Coppery-headed emerald
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. FINLAY-FR-2 Deskripsi vaksin Penyakit target COVID‑19 Jenis ? Data klinis Kat. kehamilan ? Status hukum ? Rute Intraotot Pengenal Kode ATC ? FINLAY-FR-2 juga dikenal sebagai SOBERANA-02, adalah sebuah kandidat vaksin COVID-19 yang diproduksi oleh Ins...

Basilika Bunda Maria dari PiatBasilika Minor Bunda Maria dari Piat di CagayanPiat BasilicaBasílica Menor de Nuestra Señora de Piatcode: es is deprecated (Spanyol)Basilika Bunda Maria dari PiatBasilika Bunda Maria dari PiatTampilkan peta LuzonBasilika Bunda Maria dari PiatTampilkan peta Filipina17°47′13″N 121°28′48″E / 17.78698°N 121.48013°E / 17.78698; 121.48013Koordinat: 17°47′13″N 121°28′48″E / 17.78698°N 121.48013...

Belgian footballer Christian Piot Piot in 1977Personal informationDate of birth (1947-10-04) 4 October 1947 (age 76)Place of birth Ougrée, BelgiumHeight 1.76 m (5 ft 9 in)Position(s) GoalkeeperSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)1966–1978 Standard de Liège 305 (9)International career1969–1977 Belgium 40 (1)Managerial career2000–2005 Standard de Liège (goalkeeper coach)2005–2007 R.F.C. de Liège *Club domestic league appearances and goals Christian Piot (born 4 Oc...

العلاقات الدنماركية البليزية الدنمارك بليز الدنمارك بليز تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الدنماركية البليزية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين الدنمارك وبليز.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارنة...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Ислам (значения). ИсламСтолпы ислама Свидетельство веры Молитва Пост Милостыня Паломничество Столпы веры Аллах (Единобожие) Ангелы Пророки Писания Судный день Предопределение История и представители Мухаммед Халифы С...

Canadian-American entrepreneur Martha Matilda HarperBorn(1857-09-10)September 10, 1857Oakville, Ontario, Province of CanadaDiedAugust 3, 1950(1950-08-03) (aged 92)Rochester, New York, U.S.Occupation(s)Businesswoman, entrepreneur, and inventor Martha Matilda Harper (September 10, 1857 – August 3, 1950) was an American businesswoman, entrepreneur, and inventor who launched modern retail franchising and then built an international network of 500 franchised hair salons that emphasized heal...
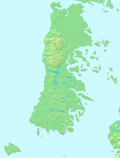
Map of the Sea of Chiloé and nearby roads. The Gulf of Ancud is seen in the centre of the upper half. Gulf of Ancud (Spanish: Golfo de Ancud) is a large body of water separating the Chiloé Island from the mainland of Chile. It is located north of the Gulf of Corcovado by which it is separated by Desertores Islands. To north Calbuco Archipelago separates it from Reloncaví Sound. External links Satellite map of Golfo de Ancud vteChiloé ArchipelagoMain islands Butachauques Caucahue Chiloé C...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Frein (homonymie). Le frein à disque est un système de freinage performant pour les véhicules munis de roues en contact avec le sol : automobile, moto, camion, avion, train, vélo tout terrain, etc. et pour diverses machines réclamant des freins performants et endurants. Ce système transforme l'énergie cinétique du véhicule en chaleur qui doit être dissipée le plus rapidement possible. Frein à disque en carbone renforcé sur une voiture ...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Révolution de 1848. Vous lisez un « article de qualité » labellisé en 2015. Révolutionnaires triomphant sur les barricades le 18 mars 1848 à Berlin. La révolution de Mars (Märzrevolution en allemand), également dénommée révolution allemande de 1848, est le Printemps des peuples germaniques. Il s'agit de l'ensemble des révolutions qui éclatent entre mars 1848 et la fin de l'été 1849 au sein de la Confédération germanique et dans l...

Satirical college newspaper in California For the animal, see Koala.This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: The Koala – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this template message)This article may be written from a fan's point of view, rather than a...

