Charles Perry McCormick
|
Read other articles:

BeningInformasi latar belakangNama lainNew BeningAsalJakarta, IndonesiaGenrePopTahun aktif1997–2000 2017–SekarangLabelMusica Studio'sAnggotaDitasiani Oktovie Dewi Murniaty Vera Hernita Soedibyo Mita MelanieMantan anggotaVonny Cornellya (1997-2000) Bening adalah sebuah girl band Indonesia yang populer di kisaran tahun 1997. Grup ini beranggotakan Vonny Cornellya (Vonny), Ditasiani Oktovie (Dita), Vera Hernita Soedibyo (Vera), dan Dewi Murniati (Dewi). Singel mereka yang paling populer adal...

Peta Bytom Bytom (['bitɔm] (bantuan·info); Jerman: Beuthencode: de is deprecated ) ialah sebuah kota di Polandia selatan dengan 205.560 penduduk (1999). Sejak 1999 terletak di Provinsi Silesia, sebelumnya di Provinsi Katowice (1975-1998). Pendidikan Wyższa Szkoła Ekonomii i Administracji Universitas Teknologi Silesia - Fakultas Transportasi Politik Konstituensi Bytom/Gliwice/Zabrze Anggota Parlemen (Sejm) yang dipilih dari konstituensi Bytom/Gliwice/Zabrze Jan Chojnacki, SLD-UP Stanisław...

Часть серии статей о Холокосте Идеология и политика Расовая гигиена · Расовый антисемитизм · Нацистская расовая политика · Нюрнбергские расовые законы Шоа Лагеря смерти Белжец · Дахау · Майданек · Малый Тростенец · Маутхаузен ·&...

Christophe Barratier (kelahiran 17 Juni 1963) adalah seorang produser, sutradara, penulis latar, dan penulis latar Prancis. Kehidupan awal dan pendidikan Barratier adalah putra dari aktris Eva Simonet dan M. Barratier. Ia adalah keponakan dari sutradara Jacques Perrin, yang mempengaruhi pilihan kariernya. Karier Barratier telah menyutradarai tiga film fitur yang sukses. Film pertamanya adalah The Chorus (2004). Sebagai pembuat lirik pada lagu film Look To Your Path, ia dinominasikan pada Aca...

Stasiun Kedungjati JS25 Stasiun Kedungjati, 2019LokasiKedungjati, Kedungjati, Grobogan, Jawa TengahIndonesiaKoordinat7°9′42″S 110°38′16″E / 7.16167°S 110.63778°E / -7.16167; 110.63778Koordinat: 7°9′42″S 110°38′16″E / 7.16167°S 110.63778°E / -7.16167; 110.63778Ketinggian+36 mOperator Kereta Api IndonesiaDaerah Operasi IV Semarang Letak km 34+131 lintas lintas Semarang Tawang-Brumbung-Gundih-Solo Balapan-Solo Jebres/Yogyaka...

2008 single by Kylie Minogue For other uses, see All I See (disambiguation). All I SeeSingle by Kylie Minoguefrom the album X Released11 March 2008GenrePopR&B[1]Length3:04LabelParlophoneSongwriter(s) Jonas Jeberg Mich Hedin Hansen Edwin Lil' Eddie Serrano Producer(s) Jonas Jeberg Cutfather Kylie Minogue singles chronology In My Arms (2008) All I See (2008) The One (2008) Music videoAll I See on YouTube All I See is a song recorded by Australian Kylie Minogue for her tenth studio a...

Physics-mathematics connection Lie groups and Lie algebras Classical groups General linear GL(n) Special linear SL(n) Orthogonal O(n) Special orthogonal SO(n) Unitary U(n) Special unitary SU(n) Symplectic Sp(n) Simple Lie groups Classical An Bn Cn Dn Exceptional G2 F4 E6 E7 E8 Other Lie groups Circle Lorentz Poincaré Conformal group Diffeomorphism Loop Euclidean Lie algebras Lie group–Lie algebra correspondence Exponential map Adjoint representation Killing formIndex Simple Lie algebra Loo...

404 Layur Halte TransjakartaHalte Layur pada Januari 2024LetakKotaJakarta TimurDesa/kelurahanJati, Pulo GadungKodepos13220AlamatJalan PemudaKoordinat6°11′37″S 106°53′56″E / 6.19349°S 106.89902°E / -6.19349; 106.89902Koordinat: 6°11′37″S 106°53′56″E / 6.19349°S 106.89902°E / -6.19349; 106.89902Desain HalteStruktur BRT, median jalan bebas 1 tengah Pintu masukJembatan penyeberangan di sudut Jalan PemudaGerbang tarifYaI...

هذه المقالة بحاجة لصندوق معلومات. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة صندوق معلومات مخصص إليها. نينتندو إس-إس إم بي نينتندو إس-إس إم بي (بالإنجليزية: Nintendo S-SMP) هي وحدة المعالجة المركزية للصوت في جهاز الألعاب سوبر نينتندو إنترتينمنت سيستم. تتكون من معالج إشارة رقمي 16 بت و�...
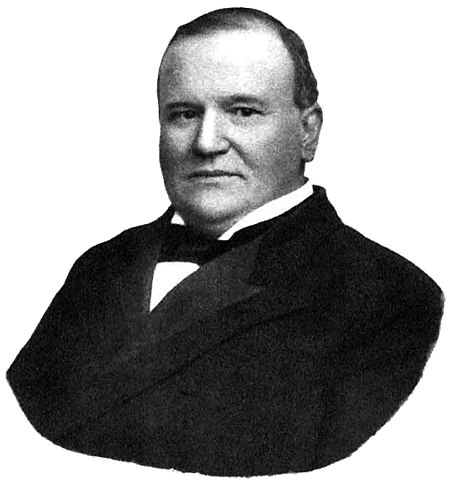
Election for Governor of Kentucky This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: 1895 Kentucky gubernatorial election – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2023) 1895 Kentucky gubernatorial election ← 1891 November 5, 1895 1899 → Nominee William O'Con...

