Arlington Springs Man
|
Read other articles:
زقر معلومات جغرافية الإحداثيات 14°00′46″N 42°44′31″E / 14.012777777778°N 42.741944444444°E / 14.012777777778; 42.741944444444 الأرخبيل جزر حنيش المسطح المائي البحر الأحمر المساحة 120 كيلومتر مربع الطول 18.8 كيلومتر العرض 12.2 كيلومتر أعلى ارتفاع (م) 524 متر الحكومة البلد...

The social and economic changes in Thailand in the past decades have important implications for the quality and quantity of labor. The economic and non-economic roles of women in Thailand can be traced back several hundred years in Thai history,[1] when there were traditional discriminatory attitudes towards women in the culture of Thailand.[2] The transformation of Thailand's social and economic structure since the 1960s led to the gender disparities in Thai society.[3&#...

Amoli: PricelessPoster dokumenterSutradaraJasmine Kaur Roy, Avinash RoyProduserCulture MachinePenata musikTajdar JunaidTanggal rilis 30 Mei 2018 (2018-05-30) (India) Durasi30 menitNegaraIndiaBahasaInggris, Hindi, Kannada, Tamil, Telugu, BengaliAmoli: Priceless adalah sebuah film dokumenter 2018 tentang eksploitasi seksual komersial anak-anak.[1][2][3][4] Film tersebut disutradarai oleh sutradara pemenang Penghargaan Nasional Jasmine Kaur Roy dan ...

Katedral Sakramen Pemberkatan, Christchurch Keuskupan Christchurch adalah sebuah keuskupan suffragan dari Keuskupan Agung Wellington. Katedral dan tahta episkopalnya terletak di Christchurch, kota terbesar di Pulau Selatan, Selandia Baru. Keuskupan tersebut terbentuk pada 5 Mei 1887 dari sebuah wilayah dari Keuskupan Wellington, yang kemudian ditingkatkan menjadi keuskupan agung pada bulan yang sama. Pranala luar Wikimedia Commons memiliki media mengenai Roman Catholic Diocese of Christchurch...

Часть серии статей о Холокосте Идеология и политика Расовая гигиена · Расовый антисемитизм · Нацистская расовая политика · Нюрнбергские расовые законы Шоа Лагеря смерти Белжец · Дахау · Майданек · Малый Тростенец · Маутхаузен ·&...

Untuk film tahun 1986 dengan judul yang sama, lihat Malam Jumat Kliwon (film tahun 1986). Malam Jumat KliwonSutradaraKoya PagayoProduserShankar RSSkenarioEry SofidPemeran Robertino Ben Joshua Gracia Indri Debby Kristy Nadiah M. Hassan Daffy Ariaga Sujiwo Tejo Penata musikTeguh PribadiSinematograferDharma YouPenyuntingAziz NatandraPerusahaanproduksiIndika EntertainmentDistributorBatavia PicturesTanggal rilis31 Mei 2007Durasi90 menitNegaraIndonesiaBahasaBahasa Indonesia Malam Jumat Kliwon...

Telecommunications provider in the United States WOW! redirects here. For other uses, see Wow (disambiguation). WideOpenWest, Inc.Company typePublicTraded asNYSE: WOWRussell 2000 ComponentIndustryTelecommunicationsPredecessorAmericast, KnologyFoundedNovember 1996; 27 years ago (1996-11)Denver, Colorado, U.S.HeadquartersDenver, Colorado, U.S.Area servedAlabamaFloridaGeorgiaIllinoisIndianaMarylandMichiganOhio (1996-2021)South CarolinaTennesseeKey peopleTeresa Elder(P...
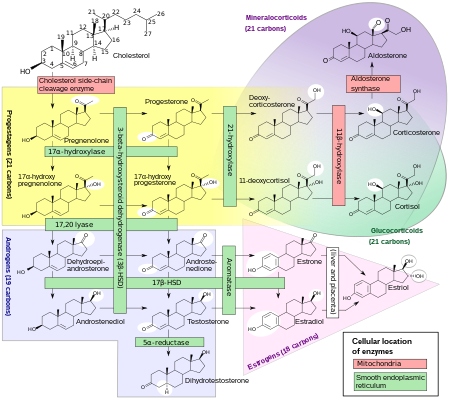
Group of corticosteroids MineralocorticoidDrug classAldosterone, the major endogenous mineralocorticoid.Class identifiersSynonymsCorticosteroid; MineralocorticosteroidATC codeH02AABiological targetMineralocorticoid receptorChemical classSteroidsLegal statusIn Wikidata Mineralocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids, which in turn are a class of steroid hormones. Mineralocorticoids are produced in the adrenal cortex and influence salt and water balances (electrolyte balance and fluid balance...

Davenport Public LibraryMain Branch in 201841°31′24″N 90°34′31″W / 41.5232°N 90.5752°W / 41.5232; -90.5752Location321 N. Main St.3000 N. Fairmount St.6000 Eastern Ave.Davenport, Iowa, United StatesTypePublicEstablished1877CollectionSize372,826Access and useCirculation946,114 (2011)Other informationDirectorJeff CollinsPublic transit access Davenport CitiBusWebsitewww.davenportlibrary.comReferences: [1] U.S. Historic districtContributing propertyDave...

