Dorothy Ashby
| |||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Amendemen Ketiga Puluh Empat Konstitusi IrlandiaLokasi IrlandiaTanggal22 Mei 2015 (2015-05-22) Hasil Suara % Ya 1.201.607 62,07% Tidak 734.300 37,93% Suara sah 1.935.907 99,29% Suara kosong atau tidak sah 13.818 0.71% Total suara 1,949,725 100.00% Pemilih terdaftar/hadir 3,221,681 60.52% Hasil menurut konstituensi Peta persebaran suara yang menyetujui amendemen: 72.5%–75% 70%–72.49% 67.5%–69.99% 65%–67.49% 62.5%–64.99%...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Februari 2023. Malin Kundang dapat mengacu pada beberapa hal berikut: Malin Kundang, cerita rakyat yang berasal dari provinsi Sumatera Barat, Indonesia Malin Kundang (lagu), lagu karya Orkes Gumarang, dengan iringan vokal oleh Juni Amir Malin Kundang (film), film ta...

Artikel ini bukan mengenai Aberasi optik. Posisi tampak dari suatu bintang yang dilihat dari Bumi bergantung pada kecepatan Bumi. Pengaruhnya biasanya jauh lebih kecil dari yang diilustrasikan. Dalam astronomi, aberasi cahaya (juga disebut lanturan cahaya) adalah sebuah fenomena yang menyebabkan suatu benda langit tampak bergerak dari posisinya yang sesungguhnya, bergantung pada kecepatan pengamat. Fenomena ini menyebabkan objek tampak berpindah mendekati arah gerakan pengamat dibandingkan de...

العلاقات الأوكرانية الشمال مقدونية أوكرانيا شمال مقدونيا أوكرانيا شمال مقدونيا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الأوكرانية الشمال مقدونية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين أوكرانيا وشمال مقدونيا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارن�...

Artikel ini bukan mengenai Badai matahari. Penggambaran seniman tentang partikel angin matahari yang berinteraksi dengan magnetosfer bumi. Ukuran tidak sesuai skala. Badai geomagnetik, juga disebut badai magnet atau badai matahari, adalah fenomena cuaca antariksa yang terjadi ketika pertukaran energi yang sangat efisien dari angin matahari ke lingkungan luar angkasa di sekitar bumi. Badai geomagnetik terjadi akibat masuknya angin surya cepat karena lontaran massa korona bersamaan dengan Bz Me...

Patent-like intellectual property right Intellectual property Authors' rights Copyleft Copyright Database right Farmers' rights Geographical indication Indigenous intellectual property Industrial design right Integrated circuit layout design protection Moral rights Patent Peasants' rights Plant breeders' rights Plant genetic resources Related rights Supplementary protection certificate Trade dress Trade secret Trademark Utility model Related topics Abandonware Artificial intelligence and copy...

Australian politician For the historian of Germany, see Geoffrey J. Giles. Geoffrey GilesMember of the Australian Parliamentfor AngasIn office20 June 1964 – 10 December 1977Preceded byAlec DownerSucceeded byDivision abolishedMember of the Australian Parliamentfor WakefieldIn office10 December 1977 – 4 February 1983Preceded byBert KellySucceeded byNeil AndrewMember of the South Australian Legislative CouncilIn office17 February 1959 – 13 May 1964 Personal detai...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant l’histoire et la Chine. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Gongsun YuanFonctionsRoiYan (en)237-238Taishou (d)BiographieNaissance LiaoningDécès 238LiaoningActivité Homme politiquePère Gongsun KangFratrie Gongsun Huang (d)Enfant Gongsun Xiu (d)Autres informationsConflit Campagne du Liaodong de Sima YiPrononciationmodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wiki...

Modern Orthodox synagogue in Manhattan, New York Ramath OrahRamath Orah synagogueReligionAffiliationModern Orthodox JudaismEcclesiastical or organizational statusSynagogueStatusActiveLocationLocationWest 110th Street, Upper West Side, Manhattan, New York City, New YorkCountryUnited StatesLocation in ManhattanGeographic coordinates40°48′13.24″N 73°57′58.02″W / 40.8036778°N 73.9661167°W / 40.8036778; -73.9661167ArchitectureTypeSynagoagueStyleGeorgian RevivalF...

Logo iNews Halaman ini memuat daftar acara yang ditayangkan di iNews. Program saat ini Berita iNews (acara televisi) Pagi Siang Sore Malam Today Room Prime Terkini Kawal Suara Rakyat (ditayangkan selama Pemilu 2024) Lapor Polisi Realita Berita lokal Selain program berita nasional, beberapa jaringan iNews juga menayangkan berita lokal yang ditayangkan setiap Senin sampai Sabtu pukul 06.30 WIB iNews Jabar (program berita lokal iNews Bandung) iNews Jateng (program berita lokal iNews Semarang dan...

