Araucanía Region
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Maret 2023. DiecisieteSutradaraDaniel Sánchez ArévaloDitulis olehDaniel Sánchez ArévaloPemeranBiel MontoroNacho SánchezPerusahaanproduksiAtípica FilmsDistributorNetflixTanggal rilis 27 September 2019 (2019-09-27) (San Sebastián)[1] 4 Oktober ...

Wongravee NateetornLahir25 Juni 1998 (umur 25)Ranong, ThailandNama lainSkyPekerjaanAktor, modelTahun aktif2014–kiniTinggi182 m (597 ft 1+1⁄2 in)Situs webinstagram.com/skywongravee?igshid=sx8m5hsoyctl Wongravee Nateetorn (Thai: วงศ์รวี นทีธรcode: th is deprecated ; RTGS: Wongrawi Nathithon atau berjuluk Sky, lahir 25 Juni 1998) adalah seorang pemeran asal Thailand yang memerankan Pala dalam seri televisi Hormones pada 2015. Ia mera...

Alfredo Martini Nazionalità Italia Ciclismo Specialità Strada Termine carriera 1957 Carriera Squadre di club 1940-1941A.C. Montecatini1941-1942S.C. Pontecchi Firenze1941-1943 Bianchi1943S.C. Taddei Empoli1944Individuale1945S.C. Stefani Lando1945 Viscontea1946-1947 Welter1948-1949 Wilier Triestina1950-1951Taurea1951-1953 Welter1954 Atala-Pirelli1954 Lygie1955-1956 Nivea-Fuchs1957 Leo-Chlorodont Nazionale 1948-1952 Italia Carriera da allenat...

Character in James Joyce's Ulysses This article is about the fictional character. For other uses, see The Citizen. Fictional character The CitizenFirst appearanceUlysses (1922)Created byJames JoyceIn-universe informationGenderMaleOccupationunclear, possibly retiredReligionCatholicNationalityIrish Portrait of Michael Cusack, on whom The Citizen is based. The Citizen is a fictional character in James Joyce's novel Ulysses. In part, he is a satirical portrait of Irish nationalist (and Gaelic Ath...

Japanese manga series Ristorante ParadisoCover of the first manga volumeリストランテ・パラディーゾ(Risutorante Paradīzo)GenreRomance[1] MangaWritten byNatsume OnoPublished byOhta PublishingEnglish publisherNA: Viz MediaMagazineManga Erotics FOriginal runMay 2005 – March 2006Volumes1 MangaGente: The People of Ristorante ParadisoWritten byNatsume OnoPublished byOhta PublishingEnglish publisherNA: Viz MediaMagazineManga Erotics FOriginal runSeptember 2...

烏克蘭總理Прем'єр-міністр України烏克蘭國徽現任杰尼斯·什米加尔自2020年3月4日任命者烏克蘭總統任期總統任命首任維托爾德·福金设立1991年11月后继职位無网站www.kmu.gov.ua/control/en/(英文) 乌克兰 乌克兰政府与政治系列条目 宪法 政府 总统 弗拉基米尔·泽连斯基 總統辦公室 国家安全与国防事务委员会 总统代表(英语:Representatives of the President of Ukraine) 总...

Phylum of amoeboid protists ForaminiferaTemporal range: 542–0 Ma[1] PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N Latest Ediacaran–Recent Live Ammonia tepida (Rotaliida) Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Clade: Diaphoretickes Clade: SAR Phylum: Retaria Subphylum: Foraminiferad'Orbigny, 1826 Subdivisions Monothalamea Allogromiida Astrorhizida Xenophyophorea Reticulomyxa Tubothalamea Miliolida Spirillinida Silicoloculinida Globothalamea Textulariida Rotaliida Globigerinida Carterin...
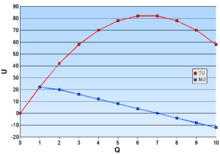
Concept in economics Part of a series onEconomics History Outline Index Branches and classifications Applied Econometrics Heterodox International Micro / Macro Mainstream Mathematical Methodology Political JEL classification codes Concepts, theory and techniques Economic systems Economic growth Market National accounting Experimental economics Computational economics Game theory Operations research Middle income trap Industrial complex By application Agricultural Behavioral Business Cultural ...

Website FundlyType of siteCrowdfundingAvailable inEnglishURLfundly.comLaunched2009 Fundly is a crowdfunding site for online fundraising. It allows non-profits, charities, politics, clubs, schools, teams, churches, and other causes to raise money online from friends, family, colleagues, donors, and other supporters via email, Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Google, and social media networks. It is also an app for social networks like Facebook and LinkedIn. It uses WePay to process donations....

Geology of Oregon and Washington (United States) and British Columbia (Canada) The Pacific Northwest from space The geology of the Pacific Northwest includes the composition (including rock, minerals, and soils), structure, physical properties and the processes that shape the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The region is part of the Ring of Fire: the subduction of the Pacific and Farallon Plates under the North American Plate is responsible for many of the area's scenic features as...

