Bretwalda
|
Read other articles:

Mengenal Bisri Effendy Informasi Pribadi Nama Bisri Effendy Lahir Jember, 12 Maret 1953 Kebangsaan Indonesia Almamater UIN Sunan Kalijaga Yogyakarta, Leiden University Organisasi Nadhatul Ulama Bisri Efendy adalah seorang jurnalis, peneliti sekaligus guru. Beberapa media menyebutnya sebagai “Guru Riset Anak Muda NU”.[1] Ia juga dikenal sebagai salah satu sahabat mantan presiden Indonesia ke-4, K.H Abdurrahman Wahid atau Gusdur. Ia juga pernah menjadi penulis kata pengantar di sal...

Miss World 1984Tanggal15 November 1984TempatRoyal Albert Hall, London, Britania RayaPembawa acaraPeter Marshall, Judith ChalmersPengisi acaraThe DriftersPenyiaranThames TelevisionPeserta72Finalis/Semifinalis15Tidak tampilIndonesia, Liberia, Tonga, TurkiTampil kembaliKenya, Nigeria, TahitiPemenangAstrid Carolina Herrera Venezuelalbs Miss World 1984, merupakan edisi ke-34 dari kontes kecantikan Miss World, yang diadakan pada 15 November 1984 di Royal Albert Hall di Lond...

Untuk penggunaan lain, lihat Dolce Vita (disambiguasi). La dolce vitaPoster rilis asli buatan Giorgio OlivettiSutradaraFederico FelliniProduserGiuseppe Amato, Angelo RizzoliSkenarioFederico Fellini, Ennio Flaiano, Tullio Pinelli, Brunello Rondi, Pier Paolo PasoliniCerita Federico Fellini Ennio Flaiano Tullio Pinelli Pemeran Marcello Mastroianni Anita Ekberg Anouk Aimée Yvonne Furneaux Magali Noël Alain Cuny Nadia Gray Penata musikNino RotaSinematograferOtello MartelliPenyuntingLeo Cat...

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Пт�...

HusseinRaja Yordania ke-4Berkuasa11 Agustus 1952 – 7 Februari 1999Penobatan11 Agustus 1952PendahuluTalal IPenerusAbdullah IIInformasi pribadiKelahiran(1935-11-14)14 November 1935Amman, YordaniaKematian7 Februari 1999(1999-02-07) (umur 63)Amman, YordaniaWangsaHashemiteNama lengkapHussein bin Talal bin Abdullah bin HusseinAyahTalal dari YordaniaIbuZein al Sharaf TalalPasanganDina bint 'Abdu'l-HamidAntoinette Avril GardinerAlia Baha ed din ToukanRatu NoorAnakPutri AliaAbdullah II dari Yor...

The Pirates of the Caribbean franchise logo Pirates of the Caribbean is a Walt Disney Company franchise that originated with the theme park attraction of the same name opened at Disneyland in 1967, the last such attraction that Walt Disney himself oversaw the building of.[1] Although the franchise originated from ride attractions, it gained mainstream popularity in the 2000s with the release of the film series created by Ted Elliott and Terry Rossio,[1] which was followed by ...

Vessel-shaped flute Vessel flutesOcarinas on display at a shop in TaiwanBlowing across the opening of empty bottle produces a basic edge-blown vessel flute. A vessel flute is a type of flute with a body which acts as a Helmholtz resonator. The body is vessel-shaped, not tube- or cone-shaped; that is, the far end is closed. Most flutes have cylindrical or conical bore (examples: concert flute, shawm). Vessel flutes have more spherical hollow bodies. The air in the body of a vessel flute resona...

1939 filmThugs with Dirty MugsTitle card from the 1944 Blue Ribbon reissueDirected byTex AveryStory byJack MillerProduced byLeon SchlesingerStarringMel BlancDanny WebbJohn DeeringTedd PierceMusic byCarl W. StallingAnimation bySidney SutherlandColor processTechnicolorDistributed byWarner Bros. PicturesThe Vitaphone CorporationRelease date May 6, 1939 (1939-05-06) Running time8:05LanguageEnglish Thugs with Dirty Mugs is a 1939 Warner Bros. Merrie Melodies cartoon directed by Tex ...

Port in the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil Porto do Rio de JaneiroPort of Rio de Janeiro in February 2011Click on the map for a fullscreen viewLocationCountryBrazilLocationRio de Janeiro, Rio de JaneiroCoordinates22°53′31″S 43°11′43″W / 22.89194°S 43.19528°W / -22.89194; -43.19528DetailsOpenedJuly 20, 1910Owned byCompanhia Docas do Rio de JaneiroType of harbourSeaportSize1,000,000 m2StatisticsAnnual cargo tonnage6.1 million tonnes (2016)Websitehttp://www.po...

Dutch business executive Barthold Theodoor Willem van Hasselt in 1948 Barthold Theodoor Willem van Hasselt (7 November 1896, Leiden - 5 August 1960, Wassenaar) was a Dutch business executive in the Dutch East Indies and the chief executive of Royal Dutch Shell from 1949 to 1951. Family Van Hasselt was the son of Marie Elise Prins (1875-1949) and the physician Sjoerd Folkert Willem van Hasselt (1868-1934). He married Elisabeth Henriette Versteegh (1898-1957) in 1920 and Marion Elizabeth Davids...

