American gentry
|
Read other articles:

Denys Arcand, sutradara The Barbarian Invasions (2003), film Kanada pertama yang meraih Penghargaan Akademi untuk Film Berbahasa Asing Terbaik. Kanada telah mengirimkan sejumlah film untuk Penghargaan Akademi untuk Film Berbahasa Asing Terbaik sejak 1971. Penghargaan tersebut diberikan secara tahunan oleh Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences Amerika Serikat kepada sebuah film durasi cerita yang dibuat di luar Amerika Serikat yang utamanya berisi dialog non-Inggris.[1] Pengharga...

National Institute for Occupational Safety and HealthInformasi lembagaDibentuk29 Desember 1970; 53 tahun lalu (1970-12-29)Wilayah hukumPemerintah federal Amerika SerikatKantor pusatWashington, D.C.Pegawai~1.200Pejabat eksekutifJohn Howard, DirectorDepartemen indukCenters for Disease Control and PreventionLembaga indukDepartment of Health and Human ServicesSitus webcdc.gov/niosh/ National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH; Institut Nasional untuk Keselamatan dan Kesehata...

العلاقات السيشلية القبرصية سيشل قبرص سيشل قبرص تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات السيشلية القبرصية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين سيشل وقبرص.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارنة سيشل قبرص المساح�...

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Sistem gugur – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Contoh penjadwalan turnamen dengan sistem gugur. Sistem gugur (atau Sistem Knockout atau sistem KO) merupakan salah satu format turnamen y...

Belgia dibagi menjadi tiga region, dua di antaranya masing-masing dibagi menjadi lima provinsi. Pembagian provinsi-provinsi ini ditetapkan dalam Artikel no. 5 Konstitusi Belgia. Provinsi-provinsi ini kemudian dibagi menjadi beberapa arondisemen. Provinsi di Flemish Provinsi Antwerpen Limburg Brabant Flandria Flandria Timur Flandria Barat Nama Belanda Antwerpen Limburg Vlaams Brabant Oost-Vlaanderen West-Vlaanderen Nama Jerman Antwerpen Limburg Flämisch-Brabant Ostflandern Westflandern Nama P...

Dallas MavericksPallacanestro Campione della NBA Southwest Division «Mavs, Los Mavs, Big D, Mavsland» Segni distintivi Uniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Terza Colori sociali Blu reale, blu marino, argento, nero[1][2] Simboli Cavallo Dati societari Città Dallas (TX) Nazione Stati Uniti Campionato NBA Conference Western Conference Division Southwest Division Fondazione 1980...

American cartoonist This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Joe Oriolo – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Joe OrioloBornJoseph Oriolo(1913-02-21)February 21, 1913Union City, New Jersey, United StatesDiedDecember 25, 1985(1985-12-25) (...

Perdana Menteri Republik Demokratik Rakyat KoreaLambang negaraPetahanaKim Tok-hunsejak 13 Agustus 2020Pejabat perdanaKim Il-sungDibentuk9 September 1948 Perdana Menteri Korea Utara (resmi Perdana Menteri Kabinet Republik Demokratik Rakyat Korea) adalah kepala pemerintahan Korea Utara. Fungsi dan sejarah Perdana menteri memimpin aktivitas Pemerintah dan mewakili itu. Perdana menteri tidak memiliki kekuasaan eksekutif yang nyata, karena kebijakan utama yang ditetapkan oleh Komite Sentral P...

Sports radio station in Manassas, Virginia, serving Washington, D.C. WJFK-FMManassas, VirginiaBroadcast areaWashington metropolitan areaFrequency106.7 MHz (HD Radio)Branding106-7 The FanProgrammingLanguage(s)EnglishFormatSports radioSubchannelsHD2: Sports radio (WTEM)HD3: Sports gambling (WJFK)[1]AffiliationsInfinity Sports NetworkWashington Nationals Radio NetworkWashington CapitalsVirginia Tech HokiesGeorgetown HoyasOwnershipOwnerAudacy, Inc.(Audacy License, LLC, as Debtor-in-Posses...
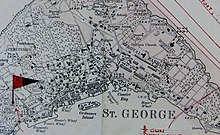
Historic site in St. George's Island, BermudaFort VictoriaA BL 9.2 inch gun Mk X at Fort Victoria, circa 1995.LocationSt. George's Garrison, St. George's Island, BermudaCoordinates32°23′27″N 64°40′28″W / 32.3907°N 64.6744°W / 32.3907; -64.6744Built1842 UNESCO World Heritage SiteTypeCulturalCriteriaivDesignated2000 (24th session)Part ofHistoric Town of St. George and Related Fortifications, BermudaReference no.983RegionEurope and North America Location...