الهوبيت: قفرة سموغThe Hobbit: The Desolation of Smaug (بالإنجليزية) معلومات عامةالتصنيف فيلم ثلاثي الأبعاد الصنف الفني القائمة ... فنتازيا عليا — فيلم فنتازيا[1] — فيلم مغامرة[1] — فيلم صيد كنوز — فيلم أكشن — فيلم مقتبس من عمل أدبي تاريخ الصدور القائمة ... 2 ديسمبر 2013 (لوس أنجلو...

Bendera Tynwald. Tynwald (bahasa Manx: Tinvaal) adalah badan legislatif Pulau Man yang diklaim sebagai parlemen tertua di dunia. Parlemen ini sudah berdiri selama lebih dari 1000 tahun. Pulau Man merupakan dependensi mahkota Britania Raya dan badan Tynwald memiliki kekuatan politik yang cukup besar di pulau tersebut. Tynwald merupakan badan bikameral, sehingga majelis ini terbagi menjadi dua, yaitu House of Keys yang dipilih secara langsung oleh rakyat Pulau Man dan Dewan Legislatif yang tida...

Gereja Ortodoks UkrainaПравославна церква УкраїниMonasteri Berkubah Emas Santo Mikael di KievPrimatEpifanius IParokiSekitar 7.000[1][2]BahasaUkraina, Slavonik Gerejawi[3]LiturgiRitus BizantiumKantor pusatMonasteri Berkubah Emas Santo Mikael, Kiev[4][5]DaerahUkrainaPendiriDewan Unifikasi Gereja-gereja Ortodoks UkrainaDidirikan15 Desember 2018 KievKemerdekaan5 Januari 2019 (autosefalus secara resmi diberikan oleh seorang tomos)[...

For the village in Iran, see Aspar, Iran. For the Grand Prix motorcycle racing team, see Aspar Team. Detail of a dish depicting Aspar and his elder son Ardabur (c. 434). Flavius Ardabur Aspar (Greek: Ἄσπαρ, fl. 400 – 471) was an Eastern Roman patrician and magister militum (master of soldiers) of Alanic-Gothic descent.[1] As the general of a Germanic army in Roman service,[2][3][4][5] Aspar exerted great influence on the Eastern Rom...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、�...

「アプリケーション」はこの項目へ転送されています。英語の意味については「wikt:応用」、「wikt:application」をご覧ください。 この記事には複数の問題があります。改善やノートページでの議論にご協力ください。 出典がまったく示されていないか不十分です。内容に関する文献や情報源が必要です。(2018年4月) 古い情報を更新する必要があります。(2021年3月)出...

American politician This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Archibald Atkinson – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Archibald AtkinsonMember of the U.S. House of Representativesfrom Virginia's 1st districtIn officeMarch 4...
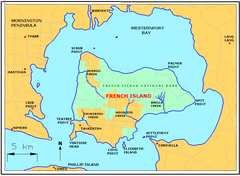
Place in Victoria, AustraliaElizabeth IslandVictoriaElizabeth IslandLocation off French IslandCoordinates38°25′0.48″S 145°22′8.4″E / 38.4168000°S 145.369000°E / -38.4168000; 145.369000 Map of French Island, with much smaller Elizabeth Island close south Elizabeth Island lies just south of French Island in Western Port, Victoria, south-eastern Australia, and just north of Phillip Island. It is over 65 acres (26 hectares) in area and is an unincorporated are...

Tethered aircraft For other uses, see Kite (disambiguation). The Yokaichi Giant Kite Festival is held every July in Higashiomi, Shiga, Japan.[1] Various kites being flown Star-shaped kite above a meadow south of Hockenheim. This sparless, ram-air inflated kite, has a complex bridle formed of many strings attached to the face of the wing. A kite is a tethered heavier-than-air or lighter-than-air craft with wing surfaces that react against the air to create lift and drag forces.[2&#...

Sacred tree in Sri Lanka This article's tone or style may not reflect the encyclopedic tone used on Wikipedia. See Wikipedia's guide to writing better articles for suggestions. (October 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Jaya Sri Maha Bodhiජය ශ්රී මහා බෝධියSacred Bodhi before c. 1913 and in the recent past.SpeciesBodhi (Ficus religiosa)LocationAnuradhapura, Sri LankaCoordinates8°20′41″N 80°23′48″E / 8.34472°N 80.39667°E...
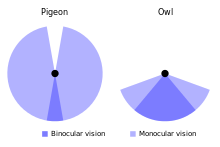
Type of vision with two eyes facing the same direction Principle of binocular vision with horopter shown In biology, binocular vision is a type of vision in which an animal has two eyes capable of facing the same direction to perceive a single three-dimensional image of its surroundings. Binocular vision does not typically refer to vision where an animal has eyes on opposite sides of its head and shares no field of view between them, like in some animals.[which?] Neurological research...