Contraceptive rights in New Zealand
|
Read other articles:

Pemandangan Karl-Marx-Allee dengan menara ganda Frankfurter Tor terlihat di belakang Bagian barat adimarga ini ditandai dengan Plattenbau (1967) Karl-Marx-Allee adalah adimarga bergaya sosialis yang dibangun oleh Jerman Timur antara tahun 1952 dan 1960 di Berlin Friedrichshain dan Mitte. Namanya diambil dari Karl Marx. Adimarga ini dinamai Stalinallee antara 1949 dan 1961 (sebelumnya Große Frankfurter Straße), dan merupakan proyek bangunan utama dari program rekonstruksi Jerman Timur setela...

1969 filmThe Diamond ArmFilm posterDirected byLeonid GaidaiWritten byLeonid GaidaiYakov KostyukovskyMoris SlobodskoyStarringYuri NikulinNina GrebeshkovaAndrei MironovAnatoli PapanovNonna MordyukovaCinematographyIgor ChernykhEdited byValentina YankovskayaMusic byAleksandr ZatsepinDistributed byMosfilmRelease date28 April 1969Running time100 minutesCountrySoviet UnionLanguageRussian The Diamond Arm (Russian: Бриллиантовая рука Brilliantovaya ruka) is a Soviet crime comedy film...

Maximum energy available for use Available energy redirects here. For the concept in particle physics, see Available energy (particle collision). Exergy, often referred to as available energy or useful work potential, is a fundamental concept in the field of thermodynamics and engineering. It plays a crucial role in understanding and quantifying the quality of energy within a system and its potential to perform useful work. Exergy analysis has widespread applications in various fields, includ...

.kpDiperkenalkan24 September 2007Jenis TLDtop-level domain kode negara InternetStatusAktifRegistriStar Joint VentureSponsorStar Joint Venture (Korea Computer Center)Pemakaian yang diinginkanEntitas yang terhubung dengan Korea UtaraPemakaian aktualDigunakan terutama oleh pemerintah Korea UtaraDomain terdaftar38 (Mulai 14 November 2021)[1]PembatasanHarus berupa perusahaan, organisasi, atau entitas pemerintah yang berbasis di Korea UtaraStrukturNama dapat didaftarkan langsung di t...

† Стеллерова корова Муляж стеллеровой коровы в Лондонском музее естествознания Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:Челюстно�...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Adobes, Spain – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message)Place in Castile-La Mancha, SpainAdobes, SpainAdobes, SpainShow map of Province of GuadalajaraAdobes, SpainShow map of Castilla-La ManchaAdobe...

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府...

1992 Indian filmAswamedhamAudio CoverDirected byK. Raghavendra RaoWritten bySatyanand (story / dialogues)Screenplay byYandamuri VeerendranathProduced byC. Aswini DuttStarringNandamuri BalakrishnaShobhan BabuMeenaNagmaCinematographyA. VincentAjayan VincentEdited byKotagiri Venkateswara RaoMusic byIlaiyaraajaProductioncompanyVyjayanthi MoviesRelease date 25 December 1992 (1992-12-25) Running time148 minutesCountryIndiaLanguageTelugu Aswamedham is a 1992 Telugu-language action fi...

وزارة الداخلية والبلديات (لبنان) وزارة الداخلية والبلديات (لبنان) تفاصيل الوكالة الحكومية البلد لبنان تأسست 1943؛ منذ 81 سنوات (1943) المركز حكومة لبنان الإدارة منصب المدير وزير الداخلية [لغات أخرى] موقع الويب الموقع الرسمي تعديل مصدري - تعديل وزارة ا...

Canadian professional esports team Toronto DefiantFoundedSeptember 7, 2018LeagueOverwatch Champions Series (2024–present)Overwatch League (2018–2023)RegionWestTeam historyToronto Defiant(2018–present)Based inToronto, CanadaArenaScotiabank ArenaColours OwnerChris OverholtAffiliation(s)Montreal RebellionMain sponsorBell CanadaParent groupOverActive MediaWebsiteOfficial websiteUniforms Toronto Defiant is a Canadian professional Overwatch esports team based in Toro...

