Baháʼí Faith in Slovakia
|
Read other articles:

1995 song by the One World OrchestraThe MagnificentSong by the One World Orchestra featuring the Massed Pipes and Drums of the Children's Free Revolutionary Volunteer Guardfrom the album The Help Album Released9 September 1995 (UK)Recorded4 September 1995GenreDrum and bassLength2:12LabelGo! Discs RecordsSongwriter(s)Bill Drummond, Jimmy Cauty and Elmer BernsteinProducer(s)Drummond/Cauty The Magnificent is a 1995 song by the One World Orchestra (Bill Drummond and Jimmy Cauty, better known as T...

Wali Kota PadangPetahanaHendri Septasejak 7 April 2021KediamanRumah Dinas Wali Kota PadangMasa jabatan5 tahun, sesudahnya dapat dipilih kembali sekaliDibentuk1945 (di bawah pemerintahan Indonesia)Pejabat pertamaAbdoel HakimSitus webwww.padang.go.id Wali Kota Padang adalah politisi yang dipilih untuk bertanggung jawab dalam mengatur dan mengelola pemerintahan Kota Padang, sebagai bagian dari sistem penyelenggaraan pemerintahan daerah di Indonesia. Abubakar Jaar adalah wali kota pertama se...
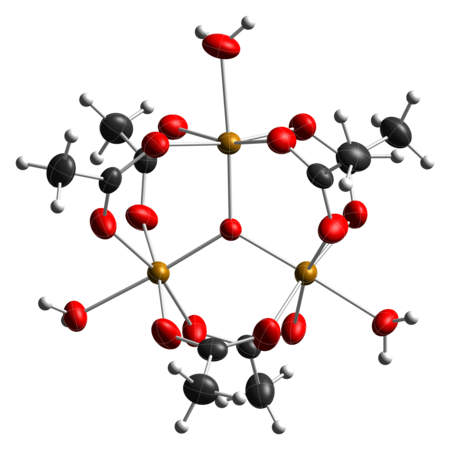
Iron(III) acetate[1] Names IUPAC name iron(III) acetate Other names basic iron(III) acetate , iron(III) oxyacetate, iron(III) Acetate Identifiers CAS Number 1834-30-6 Y 3D model (JSmol) Interactive imagecoordination complex: Interactive image ChemSpider 144555 PubChem CID 164887 UNII CZZ8832SI5 Y InChI InChI=1/3C2H4O2.Fe/c3*1-2(3)4;/h3*1H3,(H,3,4);/q;;;+3/p-3Key: PVFSDGKDKFSOTB-DFZHHIFOAZ SMILES CC(=O)[O-].CC(=O)[O-].CC(=O)[O-].[Fe+3]coordination complex: O1[...

Russian politician For other people named Nikolay Nikolaev, see Nikolay Nikolaev. In this name that follows Eastern Slavic naming customs, the patronymic is Nikolayevich and the family name is Nikolaev. You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Russian. (February 2024) Click [show] for important translation instructions. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must ...

زيني ماكس ميديازيني ماكس ميدياالشعارمعلومات عامةالبلد الولايات المتحدة التأسيس مايو 1999النوع ملكية خاصةالشكل القانوني شركة خاصة المقر الرئيسي روكفيل، الولايات المتحدةموقع الويب zenimax.com (الإنجليزية) المنظومة الاقتصاديةالشركة الأم إكس بوكس غيم ستوديوز[1] (2021 – 2022)مايك�...

2017 UCI Urban Cycling World ChampionshipsAbel Mustieles competing in the final of the men's 20 trials competition in ChengduVenueChengdu, ChinaDate(s) (2017-11-06 - 2017-11-12)6 – 12 November 2017Events102018 → The 2017 UCI Urban Cycling World Championships was the first edition of the UCI Urban Cycling World Championships and was held from 6 to 12 November 2017 in Chengdu, China.[1] The event comprised the 2017 UCI World Championships in BMX freestyle, cross-countr...

Mexican anthology drama television series La rosa de GuadalupeGenreMelodramaDramaCreated byCarlos Mercado OrduñaWritten byJulián Aguilar Carlos Mercado Mauricio Aridjis Fabián QuezadaDirected byJosé Ángel García Marta Luna Ricardo de la Parra Eduardo Said Lorena MazaPresented byHelena RojoOpening themeInstrumental themeCountry of originMexicoOriginal languageSpanishNo. of episodes1,995+ProductionExecutive producerMiguel Angel HerrosProduction locations Filming Televisa San Ángel Mexico...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Traumatisme. Traumatisme Infirmiers américains perfusant un patient blessé par balle. Données clés Causes Attaque (d) ou accident Traitement Spécialité Médecine d'urgence et traumatologie Classification et ressources externes CISP-2 A80 CIM-10 T79 CIM-9 900-957 DiseasesDB 28858 MedlinePlus 000024 eMedicine trauma MeSH D014947 Mise en garde médicale modifier - modifier le code - voir Wikidata (aide) Un traumatisme (du grec τραῦμα (trauma) = «&...