「俄亥俄」重定向至此。关于其他用法,请见「俄亥俄 (消歧义)」。 俄亥俄州 美國联邦州State of Ohio 州旗州徽綽號:七葉果之州地图中高亮部分为俄亥俄州坐标:38°27'N-41°58'N, 80°32'W-84°49'W国家 美國加入聯邦1803年3月1日,在1953年8月7日追溯頒定(第17个加入联邦)首府哥倫布(及最大城市)政府 • 州长(英语:List of Governors of {{{Name}}}]]) •&...

Holden Commodore (VE)Holden Calais V (sedan)InformasiProdusenHoldenMasa produksi2006-2013PerakitanAustralia: Elizabeth, Australia SelatanPerancangPeter Hughes (2003)Bodi & rangkaPlatformGM ZetaPenyalur dayaMesin3KronologiPendahuluHolden Commodore (VZ)PenerusHolden Commodore (VF) Holden Commodore (VE) adalah jenis mobil eksekutif yang diproduksi oleh Holden, produsen kendaraan bermotor asal Australia. Mobil eksekutif ini diproduksi antara tahun 2006 hingga 2013. Holden Commodore (VE) merup...

豪栄道 豪太郎 場所入りする豪栄道基礎情報四股名 澤井 豪太郎→豪栄道 豪太郎本名 澤井 豪太郎愛称 ゴウタロウ、豪ちゃん、GAD[1][2]生年月日 (1986-04-06) 1986年4月6日(38歳)出身 大阪府寝屋川市身長 183cm体重 160kgBMI 47.26所属部屋 境川部屋得意技 右四つ・出し投げ・切り返し・外掛け・首投げ・右下手投げ成績現在の番付 引退最高位 東大関生涯戦歴 696勝493敗...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع جون كينيدي (توضيح). هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (مارس 2019) جون كينيدي (بالإنجليزية: John Kennedy) معلومات شخصية الميلاد 22 مارس 1938 (86 سنة) يونغزتاون مواطنة الولايات المتح...

Indian politician (born 1981) Anupriya PatelPatel in 2021Minister of State for Commerce and IndustryIncumbentAssumed office 7 July 2021Prime MinisterNarendra ModiMinisterPiyush GoyalPreceded byHardeep Singh PuriMinister of State for Health and Family WelfareIn office4 July 2016 – 24 May 2019Prime MinisterNarendra ModiMinisterJagat Prakash NaddaSucceeded byAshwani Kumar ChoubeyPresident of AD(S)IncumbentAssumed office 14 December 2016Preceded byPosition establishedMember of ...

Location of Gilchist County in Florida This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Gilchrist County, Florida. This is intended to be a complete list of the properties on the National Register of Historic Places in Gilchrist County, Florida, United States. The locations of National Register properties for which the latitude and longitude coordinates are included below, may be seen in a map.[1] There are two properties listed on the National Register in the c...

Untuk Kota di Turki, lihat Batman (Turki). BatmanSampul cetakan kedua Batman #608 (Oktober 2002), oleh Jim Lee dan tinta oleh Scott Williams.Informasi publikasiPenerbitDC ComicsPenampilan pertamaDetective Comics #27(sampul Mei 1939 /tanggal rilis Maret 1939)Dibuat oleh Bob Kane Bill Finger[1][2] Informasi dalam ceritaAlter egoBruce WayneTempat asalGotham City (Bumi)Afiliasi tim Keluarga Batman Justice League Outsiders Batmen of All Nations Batman Incorporated Kemitraan Robin (...

American soccer player (born 2001) For the Australian musician, see Duncan McGuire (musician). Duncan McGuire McGuire in 2024Personal informationFull name Duncan MacAllister McGuire[1]Date of birth (2001-02-05) February 5, 2001 (age 23)[2]Place of birth Omaha, Nebraska, United StatesHeight 6 ft 1 in (1.85 m)Position(s) ForwardTeam informationCurrent team Orlando CityNumber 13Youth career2014–2018 Sporting Omaha FCCollege careerYears Team Apps (Gls)2019–...

Extinct genus of amphibians LoxommaTemporal range: ~330–306.95 Ma PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N Loxomma allmanni skull cast at the Museum für Naturkunde, Berlin Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Clade: Sarcopterygii Clade: Tetrapodomorpha Family: †Baphetidae Subfamily: †Loxommatinae Genus: †LoxommaHuxley, 1862 Loxomma (meaning “slanting eyes”) is an extinct genus of Loxommatinae and one of the first Carboniferous tetrapods.[...

Roman province from 27 BC to 69/79 AD This article is about the Roman province. For the Roman Prefecture, see Praetorian prefecture of Illyricum. For other uses, see Illyria. This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages) This article relies excessively on references to primary sources. Please improve this article by adding secondary or tertiary sources. Find sources: Illyricum Roman pr...