Crown (anatomy)
| |||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Mazmur 138Naskah Gulungan Mazmur 11Q5 di antara Naskah Laut Mati memuat salinan sejumlah besar mazmur Alkitab yang diperkirakan dibuat pada abad ke-2 SM.KitabKitab MazmurKategoriKetuvimBagian Alkitab KristenPerjanjian LamaUrutan dalamKitab Kristen19← Mazmur 137 Mazmur 139 → Mazmur 138 (disingkat Maz 138, Mzm 138 atau Mz 138; penomoran Septuaginta: Mazmur 137) adalah sebuah mazmur dalam bagian ke-5 Kitab Mazmur di Alkitab Ibrani dan Perjanjian Lama dalam Alkitab Kristen. Digubah ol...

Bagian dari seriIslam Rukun Iman Keesaan Allah Malaikat Kitab-kitab Allah Nabi dan Rasul Allah Hari Kiamat Qada dan Qadar Rukun Islam Syahadat Salat Zakat Puasa Haji Sumber hukum Islam al-Qur'an Sunnah (Hadis, Sirah) Tafsir Akidah Fikih Syariat Sejarah Garis waktu Muhammad Ahlulbait Sahabat Nabi Khulafaur Rasyidin Khalifah Imamah Ilmu pengetahuan Islam abad pertengahan Penyebaran Islam Penerus Muhammad Budaya dan masyarakat Akademik Akhlak Anak-anak Dakwah Demografi Ekonomi Feminisme Filsafat...

Questa voce sull'argomento società calcistiche cipriote è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Pezoporikos Omilos LarnakasCalcio Segni distintivi Uniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Colori sociali Bianco, verde Dati societari Città Larnaca Nazione Cipro Confederazione UEFA Federazione KOP/CFA Fondazione 1927 Scioglimento1994 Stadio Stadio Neo GSZ( posti) Palmarès Titoli nazionali 2 campionati ciprioti Trofei nazionali 1 Coppe di Cipro Si...
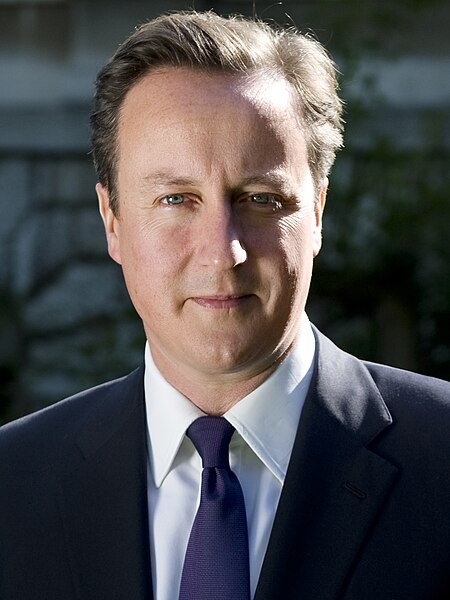

2014 European Parliament election in Gibraltar ← 2009 22 May 2014 2019 → Contributes towards 6 seats to the European Parliament First party Second party Third party Leader Nick Clegg David Cameron Ed Miliband Party Liberal Democrats Conservative Labour Alliance Liberal Social Democrats Socialist Labour Leader since 18 December 2007 6 December 2005 25 September 2010 Last election 18.18% 53.30% 19.02% Popular vote 4,822 1,236 659 Percenta...

Red Bull BrasilCalcio Toro Loko, Tourão Segni distintivi Uniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Colori sociali Bianco, rosso, blu Dati societari Città Campinas Nazione Brasile Confederazione CONMEBOL Federazione CBF Campionato Série A2 Fondazione 2007 Scioglimento2019 Proprietario Red Bull Presidente Gilmar Ramos Allenatore Antônio Carlos Zago Stadio Moisés Lucarelli(19 722 posti) Palmarès Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Il Red Bull Brasil è una società calcistica brasilia...

Jimmy ConnorsConnors in 1994Nama lengkapJames Scott ConnorsKebangsaan Amerika SerikatTempat tinggalSanta Barbara, California, ASLahir2 September 1952 (umur 71)Belleville, IL, ASTinggi5 ft 10 in (1,78 m)[1]Memulai pro1972 (amatir dari 1970)Pensiun29 April 1996Tipe pemainTangan kiri (two-handed backhand)PelatihGloria ConnorsPancho SeguraTotal hadiah$8,641,040Int. Tennis HoF1998 (member page)TunggalRekor (M–K)1274–283 (81.82%)[a]Gelar109 (1st in the O...

Indian diamond You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in German. (July 2010) Click [show] for important translation instructions. View a machine-translated version of the German article. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the En...

Basilika Santo FransiskusBasilika Minor Santo Fransiskus dari Assisibahasa Italia: Basilica di San FrancescoBasilika Santo Fransiskus43°27′52.20″N 11°52′50.88″E / 43.4645000°N 11.8808000°E / 43.4645000; 11.8808000Koordinat: 43°27′52.20″N 11°52′50.88″E / 43.4645000°N 11.8808000°E / 43.4645000; 11.8808000LokasiArezzoNegara ItaliaDenominasiGereja Katolik RomaSejarahDedikasiSanto Fransiskus dari AssisiArsitekturStatu...