坐标:43°11′38″N 71°34′21″W / 43.1938516°N 71.5723953°W / 43.1938516; -71.5723953 此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2017年5月21日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:新罕布什尔州 — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源...

30th Governor of Oregon Not to be confused with Tom McCall (Georgia politician). Tom McCall30th Governor of OregonIn officeJanuary 9, 1967 – January 13, 1975Preceded byMark HatfieldSucceeded byRobert W. Straub18th Secretary of State of OregonIn officeJanuary 4, 1965 – January 9, 1967GovernorMark HatfieldPreceded byHowell ApplingSucceeded byClay Myers Personal detailsBornThomas Lawson McCall(1913-03-22)March 22, 1913Scituate, Massachusetts, U.S.DiedJanuary 8, 1983(1983-01...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Desember 2022. Pemberontakan HimaraBagian dari Perang Turki PanjangTanggalJuli–Agustus 1596LokasiHimara, Kesultanan Utsmaniyah (sekarang Albania)Hasil Kemenangan bagi Kesultanan UtsmaniyahPihak terlibat Himariotes Turki (Kesultanan Utsmaniyah)Tokoh dan pemim...

Upper social class Aristocrat redirects here. For other uses, see Aristocrat (disambiguation). The Ladies Waldegrave, a portrait of three English aristocrats from the Waldegrave family by Joshua Reynolds A château, the primary form of residence for the French aristocracy The aristocracy[1] is historically associated with a hereditary or a ruling social class. In many states, the aristocracy included the upper class of people (aristocrats) with hereditary rank and titles.[2] I...
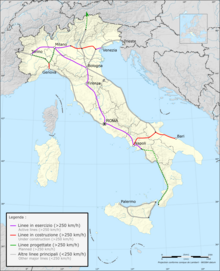
ItalyA frecciarossa high-speed train next to an older E.444R at Milano CentraleOperationNational railwayFerrovie dello StatoMajor operatorsTrenitalia (national)Nuovo Trasporto Viaggiatori (national)Trenord (local)Trenitalia Tper (local) Thello (international)Mercitalia (freight)StatisticsRidership883.3 million (2019)[1]System lengthTotal16,723 km (10,391 mi)[2]Double track7,505 km (4,663 mi)[2]Track gaugeMain1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄...

British tabloid newspaper For the RTÉ Radio 1 programme, see Weekend Sport. Sunday SportA 2021 example of the tabloid's satirical headlinesTypeSunday newspaperFormatTabloidOwner(s)David SullivanPublisherSunday Sport (2011) Ltd[1] (original publisher Sport Newspapers)EditorNick AppleyardFounded1986Political alignmentNone (yellow journalism)HeadquartersCity View House 5 Union Street, Ardwick, Manchester, M12 4JD, United KingdomCirculationN/A [a]Websitesundaysportonline.co.uk Th...

Lanskap Bellot. BellotNegaraPrancisArondisemenProvinsKantonRebaisAntarkomunenonePemerintahan • Wali kota (2008-2014) Jean Gallois • Populasi1706Kode INSEE/pos77030 / 2 Population sans doubles comptes: penghitungan tunggal penduduk di komune lain (e.g. mahasiswa dan personil militer). Bellot merupakan sebuah komune di departemen Seine-et-Marne di region Île-de-France di utara-tengah Prancis. Demografi Pada sensus 1999, penduduknya berjumlah 706 jiwa. Penduduknya d...

Head of the Government of Romania Prime Minister of the Government of RomaniaPrim-ministrul Guvernului RomânieiStandard of the prime minister of RomaniaIncumbentMarcel Ciolacusince 15 June 2023StyleHis/Her ExcellencyMember ofGovernment of RomaniaSupreme Council of National DefenceSeatVictoria Palace, BucharestAppointerPresident of RomaniaTerm length4 yearsNo term limitInaugural holderBarbu Catargiu as President of The Council of MinistersFormation22 January 1862; 162 years ...

Questa voce sull'argomento distretti del Giappone è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Takidistretto多気郡 LocalizzazioneStato Giappone RegioneKansai Prefettura Mie SottoprefetturaNon presente TerritorioCoordinate34°22′15.6″N 136°19′48″E34°22′15.6″N, 136°19′48″E (Taki) Superficie506,97 km² Abitanti49 178 (1-7-2008) Densità97 ab./km² Altre informazioniFuso orarioUTC+9 CartografiaTaki Taki – Ma...

「東京臨海高速鉄道」あるいは「東葉高速鉄道」とは異なります。 東京高速鉄道(とうきょうこうそくてつどう) (初代)利光鶴松が経営した電力資本・鬼怒川水力電気傘下の企業。1919年(大正8年)に都内の複数の地下鉄路線の免許を申請、1920年(大正9年)3月17日に新宿 - 大塚間の免許が交付されたものの、これを新宿から郊外方向へ延長する形で同じ鬼怒川水力�...


