Bonus (basketball)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Artikel atau sebagian dari artikel ini mungkin diterjemahkan dari List of emperors of the Han dynasty di en.wikipedia.org. Isinya masih belum akurat, karena bagian yang diterjemahkan masih perlu diperhalus dan disempurnakan. Jika Anda menguasai bahasa aslinya, harap pertimbangkan untuk menelusuri referensinya dan menyempurnakan terjemahan ini. Anda juga dapat ikut bergotong royong pada ProyekWiki Perbaikan Terjemahan. (Pesan ini dapat dihapus jika terjemahan dirasa sudah cukup tepat. Lihat pu...

American pastor For other people with the same name, see John Norris (disambiguation). J. Frank NorrisBorn(1877-09-18)September 18, 1877Dadeville, Alabama, USDiedAugust 20, 1952(1952-08-20) (aged 74)Jacksonville, Florida, USAlma materBaylor UniversitySouthern Baptist Theological SeminaryOccupationsPastor, First Baptist Church of Fort Worth (1909–1952)Pastor, Temple Baptist Church in Detroit, Michigan (1935–1951)Editor Baptist Standard (prior to 1909)Publisher, The Search...

American scholar (1910–1963) For other people with the same name, see Richard Weaver (disambiguation). Photo of Weaver Richard Malcolm Weaver, Jr (March 3, 1910 – April 1, 1963) was an American scholar who taught English at the University of Chicago. He is primarily known as an intellectual historian, political philosopher, and a mid-20th century conservative and as an authority on modern rhetoric. Weaver was briefly a socialist during his youth, a lapsed leftist intellectual (conservativ...

French privateer, businessman and slave trader (1773–1827) Robert SurcoufSurcouf c. 1820Born(1773-12-12)12 December 1773Saint-Malo, BrittanyDied8 July 1827(1827-07-08) (aged 53)Saint-Servan, BrittanyAllegiance French Empire Bourbon RestorationService/branch French Navy(briefly)Years of service1798–1809RankPrivateerCommands heldÉmilie Clarisse Confiance RevenantAwardsSabre of honourLegion of HonourSpouse(s)Marie BlaizeRelationsBrother to Nicolas SurcoufCousin to Joseph PotierOth...

F1 2001 beralih ke halaman ini. Untuk permainan video, lihat Formula One 2001 (permainan video) dan F1 2001 (permainan video). Kejuaraan DuniaFormula Satu FIA 2001 Juara Dunia Pembalap: Michael Schumacher Juara Dunia Konstruktor: Ferrari Sebelum: 2000 Sesudah: 2002 Balapan menurut negaraBalapan menurut musimSeri pendukung: Formula 3000Porsche Supercup Formula Satu musim 2001 merupakan musim reguler GP Formula 1 yang ke-52. Di musim 2001 ini, Michael Schumacher berhasil mempertahankan gelar ju...

Type of headgear popularised in Britain British Foreign Minister Anthony Eden, wearing his trademark hat, arriving at Gatow Airport on 15 July 1945 to attend the Potsdam Conference An Anthony Eden hat, or simply an Anthony Eden, was a type of headgear popularised in Britain in the mid-20th century by politician Anthony Eden, later 1st Earl of Avon (1897–1977). Eden, who was known for his sartorial elegance, favoured a silk-brimmed, black felt homburg at a time when most Britons preferred th...

Agriculture using powered machinery A cotton picker at work. The first successful models were introduced in the mid-1940s and each could do the work of 50 hand pickers. Mechanised agriculture or agricultural mechanization is the use of machinery and equipment, ranging from simple and basic hand tools to more sophisticated, motorized equipment and machinery, to perform agricultural operations.[1] In modern times, powered machinery has replaced many farm task formerly carried out by man...

قصر قارونمعلومات عامةنوع المبنى مستوطنة معبد مصري موقع أثري المنطقة الإدارية محافظة الفيوم البلد مصر ارتفاع المبنىالارتفاع عن سطح البحر −2 متر[1] معلومات أخرىالإحداثيات 29°24′20″N 30°25′06″E / 29.405631°N 30.418289°E / 29.405631; 30.418289 تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيان...

Chronologies Données clés 1835 1836 1837 1838 1839 1840 1841Décennies :1800 1810 1820 1830 1840 1850 1860Siècles :XVIIe XVIIIe XIXe XXe XXIeMillénaires :-Ier Ier IIe IIIe Chronologies géographiques Afrique Afrique du Sud, Algérie, Angola, Bénin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroun, Cap-Vert, République centrafricaine, Comores, République du Congo, République démocratique du Congo, Côte d'Ivoire, Djibouti, Égyp...

Johns Creek redirects here. For other uses, see Johns Creek (disambiguation). City in Georgia, United StatesJohns Creek, GeorgiaCityThe former Johns Creek City Hall Location in Fulton County and the state of GeorgiaJohns CreekLocation of Johns Creek in Metro AtlantaShow map of GeorgiaJohns CreekJohns Creek (the United States)Show map of the United StatesJohns CreekJohns Creek (Metro Atlanta)Show map of Metro AtlantaCoordinates: 34°02′00″N 84°12′10″W / 34.03333°N 84....

The Baháʼí Faith in South Carolina begins in the transition from Jim Crow to the Civil Rights Movement but defines another approach to the problem, and proceeded according to its teachings. The first mention in relation to the history of the religion came in the 1860s in a newspaper article. Following this the first individual from South Carolina to find the religion was Louis Gregory in 1909, followed by individuals inside the state. Communities of Baháʼís were soon operating in North ...