Questa voce sull'argomento stagioni delle società calcistiche italiane è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Voce principale: Benevento Calcio. Società Sportiva Littorio BeneventoStagione 1936-1937Sport calcio Squadra Littorio Benevento Allenatore Mario De Palma, poi Giuseppe Cavanna Presidente? Serie C8º in girone E Coppa ItaliaQualificazioni StadioCampo Littorio 1935-1936 1937-1938 ...

Questa voce sull'argomento microbiologia è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Come leggere il tassoboxVirus del mosaico del tabacco Classificazione scientifica Dominio Riboviria Regno Orthornavirae Phylum Kitrinoviricota Classe Alsuviricetes Ordine Martellivirales Famiglia Virgaviridae Genere Tobamovirus Specie Tobacco Mosaic Virus Modello tridimensionale del virus del mosaico del tabacco ch...

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 数字の大字(だいじ)は、漢数字の一種。通常用いる単純な字形の漢数字(小字)の代わりに同じ音の別の漢字を用いるものである。 概要 壱万円日本銀行券(「壱」が大字) 弐千円日本銀行券(「弐」が大字) 漢数字には「一」「二」「三」と続く小字と、「壱」「�...

FIBA EuroBasket under-18 2004 Sport Pallacanestro Zona FIBA FIBA Europe Paese ospitante Spagna Periodo 9 - 18 luglio 2004 Squadre 12 (da 1 federazioni) Podio Spagna (2º titolo) Turchia Francia MVP Sergio Rodríguez Sito ufficiale http: Il 21º Campionato europeo di pallacanestro maschile Under-18 (noto anche come FIBA Europe Under-18 Championship 2004) si è svolto in Spagna, presso Saragozza, dal 9 al 18 luglio 2004. Indice 1 Squadre partecipanti 2 Primo turno 2.1 Gruppo A ...
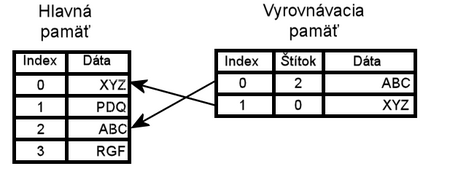
هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (ديسمبر 2021) ذاكرة وحدة المعالجة المركزية هي ذاكرة محبئية مؤقتة تستخدمها وحدة المعالجة المركزية للكمبيوتر لتقليل متوسط التكلفة (الوقت أو الطاقة) للوصول إلى البيانات من...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (مارس 2022) تتضمن المقالة قائمة بالأمراء الأردنيين من أبناء وأحفاد الملك عبد الله الأول بن الحسين، وهم من الهاشميين ال...

SHARESHARE logo as of 2021Formation1955; 69 years ago (1955)PurposeUser group for IBM mainframe computersLocationLos Angeles-areaWebsitewww.share.org SHARE Inc. is a volunteer-run user group for IBM mainframe computers that was founded in 1955 by Los Angeles-area users of the IBM 704 computer system. It evolved into a forum for exchanging technical information about programming languages, operating systems, database systems, and user experiences for enterprise users of small...

一中同表,是台灣处理海峡两岸关系问题的一种主張,認為中华人民共和国與中華民國皆是“整個中國”的一部份,二者因為兩岸現狀,在各自领域有完整的管辖权,互不隶属,同时主張,二者合作便可以搁置对“整个中國”的主权的争议,共同承認雙方皆是中國的一部份,在此基礎上走向終極統一。最早是在2004年由台灣大學政治学教授張亞中所提出,希望兩岸由一中各表�...

Part of American history 1807-1843 This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Indian removals in Ohio – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Indian removals in Ohio started in the late eighteenth century after the American victory in the ...

Vassal state of the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem (1118-87) This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (September 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Lordship of Oultrejordain1118–1187The Lordship of Oultrejordain at its greatest extent. Boundaries approximate.StatusVassal of Kingdom of JerusalemCapitalMontreal (1115 to 1140s) Kerak (1140s...

L'enregistreur de niveau du marégraphe intégrateur de Marseille (1913). Le DAS240 permet d'enregistrer jusqu'à 200 voies, avec un échantillonnage jusqu'à 1 ms (1 kHz)[réf. souhaitée]. Un enregistreur de données est un dispositif automatique, voire programmable, qui enregistre des valeurs de mesure individuelles et des séries de mesure sur une longue période (pouvant couvrir plusieurs mois). Les grandeurs sont automatiquement mesurées, souvent numérisées et enr...

1966 studio album by Hank MobleyDippin'Studio album by Hank MobleyReleasedMid August 1966[1]RecordedJune 18, 1965StudioVan Gelder Studio, Englewood Cliffs, NJGenreJazzLength42:40LabelBlue NoteBST 84209ProducerAlfred LionHank Mobley chronology The Turnaround(1965) Dippin'(1966) A Caddy for Daddy(1966) Dippin' is an album by jazz saxophonist Hank Mobley released on the Blue Note label in 1966. It is the second of nine Blue Note sessions to feature Mobley alongside Lee Morgan dur...




