеГруппа:Костные рыбыКласс:Лучепёрые рыбыПодкласс:Новопёрые рыбыИн�...

此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2021年7月4日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:美国众议院 — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源(判定指引)。 美國眾議院 United States House of Representatives第118届美国国会众议院徽章 众议院旗...

American drummer For the actor, see Joey Cramer. This biography of a living person needs additional citations for verification. Please help by adding reliable sources. Contentious material about living persons that is unsourced or poorly sourced must be removed immediately from the article and its talk page, especially if potentially libelous.Find sources: Joey Kramer – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2009) (Learn how and when to r...

Political party in Russia For Truth За правдуLeaderZakhar PrilepinFounded1 February 2020 (2020-02-01)Dissolved22 February 2021 (2021-02-22)[1]Merged intoA Just Russia — For Truth[2]HeadquartersMoscow, RussiaIdeologyNational conservatismSocial conservatismRussian nationalism[3]Anti-liberalismNational patriotismPolitical positionEconomic:Centre-left to left-wing[3]Cultural:Right-wing[4]National affilia...

Process of Finnish separation from Russia in the 19th-20th centuries The Finnish Senate of 1917, Prime Minister P. E. Svinhufvud in the head of table Finland declared its full independence on 6 December 1917. The formal Declaration of Independence was only part of the long process leading to the independence of Finland. History Proclamation of Empress Elizabeth (1742) The subject of an independent Finland was first mentioned in the 18th century, when present-day Finland was still part of Swe...

Smelt Sands State Recreation SiteFishing at Smelt SandsShow map of OregonShow map of the United StatesTypePublic, stateLocationYachats, Lincoln County, OregonCoordinates44°19′19″N 124°06′21″W / 44.32203°N 124.10574°W / 44.32203; -124.10574Operated byOregon Parks and Recreation Department Smelt Sands State Recreation Site is a state park in the U.S. state of Oregon, administered by the Oregon Parks and Recreation Department. See also List of Oregon sta...

Dharma NuclearLahir19 Januari 1985 (umur 39)Prefektur Hiroshima, JepangNama lainMr NuclearPekerjaanmusisi , Pemeran & aktor Dharma Nuclear atau dikenal sebagai Dharma Lyla (lahir 19 Januari 1985) merupakan seorang musisi berkebangsaan Indonesia yang juga merupakan keyboard dari grup musik Lyla. Pada tahun 2004, bersama Naga, Fare, Dennis dan Amec ia ikut mendirikan grup musik yang bernama Mahameru sebelum akhirnya berganti nama menjadi Lyla pada tahun 2008. Diskografi Yang Tak ...
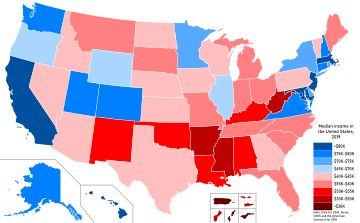
For the list of states by income inequality, see List of U.S. states and territories by income inequality. This article is part of a series onIncome in theUnited States of America Topics Household Personal Affluence Social class Income inequality gender pay gap racial pay gap Lists by income States (by inequality) Counties (highest / lowest) Locations (lowest) Metropolitan statistical areas Urban areas ZIP Code Tabulation Areas Ethnic groups United States portalvte This is a list of...

Planned soccer stadium in New York City For the York City F.C. stadium, see York Community Stadium. Not to be confused with New York Stadium. New York City FC stadiumRendering of the stadium from March 2024 showing its location within Willets PointNew York City FC stadiumLocation within New York CityShow map of New York CityNew York City FC stadiumNew York City FC stadium (New York)Show map of New YorkNew York City FC stadiumNew York City FC stadium (the United States)Show map of the United S...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Montmédy – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Commune in Grand Est, FranceMontmédyCommunePlace de l’Hôtel de Ville: the fountain and Saint-Martin's church Coat of armsLocation of Montméd...

Lambang kota Chełmża (bahasa Jerman: Kulmsee) ialah sebuah kota di Provinsi Kujawy-Pomorze, Polandia. Kota ini terletak di sekitar 53°11′5″N 18°36′15″E / 53.18472°N 18.60417°E / 53.18472; 18.60417. Pada tahun 1900, kota ini berpenduduk 8.987 jiwa. Kota ini memiliki katedral Katolik Roma yang bagus, dibangun pada abad ke-13, dan direstorasi pada abad ke-15, dan sebuah gereja Evangelis. Hingga tahun 1823 Chełmża adalah ibu kota Keuskupan Kulm. Kota ke...

Jennifer Esposito nel 2020 Jennifer Esposito (New York, 11 aprile 1973) è un'attrice statunitense. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Carriera 3 Filmografia 3.1 Cinema 3.2 Televisione 4 Doppiatrici italiane 5 Note 6 Altri progetti 7 Collegamenti esterni Biografia Di origini italoamericane[1], nasce a Brooklyn, New York, l'11 aprile 1973, secondogenita di due figlie di Phyllis, decoratrice di interni, e Robert Esposito, consulente informatico di Wall Street ed ex-produttore musicale di ascendenze n...

v · m Champions de Belgique de cyclisme sur route 1894 : Léon Houa 1895-1896 : Henri Luyten 1897-1898 : Henri Bertrand 1899 : Jules de Geytere 1900 : Mathieu Quoidbach 1901 : Paul Burger 1902 : Jules Defrance 1903 : Arthur Vanderstuyft 1904 : Jules Sales 1905 : Dieudonné Jamar 1907-1908 : François Verstraeten 1909 : Cyrille Van Hauwaert 1910 : Henri Hanlet 1911 : Odile Defraye 1912 : Omer Verschoore 1913 ...