1893–1953 French protectorate in Southeast Asia Kingdom of Luang PrabangພຣະຣາຊອານາຈັກຫລວງພະບາງPhrà Ràaj Aanaachak Luang PràabàngRoyaume de Luang Prabang(1893–1945; 1946–1947)Kingdom of LaosພຣະຣາຊອານາຈັກລາວPhra Raja A-na-chak LaoRoyaume du Laos(1945–1946; 1947–1953)1893–19451946–1953 Flag(1893–1952) Coat of arms(1949–1953) StatusProtectorate of France (1893–1899); constituent territory of French...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Shenavan. Shenavan (hy) Շենավան Administration Pays Arménie Région Lorri Maire Mandat Garush Dunamalyan (HHK)[1],[2] 2012-2016 Démographie Population 510 hab. (2008) Densité 35 hab./km2 Géographie Coordonnées 40° 52′ 00″ nord, 44° 14′ 00″ est Superficie 1 464 ha = 14,64 km2 Fuseau horaire UTC+4 Localisation Géolocalisation sur la carte : Arménie Shenavan Géolocali...

State in northeastern India State in Northeast India, IndiaNagalandStateState of NagalandClockwise from top: Kohima Doyang Western Dzüko Valley Kapamüdzü Peak Emblem of NagalandEtymology: Land of NagasNickname(s): Land of Festivals, Falcon Capital of the WorldMotto: UnityLocation of Nagaland in IndiaCoordinates: 25°40′N 94°07′E / 25.67°N 94.12°E / 25.67; 94.12Country IndiaRegionNortheast IndiaBefore wasPart of AssamFormation1 December 1963 Cap...

2009 edition of the IIHF World Championship 2009 IIHF World ChampionshipTournament detailsHost country SwitzerlandVenue(s)2 (in 2 host cities)Dates24 April – 10 MayOpened byHans-Rudolf MerzTeams16Final positionsChampions Russia (3rd title)Runner-up CanadaThird place SwedenFourth place United StatesTournament statisticsGames played56Goals scored323 (5.77 per game)Attendance379,044 (6,769 per game)Scoring leader(s)...

2021 MMA event UFC Fight Night: Costa vs. VettoriThe poster for UFC Fight Night: Costa vs. VettoriInformationPromotionUltimate Fighting ChampionshipDateOctober 23, 2021 (2021-10-23)VenueUFC ApexCityEnterprise, Nevada, United StatesAttendanceNot announced[1]Event chronology UFC Fight Night: Ladd vs. Dumont UFC Fight Night: Costa vs. Vettori UFC 267: Błachowicz vs. Teixeira UFC Fight Night: Costa vs. Vettori (also known as UFC Fight Night 196, UFC Vegas 41 and UFC on ESP...

「後藤ヒロキ」あるいは「後藤広喜」とは別人です。 後藤浩輝 2011年京都大賞典表彰式基本情報国籍 日本出身地 神奈川県[1]相模原市(現在の神奈川県相模原市中央区)出生は神奈川県横浜市生年月日 (1974-03-19) 1974年3月19日死没 (2015-02-27) 2015年2月27日(40歳没)身長 157cm[1]体重 50kg[1]血液型 B型[1]騎手情報所属団体 JRA所属厩舎 フリー[1]初免�...

هبة مشاري حمادة معلومات شخصية تاريخ الميلاد 2 فبراير 1978 (العمر 46 سنة) الجنسية الكويت الحياة العملية النوع دراما المهنة كاتبة قصص وسيناريو وحوار بوابة الأدب تعديل مصدري - تعديل هبة مشاري حمادة (2 فبراير 1978 -)، كاتبة كويتية. حاصلة على شهادة الماجستير في الأدب والنقد. عرف�...
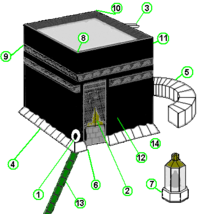
لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع الحجر الأسود (توضيح). الحجر الأسود لقطة مقربة للحجر الأسود ويظهر الإطار الفضي حوله تقديم البلد السعودية مدينة مكة المكرمة إحداثيات 21°25′21″N 39°49′34″E / 21.4225°N 39.826166666667°E / 21.4225; 39.826166666667 نوع مكان مقدس تصنيف إسلام الموقع الجغرافي تعدي...

العلاقات المكسيكية الكمبودية المكسيك كمبوديا المكسيك كمبوديا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات المكسيكية الكمبودية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين المكسيك وكمبوديا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه ال...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (يوليو 2020) نهائي دوري أبطال أفريقيا 1998الحدثدوري أبطال أفريقيا ديناموز أسيك ميموزا 2 4 تعادلا في الذهاب 0–0 وفي الإياب ...