TeldeMunisipalitas dan kota kecil BenderaLambang kebesaranLokasi munisipalitas di Gran CanariaTeldeLokasi di provinsi Las PalmasTampilkan peta Province of Las PalmasTeldeTelde (Canary Islands)Tampilkan peta Canary IslandsTeldeTelde (Spain, Canary Islands)Tampilkan peta Spain, Canary IslandsKoordinat: 27°59′N 15°25′W / 27.983°N 15.417°W / 27.983; -15.417NegaraSpanyolKomunitas otonomKepulauan CanaryProvinsiLas PalmasPulauGran CanariaPemerintahan • Wal...

大宮競輪場(大宮双輪場) 基本情報所在地 埼玉県さいたま市大宮区高鼻町4大宮公園内座標 北緯35度55分8.9秒 東経139度38分1.8秒 / 北緯35.919139度 東経139.633833度 / 35.919139; 139.633833座標: 北緯35度55分8.9秒 東経139度38分1.8秒 / 北緯35.919139度 東経139.633833度 / 35.919139; 139.633833電話投票 25#開設 1949年(昭和24年)1月14日民間委託 日本トーター施行�...

Direktorat Jenderal PenguatanDaya Saing Produk Kelautan dan Perikanan Kementerian Kelautan dan Perikanan Republik IndonesiaGambaran umumDasar hukumPeraturan Presiden Nomor 63 Tahun 2015 dan Peraturan Presiden Nomor 2 Tahun 2017Susunan organisasiDirektur JenderalBudi SulistiyoSitus webwww.kkp.go.id Direktorat Jenderal Penguatan Daya Saing Produk Kelautan dan Perikanan merupakan unsur pelaksana pada Kementerian Kelautan dan Perikanan Republik Indonesia yang berada di bawah dan bertanggung ...

Konflik internal di MyanmarPeta situasi militer di Myanmar (per Februari 2022)Tanggal02 April 1948 (1948-04-02) – sekarang(76 tahun, 3 bulan, 1 minggu dan 4 hari)LokasiMyanmar (Burma)Hasil Masih berlangsung Konflik etnis besar di negara bagian Kachin, Kayah, Kayin, Rakhine, dan Shan Gencatan senjata ditandatangani oleh berbagai kelompok sejak tahun 1989 Zona otonom diciptakan untuk enam etnis minoritas berdasarkan Konstitusi Myanmar tahun 2008 Junta militer mengakui...

This article is about the 1986 film. For the Telugu lyricist, see Sirivennela Seetharama Sastry. 1986 Indian filmSirivennela సిరివెన్నలFilm posterDirected byK. ViswanathWritten byK. ViswanathSainath Thotapalli (dialogues)Produced byCh. Ramakrishna ReddyN. Bhaskara ReddyUjjuri ChinaveerrajuStarringSuhasiniSarvadaman BanerjeeMoon Moon SenCinematographyM. V. RaghuEdited byG. G. Krishna RaoMusic byK. V. MahadevanProductioncompanyGeetha Krishna Movie CombinesRelease date 5 ...
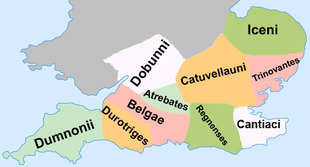
La statua di Boudicca (Boadicea), regina degli Iceni, a Westminster I Britanni erano un insieme di popolazioni celtiche stanziate nell'antichità nelle Isole britanniche (Gran Bretagna e Irlanda). Giunti nella regione a partire dall'VIII secolo a.C., i Celti della Britannia rimasero frazionati in numerose tribù, facilitando così la conquista del loro territorio prima da parte dei Romani (I secolo d.C.) e poi dagli Anglosassoni (V secolo). I Britanni furono sottomessi politicamente e cultura...

German poet (1748–1776) Ludwig Hölty Ludwig Christoph Heinrich Hölty (21 December 1748 – 1 September 1776) was a German poet, known especially for his ballads. Hölty was born in the Electorate of Hanover in the village of Mariensee (today part of Neustadt am Rübenberge) where his father was pastor. In 1769, he went to study theology at the University of Göttingen. There he formed a close friendship with Johann Martin Miller, Johann Heinrich Voss, Heinrich Christian Boie, the brothers...

أفني حيفتس مستوطنة بشرية الإحداثيات 32°17′05″N 35°04′26″E / 32.284627777778°N 35.073980555556°E / 32.284627777778; 35.073980555556 تأسست 1987 تقسيم إداري البلد الأراضي الفلسطينيةالضفة الغربية الموقع مدينة طولكرم، الضفة الغربية خصائص جغرافية ارتفاع 200 متر عدد السكان (2018) المج�...

1999 Indian filmRajajiDirected byVimal Kumar[2][1]Written bySatish Jain[2][1]Screenplay bySatish Jain[2][1]Story bySatish Jain[2][1]Produced byVimal Kumar[2][1]StarringGovindaRaveena TandonShakti KapoorRanjeetAruna IraniKader KhanGuddi Maruti[2][1]CinematographyAnil Dhanda[2]Edited byPrakash Dave[2]Music byAnand–Milind & Vishwajeet Mukherjee.[2][1]Release date...