Voce principale: Football Club Forlì. Football Club Forlì DilettantisticaStagione 2011-2012Sport calcio Squadra Forlì Allenatore Attilio Bardi Presidente Romano Conficconi Serie D1º posto nel girone D (promosso in Lega Pro Seconda Divisione). Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Andrea Martini (38) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Petrașcu (27) StadioTullo Morgagni 2010-2011 2012-2013 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa voce raccoglie le informazioni riguardanti il Football Club Forl...
此條目介紹的是拉丁字母中的第2个字母。关于其他用法,请见「B (消歧义)」。 提示:此条目页的主题不是希腊字母Β、西里尔字母В、Б、Ъ、Ь或德语字母ẞ、ß。 BB b(见下)用法書寫系統拉丁字母英文字母ISO基本拉丁字母(英语:ISO basic Latin alphabet)类型全音素文字相关所属語言拉丁语读音方法 [b][p][ɓ](适应变体)Unicode编码U+0042, U+0062字母顺位2数值 2歷史發...

Location of Spotsylvania County in Virginia This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Spotsylvania County, Virginia. This is intended to be a complete list of the properties and districts on the National Register of Historic Places in Spotsylvania County, Virginia, United States. The locations of National Register properties and districts for which the latitude and longitude coordinates are included below, may be seen in an online map.[1] There are 17 pro...

Overview of naming conventions in the United States The United States has very few laws governing given names. This freedom has given rise to a wide variety of names and naming trends. Naming traditions play a role in the cohesion and communication within American cultures. Cultural diversity in the U.S. has led to great variations in names and naming traditions and names have been used to express creativity, personality, cultural identity, and values.[1][2] A person's middle ...

ХристианствоБиблия Ветхий Завет Новый Завет Евангелие Десять заповедей Нагорная проповедь Апокрифы Бог, Троица Бог Отец Иисус Христос Святой Дух История христианства Апостолы Хронология христианства Раннее христианство Гностическое христианство Вселенские соборы Н...

روأنوك الإحداثيات 40°47′51″N 89°11′59″W / 40.7975°N 89.1997°W / 40.7975; -89.1997 [1] تقسيم إداري البلد الولايات المتحدة[2][3] التقسيم الأعلى مقاطعة وودفورد خصائص جغرافية المساحة 0.98 ميل مربع ارتفاع 724 قدم عدد السكان عدد السكان 1960 (1 أبريل...

العم سام يحتضن جون بل، بينما تمسك كل من بريتانيا وكولومبيا يدهما وتجلسان معًا في الخلفية في مصلق ترويجي لمعرض الولايات المتحدة وبريطانيا العظمى الصناعي (1898). يصف التقارب العظيم، وفقًا للمؤرخين بمن فيهم برادفورد بيركنز، تقارب الأهداف الدبلوماسية والسياسية والعسكرية والاق...

Deep blue purple color pigment which was originally made with ground lapis lazuli This article is about the pigment and the color. For other uses, see Ultramarine (disambiguation). Ultramarine blue redirects here. For the RAL color, see Ultramarine blue (RAL). Ultramarine Ultramarine pigment Color coordinatesHex triplet#120A8FsRGBB (r, g, b)(18, 10, 143)HSV (h, s, v)(244°, 93%, 56%)CIELChuv (L, C, h)(17, 65, 266°)SourceColorHexa[1]ISCC–NBS descriptorDeep blu...

Historical term Vis viva (from the Latin for living force) is a historical term used to describe a quantity similar to kinetic energy in an early formulation of the principle of conservation of energy. Overview Proposed by Gottfried Leibniz over the period 1676–1689, the theory was controversial as it seemed to oppose the theory of conservation of quantity of motion advocated by René Descartes.[1] Descartes' quantity of motion was different from momentum, but Newton defined the qua...

Monolito Bennett en la Plaza del Monolito en la ciudad de La Paz antes de ser enviado de vuelta a su lugar de origen Tiahuanaco. El Monolito Bennett, también conocido como Estela o Monolito Pachamama o Estela 10, es el monumento más grande que ha sido hallado dentro del Complejo Arqueológico Monumental de Tiahuanaco, (yacimiento catalogado como Patrimonio de la Humanidad por la Unesco desde el año 2000), construido por los integrantes de la Cultura Tiahuanaco, civilización precolombina q...

NJ Transit and Metro-North Railroad station SuffernThe station at Suffern, looking north along the tracks toward Nordkop Mountain.General informationLocation2 Ramapo AvenueSuffern, New YorkCoordinates41°06′50″N 74°09′14″W / 41.113972°N 74.153894°W / 41.113972; -74.153894Owned byNew Jersey TransitPlatforms2 side platformsTracks2Connections Transport of Rockland: 59, 93, Monsey Loop 3, Tappan ZEExpress Short Line Bus: 17M/MD/SFConstructionParki...

Performing art in which practitioners appear to demonstrate exceptional mental abilities This article is about the performing art. For other uses, see Mentalism (disambiguation). Mentalist redirects here. For the TV series, see The Mentalist. For other uses, see Mentalist (disambiguation). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Mental...