IvittuutTambang kriolit di Ivittuut pada tahun 1940Koordinat: 61°12′30″N 48°10′10″W / 61.20833°N 48.16944°W / 61.20833; -48.16944Koordinat: 61°12′30″N 48°10′10″W / 61.20833°N 48.16944°W / 61.20833; -48.16944Negara Kerajaan DenmarkNegara bagian GreenlandKotamadya SermersooqDitinggalkan1980-anZona waktuUTC-03 Ivittuut, sebelumnya dieja Ivigtût (Kalaallisut: Tempat Berumput,[1]) adalah sebuah kota tambang ...

The library is in the center of the photo. The Bibliothèque municipale de Grenoble is a library in Grenoble, France. It was founded in 1772,[1] following the succession of Bishop, Jean de Caulet. The current building located Boulevard Maréchal Lyautey was opened in January 1960 for the University and since 1970, for all audiences. References ^ Tedder, Henry Richard; Brown, James Duff (1911). Libraries . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 16 (11th ...

الاتحاد السلوفاكي لكرة القدم الاسم المختصر SFZ الرياضة كرة القدم أسس عام 1938 الانتسابات الفيفا : 1994 الاتحاد الأوروبي : 1993 رمز الفيفا FRO الموقع الرسمي www.futbalsfz.sk تعديل مصدري - تعديل الشعار السابق للاتحاد السلوفاكي تأسس الاتحاد السلوفاكي لكرة القدم في عام 1938م وانضم �...

The World's Most Livable Cities adalah nama informal yang diberikan pada daftar kota dalam survei tahunan kondisi hidup. Dua yang terkenal[butuh rujukan] adalah Mercer Quality of Living Survey dan World's Most Livable Cities dari The Economist. Quality of Living Survey The Economist's World's Most Liveable Cities 2011 (Top 10)[1] Kota Negara Rating 1 Melbourne Australia 97.5 2 Vienna Austria 97.4 3 Vancouver Kanada 97.3 4 Toronto Kanada 97.2 5 Calgary &...

PlaceNew York City's 14th City Council districtGovernment • Councilmember Pierina Sanchez (D—Kingsbridge)Population (2010)[1] • Total158,876Demographics • Hispanic72% • Black21% • Asian3% • White3% • Other2%Registration • Democratic76.4% • Republican4.7% • No party preference16.4%Registered voters (2021) 94,515[2] New York City's 14th City Counc...
Ballon d'or 1990 Lothar MatthäusGénéralités Sport Football Organisateur(s) France Football Édition 35e Catégorie Trophée mondial Date 1990 Palmarès Vainqueur Lothar Matthäus (1) Deuxième Salvatore Schillaci Troisième Andreas Brehme Navigation Édition précédente Édition suivante modifier Le Ballon d'or 1990 est la 35e cérémonie du Ballon d'or, organisée par France Football. Il récompense l'Allemand Lothar Matthäus. Résultats Rang Nom Club Sélection Points 1 Lothar M...
Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento fumetti statunitensi non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Sonic Xfumetto logo del fumetto, identico a quello dell'anime Lingua orig.inglese PaeseStati Uniti TestiIan Flynn, Joe Edkin DisegniTim Smith, Tracy Yardley EditoreArchie Comics 1ª edizione18 settembre 2005 – 31 d...

Shaina MagdayaoMagdayao di sebuah acara, 2011LahirShaina García Magdayao6 November 1989 (umur 34)[1]Quezon City, FilipinaKebangsaanFilipinaNama lainShin, Ina, Shai, Maggie, ShadamPekerjaanAktris, penari, presenter televisi, modelTahun aktif1996–sekarangAgenGMA Network (1996) Star Magic (1996–sekarang) ABS-CBN Entertainment (1996–sekarang)Tinggi5 ft 6 in (168 cm) [2]KerabatVina Morales (saudara) Luis Gabriel Moreno (keponakan) Shaina Garcia Magdayao (pela...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Apollinaire. Ne doit pas être confondu avec le capucin Apollinaire de Valence (1829-1899). Apollinaire de ValenceVitrail de la cathédrale Saint-Apollinaire de Valence.FonctionÉvêque de ValenceDiocèse de Valence (d)491-520BiographieNaissance Vers 453VienneDécès Vers 520ValenceActivités Prêtre, évêque catholiquePère Isice IFratrie Avit de VienneAutres informationsÉtape de canonisation SaintFête 5 octobremodifier - modifier le code - modifier...

Kiviõli Football Club IrbisCalcio Segni distintiviUniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Colori sociali Rosso, blu Dati societariCittàKiviõli Nazione Estonia ConfederazioneUEFA Federazione EJL Fondazione1990 Scioglimento2016StadioKiviõli Staadion(180 posti) Sito web[http://[1] [2]] PalmarèsSi invita a seguire il modello di voce Il Kiviõli Football Club Irbis, meglio noto come Irbis Kiviõli, è una società calcistica estone con sede nella città di Kiviõli, partecipante dal 1992 al 2016...