Loch Lomond Single MatJeniswhisky distillery AsalInggris Raya Diperkenalkan1966 Situs webhttp://www.lochlomonddistillery.com [sunting di Wikidata]lbs Loch Lomond atau lebih lengkapnya adalah Loch Lomond Single Mat adalah minuman keras, wisky yang diprpduksi oleh pabrik minuman keras Loch Lomond Distillery di Alexandria, Skotlandia dekat dengan kota Loch Lomond. Dalam buku komik Petualangan Tintin, merek ini adalah merek wisky favorit dari Kapten Haddock dan juga anjing Tintin yang se...

Protests against the presidency of Joe Biden Not to be confused with 2020–21 United States election protests. For the violent attack on January 6, 2021, see January 6 United States Capitol attack. 2021 United States inauguration week protestsPart of the 2020–21 United States election protests and attempts to overturn the 2020 United States presidential electionAn armored vehicle at the Ohio Statehouse prior to a planned pro-Trump armed marchDateJanuary 16–20, 2021(5 days)LocationUn...

Questa voce o sezione tratta di una competizione calcistica in corso. Le informazioni possono pertanto cambiare rapidamente con il progredire degli eventi. Se vuoi scrivere un articolo giornalistico sull'argomento, puoi farlo su Wikinotizie. Non aggiungere speculazioni alla voce. Voce principale: Serie D 2023-2024. Questa voce raccoglie un approfondimento sui gironi D, E ed F dell'edizione 2023-2024 della Serie D. Indice 1 Girone D 1.1 Squadre partecipanti 1.2 Classifica 1.3 Risultati 1.3.1 ...

French printer and inventor (1817–1879) Édouard-Léon Scott de MartinvillePortrait from Les Merveilles de la science by Louis FiguierBorn(1817-04-25)25 April 1817Paris, FranceDied26 April 1879(1879-04-26) (aged 62)Paris, FranceOccupations Printer Bookseller Known forInventing the earliest known sound recording device Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville ([e.dwaʁ.le.ɔ̃ skɔt də maʁ.tɛ̃.vil]; 25 April 1817 – 26 April 1879) was a French printer, bookseller and invent...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Chandernagor (homonymie). André Chandernagor Fonctions Premier président de la Cour des comptes 7 décembre 1983 – 19 septembre 1990 (6 ans, 9 mois et 12 jours) Prédécesseur Jean Rosenwald Successeur Pierre Arpaillange Ministre délégué aux Affaires européennes 22 mai 1981 – 7 décembre 1983 (2 ans, 6 mois et 15 jours) Président François Mitterrand Premier ministre Pierre Mauroy Gouvernement Mauroy I, II et III Pré...

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁�...

「アプリケーション」はこの項目へ転送されています。英語の意味については「wikt:応用」、「wikt:application」をご覧ください。 この記事には複数の問題があります。改善やノートページでの議論にご協力ください。 出典がまったく示されていないか不十分です。内容に関する文献や情報源が必要です。(2018年4月) 古い情報を更新する必要があります。(2021年3月)出...
أبراهام إيمانويل فروليش معلومات شخصية الميلاد 1 فبراير 1796 [1] بروغ الوفاة 1 ديسمبر 1865 (69 سنة) [1] مواطنة سويسرا عضو في زوفينجيا [لغات أخرى] الحياة العملية المهنة شاعر، وعالم عقيدة، وكاتب[2] اللغات الألمانية تعديل مصدري - تعديل ...

More Than a Game: The Story of Cricket's Early Years AuthorJohn MajorCountryUnited KingdomLanguageEnglishPublisherHarperCollinsPublication date2007Media typePrintPages400ISBN9780007280117 More Than a Game: The Story of Cricket's Early Years is a 2007 book about the history of cricket written by former British prime minister John Major. It was published by HarperCollins. Background John Major had been known to have a life long love of cricket.[1] After losing the 1997 United Kingd...

Lighthouse in Massachusetts, United States LighthouseSandy Neck Light US Coast Guard photoLocationBarnstable, MassachusettsCoordinates41°43′22″N 70°16′52″W / 41.72278°N 70.28111°W / 41.72278; -70.28111TowerConstructed1826Height16 m (52 ft) ShapeCylindrical Stone TowerMarkingsWhite with black bands and lanternHeritageNational Register of Historic Places contributing property Fog signalnoneLightFirst lit1857 (current structure)Deactiva...