Indian chess grandmaster In this Indian name, the name Panneerselvam is a patronymic, and the person should be referred to by the given name, Iniyan. P. IniyanIniyan at the 2017 Andorra openFull namePanneerselvam IniyanCountryIndiaBorn (2002-09-13) 13 September 2002 (age 21)Erode, Tamil Nadu, IndiaTitleGrandmaster (2019)FIDE rating2493 (May 2024)Peak rating2556 (August 2022) Panneerselvam Iniyan (born 13 September 2002) is an Indian chess professional player.He is India's ...

Historic district in North Carolina, United States 1865 map of Fort Anderson Fort Anderson is a mid-19th-century earthen fort in the lower Cape Fear Region of North Carolina, located over the ruins of the colonial town of Brunswick in Brunswick County. It was built as a Confederate Fort by major general Samuel Gibbs French during the American Civil War.[1] The fort was pivotal in protecting the Cape Fear River inlets and Wilmington upstream. Earthen batteries comprise the fort and wer...

Institutional corruption in the country Political corruption Forms and concepts Bribery Cronyism Economics of corruption Electoral fraud Elite capture Influence peddling Kleptocracy Mafia state Nepotism Pyrrhic defeat theory Slush fund Simony State capture State-corporate crime Throffer Anti-corruption International Anti-Corruption Court Group of States Against Corruption International Anti-Corruption Academy International Anti-Corruption Day United Nations Convention against Corruption Corru...

土間(箱木家住宅) 土間(どま)は、家屋内にあって床板を敷かずに、地面のままか三和土(たたき、(漆喰を塗り固めた床)にした空間[1]。主に玄関近くに設けられ、屋内では靴を脱ぐ習慣がある日本などにおいても、土間は土足のまま屋外と出入りでき、台所や作業場、土汚れがつくもの保管場所などとして使う[2]。 概説 土間は板敷と対比され、土間�...

American investment bank For the company after its acquisition by Credit Suisse, see Credit Suisse First Boston (known as CSFB and CS First Boston) The First Boston CorporationCompany typePrivateIndustryInvestment servicesFoundedJuly 12, 1932; 92 years ago (1932-07-12)FateAcquired by Credit Suisse in 1988 and merged into Credit Suisse First BostonSuccessorCredit Suisse First Boston Credit SuisseHeadquartersNew York City, New York, United StatesProductsFinancial servicesInves...

Mythical bird with healing capabilities For the video game, see Caladrius (video game). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Caladrius – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) An illustration of the Caladrius' prophecies from the 1588 edi...
San Luca di MelicuccàIcona di San Luca di Melicuccà presso la chiesa dei Santi Elia e Filarete a Seminara Vescovo NascitaMelicuccà, 1035/1040 MorteAmaroni, 10 dicembre 1114 Venerato daChiesa cattolica Ricorrenza10 dicembre Manuale Luca di Melicuccà, detto Luca il Grammatico (Melicuccà, 1035/1040 – Amaroni, 10 dicembre 1114), fu monaco basiliano e vescovo. Venerato come santo dalla Chiesa cattolica, è ricordato il 10 dicembre. Biografia Nacque a metà dell'XI secolo in provi...

American politician Charles Perkins ThompsonMember of the U.S. House of Representativesfrom Massachusetts's 6th districtIn officeMarch 4, 1875 – March 3, 1877Preceded byBenjamin ButlerSucceeded byGeorge B. LoringMember of the Massachusetts House of RepresentativesIn office1871–1872 Personal detailsBorn(1827-07-30)July 30, 1827Braintree, MassachusettsDiedJanuary 19, 1894(1894-01-19) (aged 66)Gloucester, MassachusettsResting placeOak Grove CemeteryPolitical partyDe...

American mathematician (born 1941) For other uses, see Dennis Sullivan (disambiguation). Dennis SullivanSullivan in 1968BornDennis Parnell Sullivan (1941-02-12) February 12, 1941 (age 83)Port Huron, Michigan, U.S.EducationRice University (BA)Princeton University (MA, PhD)Known for Connes–Donaldson–Sullivan–Teleman index theorem Parry–Sullivan invariant Sullivan conjecture Density conjecture Localization of a topological space No-wandering-domain theorem Rational homotopy the...

Joint military aircrew training program during World War II British Commonwealth Air Training PlanPart of the Second World WarAustralia, Canada, New Zealand, United States RCAF HarvardSite historyIn use1939–45 de Havilland DH.82C Tiger Moth in British Commonwealth Air Training Plan trainer yellow at the Western Canada Aviation Museum (note the skis, and the enclosed cockpit common to Canadian-built Tiger Moths) The British Commonwealth Air Training Plan (BCATP), often referred to as si...