For the more general sports concepts, see Dead ball and Out of bounds. Balls A, B and C are still in play as they have not wholly crossed the touchline. Ball D has completely passed over the touchline, and is out of play. The ball in and out of play is the ninth law of the Laws of the Game of association football, and describes to the two basic states of play in the game. In play The ball remains in play from the beginning of each period to the end of that period, except when: The ball leaves...

Beliefs of John Calvin Lithograph of John Calvin, c. 1830. The theology of John Calvin has been influential in both the development of the system of belief now known as Calvinism and in Protestant thought more generally. Publications See also: John Calvin bibliography John Calvin developed his theology in his biblical commentaries as well as his sermons and treatises, but the most concise expression of his views is found in his magnum opus, the Institutes of the Christian Religion. He intende...

Private university in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, U.S. Wilkes UniversityFormer namesBucknell University Junior College (1933–1947)Wilkes College (1947–1989)MottoUnity Amidst DiversityTypePrivate universityEstablished1933; 91 years ago (1933)AccreditationMSCHEEndowment$65.8 million (2021)[1][2]PresidentAlan Gregory CantProvostDavid M. WardAcademic staff157 full time[3]Undergraduates2,245Postgraduates2,254LocationWilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, U.S...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Charlot (homonymie). Edmond CharlotEdmond Charlot, Pézenas, 2002BiographieNaissance 15 février 1915AlgerDécès 10 avril 2004 (à 89 ans)BéziersNationalité françaiseActivités Éditeur, bibliothécaireSignaturemodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata Edmond Charlot, né le 15 février 1915 à Alger (département d'Alger) et mort le 10 avril 2004 à Béziers (Hérault), libraire et éditeur à Alger, Paris et Pézenas, publia les premiers liv...

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang sebuah partai politik di Indonesia. Untuk organisasi massa yang memiliki singkatan nama yang sama, lihat Nasional Demokrat (Indonesia). Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Partai Nasional Demokrat. Artikel ini bukan mengenai Partai Nasional Demokrat (1998). Partai NasDem Ketua Fraksi di DPRRoberth RouwDibentuk26 Juli 2011; 12 tahun lalu (2011-07-26)Kantor pusatNasDem TowerJl. R.P. Soeroso No. 46, Gondangdia, Menteng, Jakarta Pusat 10350Sayap pelajarLiga Mahasisw...

Peningkatan alami dalam populasi per 1000 orang, dari CIA World Factbook, 2010 Tingkat pertumbuhan penduduk alami (TPPA) dalam demografi dihitung dengan cara angka kelahiran kasar dikurangi dengan angka kematian kasar pada suatu wilayah tertentu.[1] Angka ini memberi gambaran dalam demografi tentang bagaimana pertumbuhan populasi suatu negara. TPPA tidak termasuk migrasi ke dalam dan migrasi ke luar, memberikan indikasi pertumbuhan populasi hanya berdasarkan kelahiran dan kematian. TP...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (أكتوبر 2019) نادي سكك الحديد التونسي تأسس عام 1 أكتوبر 1919 البلد تونس الإدارة المدير نور الدين العبيدي المدرب سهيل ش...

2004 single by Kings of Leon California WaitingSingle by Kings of Leonfrom the album Youth & Young Manhood B-sideJoe's Head (Live)ReleasedFebruary 16, 2004 (2004-02-16)[1]Genre Garage rock Southern rock Length3:29Songwriter(s) Caleb Followill Nathan Followill Angelo Petraglia Kings of Leon singles chronology Wasted Time (2003) California Waiting (2004) The Bucket (2004) California Waiting is the fourth single taken from the Youth & Young Manhood album by the Ame...

Konya province Konya iliProvince of TurkeyLocation of Konya Province in TurkeyCountryTurkeyRegionCentral AnatoliaElectoral districtKonyaLuas • Total38,257 km2 (14,771 sq mi)Populasi (2010-12-31)[1] • Total2.013.845 • Kepadatan53,000/km2 (140,000/sq mi)Kode area telepon0332Pelat kendaraan42Situs webkonya.gov.tr Konya (Turki: Konya ili) adalah sebuah provinsi Turki yang berada di tengah-tengah Anatolia. Ibu kotanya adalah ...
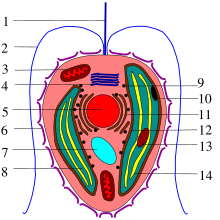
Type of algae Haptophytes Coccolithophore (Coccolithus pelagicus) Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Clade: Diaphoretickes Phylum: Haptista Subphylum: HaptophytinaHibberd, 1976 stat. nov. Cavalier-Smith, 2015[1] Classes & Orders Rappephyceae Pavlomulinales Pavlovophyceae Pavlovales Prymnesiophyceae s.s. (=Coccolithophyceae) †Discoasterales Phaeocystales Prymnesiales Isochrysidales Stephanolithiales Coccolithales †Eiffellithales Syracosphaerales †Arkhangelskiales †...
